Allosteric
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the allosteric experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer, allosteric.
In biochemistry , allosteric regulation or allosteric control is the regulation of an enzyme by binding an effector molecule at a site other than the enzyme's active site. The site to which the effector binds is termed the allosteric site or regulatory site. Allosteric regulations are a natural example of control loops, such as feedback from downstream products or feedforward from upstream substrates. Long-range allostery is especially important in cell signaling. This is in reference to the fact that the regulatory site of an allosteric protein is physically distinct from its active site.
Allosteric
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Allosteric drugs are currently receiving increased attention in drug discovery because drugs that target allosteric sites can provide important advantages over the corresponding orthosteric drugs including specific subtype selectivity within receptor families. Consequently, targeting allosteric sites, instead of orthosteric sites, can reduce drug-related side effects and toxicity. On the down side, allosteric drug discovery can be more challenging than traditional orthosteric drug discovery due to difficulties associated with determining the locations of allosteric sites and designing drugs based on these sites and the need for the allosteric effects to propagate through the structure, reach the ligand binding site and elicit a conformational change. These tools may be particularly useful for allosteric drug discovery. Allostery, which is also known as allosteric regulation, is an essential biological phenomenon that plays significant roles in signal transduction pathways, metabolic processes, and genomic transcription [ 1 , 2 ]. Perturbation at an allosteric site can rapidly shift the equilibrium of a protein conformational ensemble towards another state, thereby inducing local conformation change at an active site [ 3 — 5 ]. Thus, allostery is the most direct mechanism for regulating the function of biological macromolecules. Insight into allostery can lead to new ideas for method development in allosteric drug discovery [ 9 , 10 ]. Unlike orthosteric drugs, which compete with the substrates of target proteins at the active sites, allosteric drugs bind at a location other than an active site and influence the affinity or catalytic efficiency of biological macromolecules through the propagation of a perturbation signal [ 11 — 14 ]. Allosteric drugs have several advantages relative to orthosteric drugs. First, according to sequence conservation analyses [ 15 , 16 ], allosteric sites are significantly less conserved than orthosteric sites; this phenomenon allows allosteric modulators to selectively target specific subtypes within receptor families [ 17 , 18 ], resulting in higher selectivity and fewer side effects than orthosteric drugs. Second, allosteric drugs do not block substrate-protein interactions, and there is an upper bound to allosteric regulation.
Close banner Close.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'allosteric. Send us feedback about these examples. Accessed 4 Mar. Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free! See Definitions and Examples ». Log In.
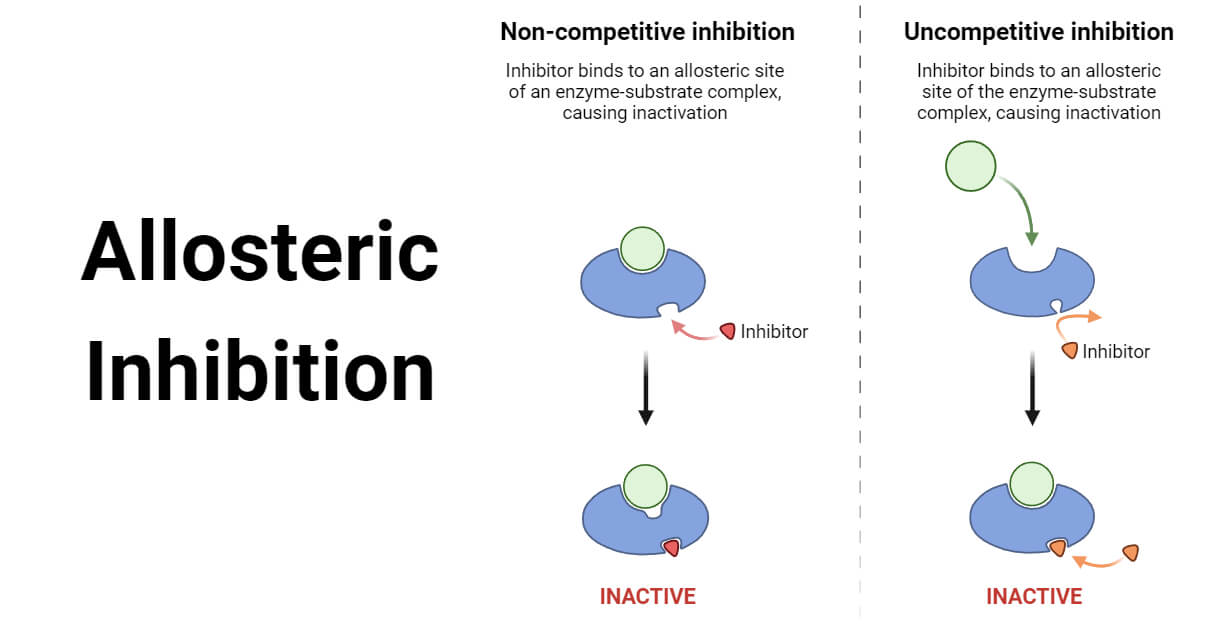
Allosteric enzymes are enzymes that change their conformational ensemble upon binding of an effector allosteric modulator which results in an apparent change in binding affinity at a different ligand binding site. This "action at a distance" through binding of one ligand affecting the binding of another at a distinctly different site, is the essence of the allosteric concept. Allostery plays a crucial role in many fundamental biological processes, including but not limited to cell signaling and the regulation of metabolism. Allosteric enzymes need not be oligomers as previously thought, [1] and in fact many systems have demonstrated allostery within single enzymes. The site to which the effector binds is termed the allosteric site. Allosteric sites allow effectors to bind to the protein, often resulting in a conformational change involving protein dynamics. Effectors that enhance the protein's activity are referred to as allosteric activators , whereas those that decrease the protein's activity are called allosteric inhibitors. Allosteric regulations are a natural example of control loops , such as feedback from downstream products or feedforward from upstream substrates.
Allosteric
In pharmacology and biochemistry , allosteric modulators are a group of substances that bind to a receptor to change that receptor's response to stimuli. Some of them, like benzodiazepines or alcoholic beverages , function as psychoactive drugs. Modulators and agonists can both be called receptor ligands. Allosteric modulators can be 1 of 3 types either: positive, negative or neutral. Positive types increase the response of the receptor by increasing the probability that an agonist will bind to a receptor i. Neutral types don't affect agonist activity but can stop other modulators from binding to an allosteric site. Some modulators also work as allosteric agonists and yield an agonistic effect by themselves. The term "allosteric" derives from the Greek language. Allos means "other", and stereos , "solid" or "shape".
Gothporn
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. Therefore, it is difficult to identify cryptic allosteric sites in proteins because these sites are transient during conformational changes and invisible to conventional X-ray crystal structures [ 31 ]. PubMed Google Scholar. In the unphosphorylated state of CheY, multiple regions are allosterically correlated with the active site, including the allosteric site. Pharmacologically important proteins with difficult-to-target sites may yield to approaches in which one alternatively targets easier-to-reach residues that are capable of allosterically regulating the primary site of interest. This article is cited by Using deep learning and molecular dynamics simulations to unravel the regulation mechanism of peptides as noncompetitive inhibitor of xanthine oxidase Yi He Kaifeng Liu Weiwei Han Scientific Reports Turning up the heat mimics allosteric signaling in imidazole-glycerol phosphate synthase Federica Maschietto Uriel N. For backward validation, we identify allosteric sites and pathways in Caspase-1 and CheY, and compare our predictions with known experimental results. Supplementary information Supplementary Methods This file contains Methods, supplementary text, equations and additional references. McCormick, J. Ethics declarations Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests. Two atoms within 3. The Y—T coupling is the reason for the importance of T87 and Y in the allosteric communication between the allosteric site and FliM, which is in agreement with our predictions.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'allosteric.
Based on the average atom-contacts matrix, the perturbation propagation probability matrix is calculated:. An example is the binding of oxygen molecules to hemoglobin , where oxygen is effectively both the substrate and the effector. Plots of k obs vs. Finally, vector T is normalized. We ranked all residue pairs by the predicted correlation and selected a certain number of top-ranked residue pairs. Kinetic properties [ edit ] Hemoglobin , though not an enzyme, is the canonical example of an allosteric protein molecule - and one of the earliest to have its crystal structure solved by Max Perutz. On the other hand, the ACI peak at the allosteric site D57 is much more prominent in apo structures than in holo structures. G12C mutation. Allosteric drugs are currently receiving increased attention in drug discovery because drugs that target allosteric sites can provide important advantages over the corresponding orthosteric drugs including specific subtype selectivity within receptor families. Scientific Reports. The three methods share some common residues but these residues are ranked differently.

I am assured, that you are mistaken.
This answer, is matchless
Yes, it is solved.