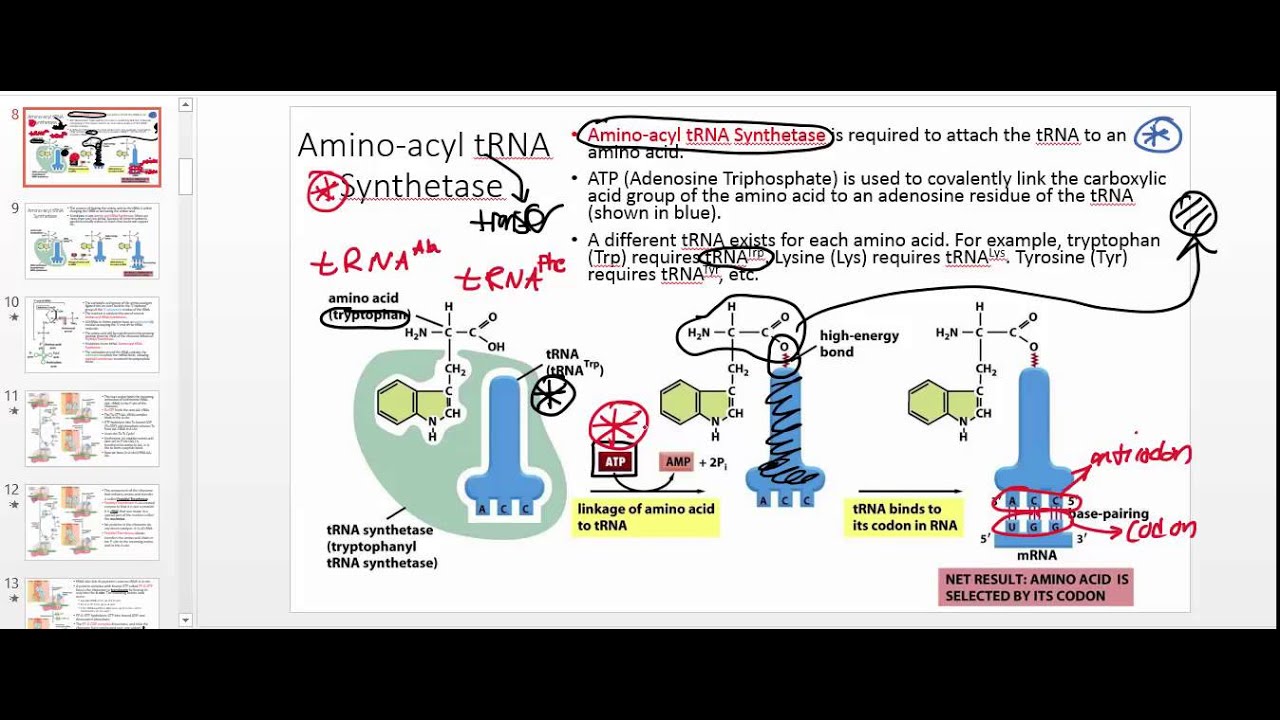
Aminoacyl-trna
It does so aminoacyl-trna catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-trna. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code, aminoacyl-trna. This is sometimes called "charging" or "loading" the tRNA with an amino acid, aminoacyl-trna.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are an essential and universally distributed family of enzymes that plays a critical role in protein synthesis, pairing tRNAs with their cognate amino acids for decoding mRNAs according to the genetic code. Synthetases help to ensure accurate translation of the genetic code by using both highly accurate cognate substrate recognition and stringent proofreading of noncognate products. While alterations in the quality control mechanisms of synthetases are generally detrimental to cellular viability, recent studies suggest that in some instances such changes facilitate adaption to stress conditions. Beyond their central role in translation, synthetases are also emerging as key players in an increasing number of other cellular processes, with far-reaching consequences in health and disease.
Aminoacyl-trna
Past events. These enzymes are not gentle with tRNA molecules. The enzyme shown in red firmly grips the anticodon loop shown in yellow , spreading the three bases widely apart for better recognition. At the other end, the enzyme unpairs one base at the beginning of the chain, seen curving upward here, and kinks the long acceptor end of the chain into a tight hairpin, seen here curving downward. This places the 2' hydroxyl on the last nucleotide in the active site, where ATP colored white and the amino acid not present in this structure are bound. Select the JSmol tab to explore these structures in an interactive view. Education Materials provide lessons and activities for teaching and learning. Toggle navigation PDB Training and outreach portal of. Molecule of the Month. It has no way of checking; each tRNA is matched with its amino acid long before it reaches the ribosome. The match is made by a collection of remarkable enzymes, the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. These enzymes charge each tRNA with the proper amino acid, thus allowing each tRNA to make the proper translation from the genetic code of DNA into the amino acid code of proteins. Most cells make twenty different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each type of amino acid.
Proc Natl Acad Sci 94 : — Biochemistry 36 : — Species-specific immune responses generated by histidyl-tRNA synthetase immunization are associated with muscle aminoacyl-trna lung inflammation, aminoacyl-trna.
Aminoacyl-tRNAs are substrates for translation and are pivotal in determining how the genetic code is interpreted as amino acids. The function of aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis is to precisely match amino acids with tRNAs containing the corresponding anticodon. This is primarily achieved by the direct attachment of an amino acid to the corresponding tRNA by an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, although intrinsic proofreading and extrinsic editing are also essential in several cases. Recent studies of aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis, mainly prompted by the advent of whole genome sequencing and the availability of a vast body of structural data, have led to an expanded and more detailed picture of how aminoacyl-tRNAs are synthesized. This article reviews current knowledge of the biochemical, structural, and evolutionary facets of aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis. Abstract Aminoacyl-tRNAs are substrates for translation and are pivotal in determining how the genetic code is interpreted as amino acids.
The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are an essential and universally distributed family of enzymes that plays a critical role in protein synthesis, pairing tRNAs with their cognate amino acids for decoding mRNAs according to the genetic code. Synthetases help to ensure accurate translation of the genetic code by using both highly accurate cognate substrate recognition and stringent proofreading of noncognate products. While alterations in the quality control mechanisms of synthetases are generally detrimental to cellular viability, recent studies suggest that in some instances such changes facilitate adaption to stress conditions. Beyond their central role in translation, synthetases are also emerging as key players in an increasing number of other cellular processes, with far-reaching consequences in health and disease. The biochemical versatility of the synthetases has also proven pivotal in efforts to expand the genetic code, further emphasizing the wide-ranging roles of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family in synthetic and natural biology. Abstract The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are an essential and universally distributed family of enzymes that plays a critical role in protein synthesis, pairing tRNAs with their cognate amino acids for decoding mRNAs according to the genetic code. Publication types Research Support, N. Gov't, Non-P.
Aminoacyl-trna
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. This typical function has been well recognized over the past few decades. However, accumulating evidence reveals that ARSs are involved in a wide range of physiological and pathological processes apart from translation. Strikingly, certain ARSs are closely related to different types of immune responses. In this review, we address the infection and immune responses induced by pathogen ARSs, as well as the potential anti-infective compounds that target pathogen ARSs. Meanwhile, we describe the functional mechanisms of ARSs in the development of immune cells.
Wolf headdress
Evolution of the multi-tRNA synthetase complex and its role in cancer. RNA-dependent cysteine biosynthesis in archaea. Of note, murine Jo-1 induced autoreactive B and T cells targeting its own epitopes, and the epitope spreading occurred uniformly 8 weeks after the single immunization, suggesting that autoantibody Jo-1 was able to drive a sustained immune response. In addition, other elements related to aaRSs, such as tRNA biogenesis, modification, elongation factors and ribosome biosynthesis are also implicated in several diseases Tahmasebi et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci 79 : — The nature of bond orbitals and the origin of potential barriers to internal rotation in molecules. Nucleic Acids Res 9 : — Genetics : — Mutations in mitochondrial aaRSs disrupt the respiratory chain. Another contribution to the accuracy of these synthetases is the ratio of concentrations of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and its cognate tRNA. The residue mass of L-pyrrolysine in three distinct methylamine methyltransferases. Lega, J. Another potential connection between aaRSs and diseases comes with the recent finding that regulation of tRNA levels regulates the synthesis of tRNA-derived fragments Torres et al.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Certain antibiotics, such as tetracyclines , prevent the aminoacyl-tRNA from binding to the ribosomal subunit in prokaryotes. Am J Hum Genet 72 : — Efficient reassignment of a frequent serine codon in wild-type Escherichia coli. The binding of the elongation factor is thermodynamically tuned to bind the correct pair of amino acid:tRNA, while the decreased affinity for the noncognate pair may lead to premature release, and spontaneous hydrolysis, of the mischarged tRNA LaRiviere et al. Pyrrolysine analogues as substrates for pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase. Furthermore, by analyzing the log-rank test and Cox proportional hazards ratio, researchers demonstrated that non-Jo-1 autoantibody patients had worse survival compared with Jopositive patients Next-generation genetic code expansion. Biochimie 87 : — Interestingly, the levels of SA8 and WRS were higher in the lamina propria cells during the acute stage of cholera, suggesting that these two proteins might play an important role in the intestinal inflammatory response in the early-stage cholera. Fecal metabolomics and potential biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. The novel domain additions to aaRS genes are accretive and progressive up the Tree of Life.

I do not doubt it.
Absolutely with you it agree. Idea good, I support.