Alpha glucosidase inhibitors
Cardiovascular Diabetology volume 18Article number: Cite this article. Metrics details.
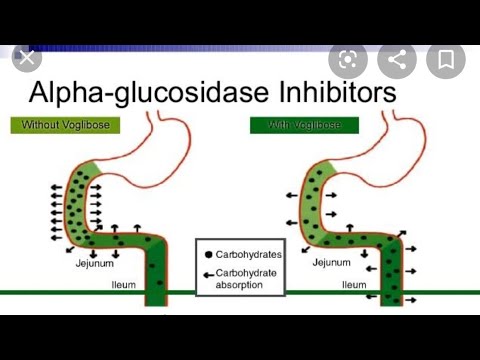
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors AGIs are oral anti-diabetic drugs used for diabetes mellitus type 2 that work by preventing the digestion of carbohydrates such as starch and table sugar. Carbohydrates are normally converted into simple sugars monosaccharides by alpha-glucosidase enzymes present on cells lining the intestine, enabling monosaccharides to be absorbed through the intestine. Hence, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors reduce the impact of dietary carbohydrates on blood sugar. Even though the drugs have a similar mechanism of action, there are subtle differences between acarbose and miglitol. Acarbose is an oligosaccharide , whereas miglitol resembles a monosaccharide. Miglitol is fairly well absorbed by the body, as opposed to acarbose. Moreover, acarbose inhibits pancreatic alpha-amylase in addition to alpha-glucosidase, and is degraded by gut bacterial maltogenic alpha-amylase and cyclomaltodextrinase.
Alpha glucosidase inhibitors
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Manahil Akmal ; Roopma Wadhwa. Authors Manahil Akmal ; Roopma Wadhwa 1. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors AGIs are a group of antidiabetic drugs used for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, contraindications, adverse effects, monitoring, and other key elements required by healthcare professionals involved in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Objectives: Identify the mechanism of action and administration of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. Describe the adverse effects and contraindications of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. Review the appropriate monitoring and toxicity of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. Summarize interprofessional team strategies for improving care coordination and communication to optimize the use of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors and improve outcomes. Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
They have shown some benefits in type 1 diabetes mellitus and gestational diabetes mellitus but are not FDA-approved for these indications.
There is only one tablet of this type used, called acarbose. It is usually used when a healthy diet and physical activity alone has been unsuccessful, although it is sometimes used together with a sulphonylurea. Acarbose works by slowing down the absorption of starchy foods from the intestine. This means that blood glucose levels rise more slowly after meals. Acarbose should always be chewed with the first mouthful of food or swallowed whole with a little liquid immediately before the meal.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Manahil Akmal ; Roopma Wadhwa. Authors Manahil Akmal ; Roopma Wadhwa 1. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors AGIs are a group of antidiabetic drugs used for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, contraindications, adverse effects, monitoring, and other key elements required by healthcare professionals involved in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Objectives: Identify the mechanism of action and administration of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors.
Alpha glucosidase inhibitors
The alpha-glucosidase inhibitors acarbose, miglitol, voglibose have been studied extensively in Europe and Japan; two of them, acarbose and miglitol, are available in the United States. Taken orally, they inhibit the upper gastrointestinal enzymes alpha-glucosidases that convert complex polysaccharide carbohydrates into monosaccharides in a dose-dependent fashion. These drugs therefore slow the absorption of dietary carbohydrate; the slower rise in postprandial blood glucose concentrations is potentially beneficial in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In addition, the transfer of polysaccharides to the more distal small intestine increases the secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 GLP-1 and several other gut hormones [ 1 ]. In older patients with type 2 diabetes, acarbose may also increase insulin sensitivity [ 2 ], although this may have been a nonspecific effect associated with improved glycemia. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors do not cause hypoglycemia when used as monotherapy or with other agents that do not cause hypoglycemia. Acarbose and voglibose have also been evaluated for the prevention of type 2 diabetes. See "Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Drugs not recommended for prevention'. Glycemic efficacy — Several trials have demonstrated the glycemic efficacy of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes [ ].
Mypleasure madrid
Journal of Microbiology. We performed a random effects meta-analysis, with each study weighted according to the inverse variance method. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are administered orally. A carbohydrate-rich diet also increases the severity of gastrointestinal side effects. These result from the degradation of undigested carbohydrates by bacteria in the colon, which causes excessive gas formation. Others include voglibose and miglitol. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Nutr Diabetes. Controlling postprandial hyperglycemia is essential as it correlates with the development of microvascular complications and increases the risk for the development of cardiovascular diseases. ZL is an employee of Bayer Healthcare, China. Language Chinese English. In the colon , bacteria will digest the complex carbohydrates, thereby causing gastrointestinal side effects such as flatulence and diarrhea. Background Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors AGIs such as acarbose, miglitol and voglibose are oral drugs used in the management of diabetes, primarily to reduce post-prandial glucose concentrations. Mitiglinide Nateglinide Repaglinide.
There's more to see -- the rest of this topic is available only to subscribers. Renew my subscription.
We performed a random effects meta-analysis, with each study weighted according to the inverse variance method. Toggle limited content width. Download citation. To date, although many countries have licensed AGIs for use in IGT, very few currently approve any medication for diabetes prevention. Journal of Pharmacy Practice Vol 29, Issue 2, pp. Article Talk. Glycemic efficacy — Several trials have demonstrated the glycemic efficacy of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes [ ]. Oral diabetes medication , insulins and insulin analogs , and other drugs used in diabetes A Unlike sulfonylureas, this group of drugs does not cause hypoglycemia. Review Questions Access free multiple choice questions on this topic. Carbohydrates are normally converted into simple sugars monosaccharides by alpha-glucosidase enzymes present on cells lining the intestine, enabling monosaccharides to be absorbed through the intestine. Scott, M.

I join. And I have faced it. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.
Completely I share your opinion. In it something is also to me it seems it is excellent idea. Completely with you I will agree.