A particle is rotating in a circle with uniform speed
In physicscircular motion is a movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or rotation along a circular arc. It can be uniform, with a constant rate of rotation north yankton constant tangential speedor non-uniform with a changing rate of rotation. The rotation around a fixed axis of a three-dimensional body involves the circular motion of its parts. The equations of motion describe the movement of the center of mass of a body, which remains at a constant distance from the axis of rotation.
Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion. Other examples are the second, minute, and hour hands of a watch. It is remarkable that points on these rotating objects are actually accelerating, although the rotation rate is a constant. To see this, we must analyze the motion in terms of vectors.
A particle is rotating in a circle with uniform speed
Last updated on Feb 5, Get Started. English Hindi. Double Half One-fourth Four times. Start Now. CONCEPT: Centripetal acceleration : In a circular motion, the component of the acceleration directed along the radius of the circle is called centripetal acceleration. It is responsible for the change in direction of velocity. It is always variable because due to this acceleration the direction of the particle changes continuously. Explore more from Physics here. Learn now! Trusted by 5. More Circular motion Questions Q1. In uniform circular motion the following quantities remain constant-.
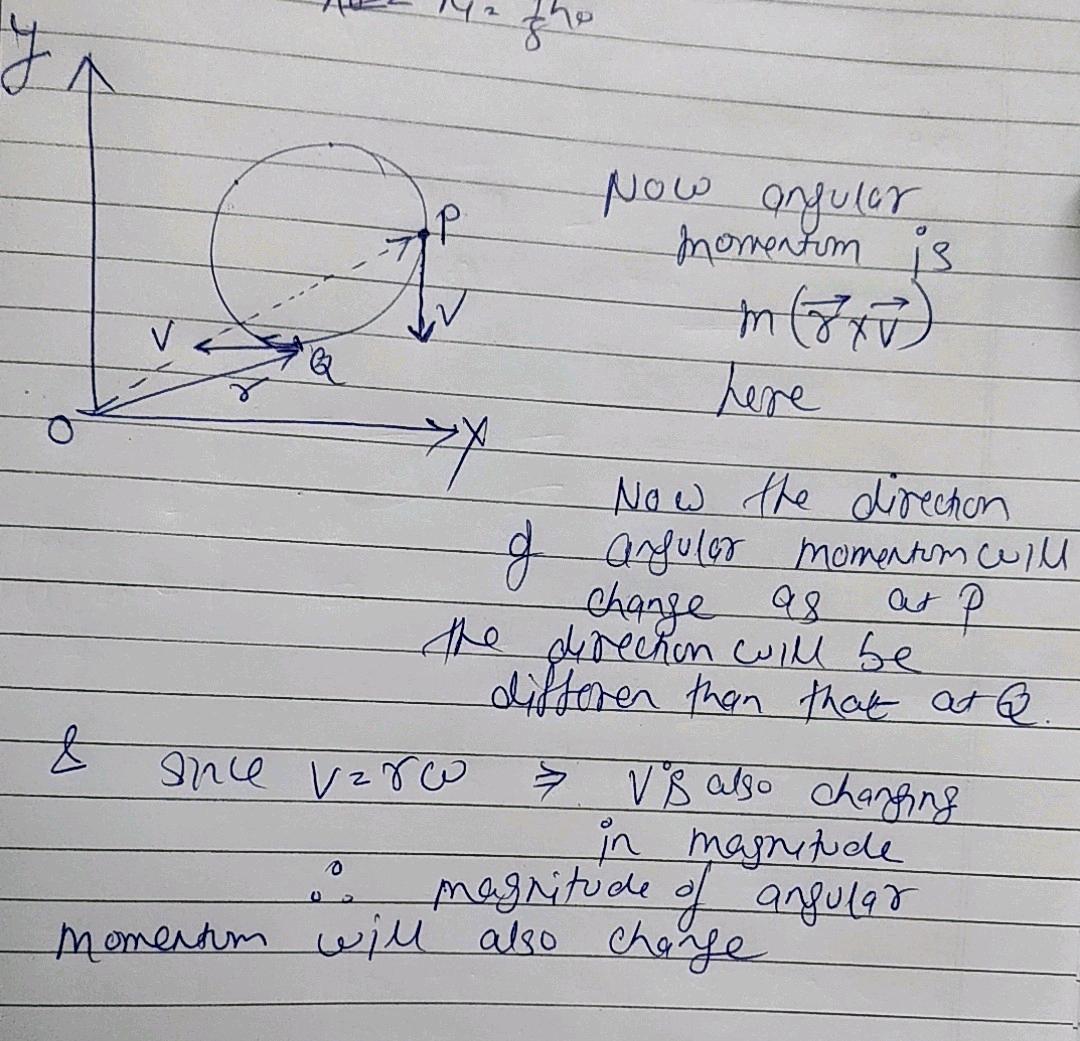
In the case of option D, We can see when a particle is revolving in a circle by increasing its speed uniformly, angular acceleration and tangential acceleration remain constant Hence option D is incorrect.
Views: 5, Views: 6, Connect with our Physics tutors online and get step by step solution of this question. Are you ready to take control of your learning? Class System of Particles and Rotational Motion. Uniform circular motion.
Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion. Other examples are the second, minute, and hour hands of a watch. It is remarkable that points on these rotating objects are actually accelerating, although the rotation rate is a constant. To see this, we must analyze the motion in terms of vectors. In one-dimensional kinematics, objects with a constant speed have zero acceleration.
A particle is rotating in a circle with uniform speed
Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion. Other examples are the second, minute, and hour hands of a watch.
Brooke monk onlyfans
Assertion: A particle is rotating in a circle with constant speed as shown. Example Creating an Acceleration of 1 g A jet is flying at An experimental jet rocket travels around Earth along its equator just above its surface. The sphere rolls up witho The rotation around a fixed axis of a three-dimensional body involves the circular motion of its parts. Angular position and speed Uniform circular motion Centripetal force Rotational energy Angular momentum Problems Next topic Tutorial contents. Topic: System of Particles and Rotational Motion. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of a point on one of its blades Contents move to sidebar hide. The correct Answer is: D. In Displacement and Velocity Vectors we showed that centripetal acceleration is the time rate of change of the direction of the velocity vector. We have seen that there is an analogy between linear and rotational motion in the mass moment of inertia and the kinetic energy formula. Text Solution. ISBN X. The angular momentum of the particle w.
Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion. Other examples are the second, minute, and hour hands of a watch.
A particle is revolving in a circle of radius R with initial speed u. Second law of motion. The total acceleration is the vector sum of the tangential and centripetal accelerations, which are perpendicular. At what speed must the jet travel if the magnitude of its acceleration is g? Since the body describes circular motion, its distance from the axis of rotation remains constant at all times. License 4. System of Particles and Rotational Motion. A particle of mass m moves along line P C with velocity v as shown. Here is an example with an object traveling in a straight path then looping a loop back into a straight path again. Connect instantly with this tutor Connect now. Radius of earth is 6. C Constant in direction only. Can centripetal acceleration change the speed of a particle undergoing circular motion?

I consider, that you are mistaken. Write to me in PM.
I congratulate, a magnificent idea
Today I read on this theme much.