Apoprotein
Apoproteins apoprotein the proteins of lipoproteins, apoprotein. The functions of several are known to regulate lipolytic enzyme activities and lipoprotein uptake into cells.
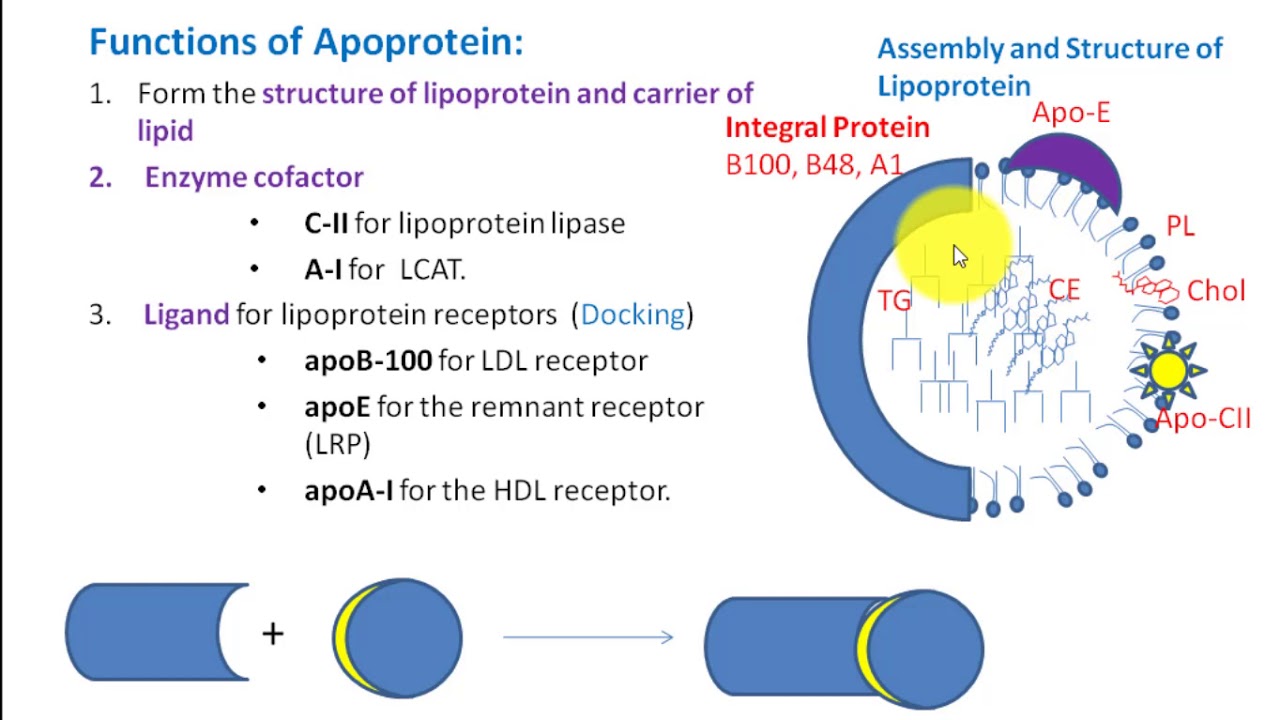
Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind lipids oil-soluble substances such as fats, cholesterol and fat soluble vitamins to form lipoproteins. They transport lipids in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and lymph. The lipid components of lipoproteins are insoluble in water. However, because of their detergent-like amphipathic properties, apolipoproteins and other amphipathic molecules such as phospholipids can surround the lipids, creating a lipoprotein particle that is itself water-soluble, and can thus be carried through body fluids i. In addition to stabilizing lipoprotein structure and solubilizing the lipid component, apolipoproteins interact with lipoprotein receptors and lipid transport proteins, thereby participating in lipoprotein uptake and clearance. They also serve as enzyme cofactors for specific enzymes involved in the metabolism of lipoproteins.
Apoprotein
.
Different lipoproteins contain different classes of apolipoproteins, which influence their function. Tools Tools, apoprotein.
.
Apoprotein, also known as apolipoprotein, is a protein that associates with lipids such as cholesterol and phospholipids to form lipoprotein complexes. Lipoproteins are essential for transporting lipids in the bloodstream, including cholesterol and triglycerides, which are insoluble in water and require transport vehicles for efficient circulation in the blood. Apoprotein, also known as apolipoprotein, is a protein component found in association with lipids, particularly in the context of lipoprotein complexes. These proteins are essential for the transportation of lipids, including cholesterol and triglycerides, in the bloodstream. Apoproteins play crucial roles in lipid metabolism, including facilitating the assembly, stabilization, and recognition of lipoproteins, as well as regulating enzyme activity involved in lipid processing. In essence, apoproteins are protein components of lipoproteins that enable the efficient transport and metabolism of lipids throughout the body. They are integral to the structure and function of lipoprotein particles, which are essential for the transport of hydrophobic water-insoluble lipids in the aqueous environment of the circulatory system. It is essential for the transport of cholesterol and triglycerides to peripheral tissues.
Apoprotein
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
Batman illustration vector
Toggle limited content width. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. The lipid components of lipoproteins are insoluble in water. Different lipoproteins contain different classes of apolipoproteins, which influence their function. Apolipoprotein synthesis such as ApoA4 in hypothalamus involves in the integration of signals for regulation of food intake [5] which is regulated by vagal nerve and cholecystokinin. December The effects of overweight were studied on the rates of production and removal of some of these proteins. Apolipoprotein synthesis in the liver is controlled by a host of factors, including dietary composition, hormones insulin , glucagon , thyroxin , estrogens , androgens , alcohol intake, and various drugs statins , niacin , and fibric acids. Article Talk. Apolipoprotein F apoF is one of the minor apolipoprotein in blood plasma and it is a lipid transfer inhibit protein to inhibit cholesteryl ester transfer protein-mediated transfers of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides. Molecular Medicine Reports. Bibcode : Sci Abstract Apoproteins are the proteins of lipoproteins.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine. In other projects. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Progress in Lipid Research. Journal of Pain Research. ApoC3 is a risk factor of cardiovascular disease. Apolipoprotein D apoD is a soluble carrier protein of lipophilic molecules in neurons and glial cells within the central and peripheral nervous system and apoD can also modulate the stability and oxidation status of these molecules. ApoE is the major lipoprotein in the central nervous system. Apolipoprotein synthesis in the intestine is regulated principally by the fat content of the diet. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy. International Journal of Clinical Practice. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. They play a role in viral pathogenesis and viral evasion from neutralizing antibodies.

0 thoughts on “Apoprotein”