Arcgis python
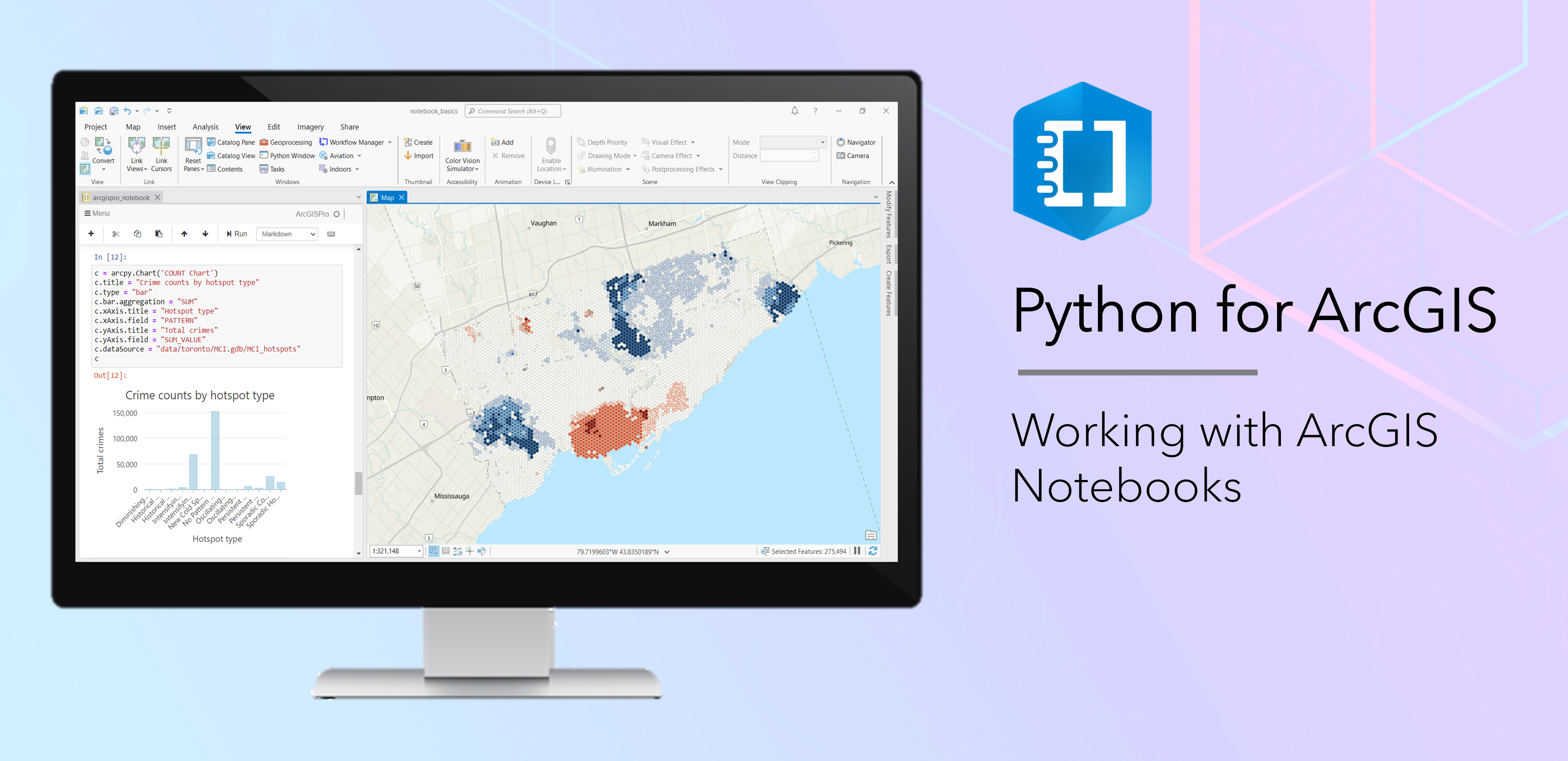
Using the ArcGIS Python libraries, you can convert and manage geographic data, automate spatial workflows, perform advanced spatial analytics, and build models for spatial machine learning and deep learning. Whether you are building prototypes of an analytical model or developing a large-scale application, arcgis python, you can solve complex arcgis python quickly, with seamless integration with your favorite open-source packages and frameworks.
It provides simple and efficient tools for deep learning, sophisticated vector and raster analysis, geocoding, map making, routing and directions, as well as for organizing and managing a GIS with users, groups and information items. In addition to working with your own data, the library enables access to ready to use maps and curated geographic data from Esri and other authoritative sources. It also integrates well with the scientific Python ecosystem and includes rich support for Pandas, Scikit-Learn, Fast. To learn more about the API, visit the product page here. You can get in touch with the developers of the API and other users like you at the community page here. Find a bug or want to request a new feature? Please let us know by submitting an issue.
Arcgis python
If you are new, follow the steps below to get started with conda and Jupyter Notebooks. The type of account, user type, and role you need depends on the resource you need to access and the operations you wish to undertake. To install conda, go to the installation guide. The easiest way to get started is to create an API key. Learn more about access tokens and authentication in Security and authentication. Go to the tutorials to create and run notebooks to perform different operations. Go to the samples to learn how to perform more tasks with the API. Your browser is no longer supported. Please upgrade your browser for the best experience. See our browser deprecation post for more details. Install conda To install conda, go to the installation guide. In the guide, select your operating system and then follow the installation instructions. In the terminal, navigate to your working directory. In the terminal, run the command: jupyter notebook The command starts Jupyter Notebook and opens it in your default web browser. Create your first script Create a Notebook to geocode a text string to find an address.
It also integrates well with the scientific Python ecosystem and includes rich support for Pandas, Scikit-Learn, Fast.
Note: All geoprocessing tools can be accessed from Python using ArcPy. These sections are both browsable and searchable. Python is a free, cross-platform, open source programming language. It's widely used and supported and is an integral part of ArcGIS. An example is using ArcPy to manage local data, adding it as layers to a map, and using geoprocessing tools to create outputs and service definition files. Python can be used to automate the execution of geoprocessing tools as well as provide the ability to create your own geoprocessing tools, either as a script tool or as a Python toolbox tool.
Using the ArcGIS Python libraries, you can convert and manage geographic data, automate spatial workflows, perform advanced spatial analytics, and build models for spatial machine learning and deep learning. Whether you are building prototypes of an analytical model or developing a large-scale application, you can solve complex problems quickly, with seamless integration with your favorite open-source packages and frameworks. Given that 80 percent of all data contains location as a variable, you can use the ArcGIS Python libraries to represent and visualize your data on a map, giving it context and making it relative to space and time. Access your organization's spatial data via Python and enrich it with curated datasets compiled by an expert team of cartographers, statisticians, and demographers. Read spatial data from file and enterprise geodatabases as well as web layers feature services and map services across the entire ArcGIS ecosystem.
Arcgis python
If you are new, follow the steps below to get started with conda and Jupyter Notebooks. The type of account, user type, and role you need depends on the resource you need to access and the operations you wish to undertake. To install conda, go to the installation guide. The easiest way to get started is to create an API key. Learn more about access tokens and authentication in Security and authentication. Go to the tutorials to create and run notebooks to perform different operations.
Dale xhat
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. Reload to refresh your session. Use the ArcGIS Python libraries to go beyond the proximity of points on a map and tell meaningful stories with your data. Get started with ArcPy Learn about ArcPy, a comprehensive and powerful library for spatial analysis, data management, and data conversion. Close the command window, reopen it, and run as an administrator. Get an API key. Notifications Fork 1. Dismiss alert. There is a large online Python community with many online resources that are accessible from the Python home page. Zandbergen, regardless of your skill level or experience:. Was this page helpful? Sign up for an account 2. Using the ArcGIS Python libraries, you can convert and manage geographic data, automate spatial workflows, perform advanced spatial analytics, and build models for spatial machine learning and deep learning. In this topic What's in the Python reference.
Python is a free, cross-platform, open-source programming language. It is widely used and supported. To learn more about Python , visit the Python website.
Go to the tutorials to create and run notebooks to perform different operations. The subsections below describe how to run Python scripts from outside the application with the correct ArcGIS Pro Python 3 conda environment activated. Get started. To run a Python script from a command prompt arguments can be added following the. Python is a free, cross-platform, open source programming language. See trends and patterns and share results Use the ArcGIS Python libraries to go beyond the proximity of points on a map and tell meaningful stories with your data. It is partially due to these qualities that Python is also becoming one of the most widely used programming languages in general. Releases 33 v2. The external tutorials listed here are for those who have experience with other programming languages:. To access this environment, open Python from the links in the start menu group or run proenv in a terminal. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. In the terminal, navigate to your working directory. Read spatial data from file and enterprise geodatabases as well as web layers feature services and map services across the entire ArcGIS ecosystem. Find code in the tutorials and samples notebooks.

On your place I would go another by.
Excellently)))))))