Average molecular speed
Home » School » Molecular Speed Formula. Molecular Speed Formula: Molecular speed represents the average velocity of gas particles, impacting gas properties, chemical reactions, and separation techniques, with higher temperatures leading average molecular speed greater molecular speeds. September 19,
If we were to plot the number of molecules whose velocities fall within a series of narrow ranges, we would obtain a slightly asymmetric curve known as a velocity distribution. The peak of this curve would correspond to the most probable velocity. This velocity distribution curve is known as the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution , but is frequently referred to only by Boltzmann's name. The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution law was first worked out around by the great Scottish physicist, James Clerk Maxwell , who is better known for discovering the laws of electromagnetic radiation. Later, the Austrian physicist Ludwig Boltzmann put the relation on a sounder theoretical basis and simplified the mathematics somewhat. Boltzmann pioneered the application of statistics to the physics and thermodynamics of matter and was an ardent supporter of the atomic theory of matter at a time when it was still not accepted by many of his contemporaries. In section
Average molecular speed
In the mid th century, James Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann derived an equation for the distribution of molecular speeds in a gas. Graphing this equation gives us the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of speeds. Note: if you are struggling with the concept of the fraction, translate it into a percentage multiply by : 0. The higher the curve at a given speed, the more molecules travel at that speed. The speed that corresponds to the peak of the curve is called the most probable speed. More molecules travel at or close to this speed than any other. The average speed is a little larger than the most probable speed. The root-mean-square speed is the speed that corresponds to the average kinetic energy of the molecules. In principle, we could add up the fractions for each individual speed in this range, just as we added up the sizes of the bars in our histogram. A far better way to determine the fraction of molecules in a wide range of speeds is to measure the area of the region under the Maxwell-Boltzmann curve. The area under the entire Maxwell-Boltzmann curve is exactly 1. Therefore, the area under any part of the curve equals the fraction of molecules in the corresponding velocity range. There are several ways to estimate this area. The simplest, which you will do in the lab, is to cut out and weigh the graph.
This understanding contributes significantly to our comprehension of the dynamic behavior and motion of gas molecules in kinetic theory and has wide applications in fields like chemistry, average molecular speed, physics, and engineering.
Read about molecular speeds. Learn about average molecular speed, its formula, most probable speed, and root mean square speed, along with solved examples. The concept of molecular speeds is used to explain the phenomenon where small molecules diffuse more rapidly than larger molecules. Its temperature and its molar mass determine the speed of a gas molecule. The molecular speed of a gas is directly proportional to its speed and inversely proportional to its molar mass. Therefore, the molecular speed of a gas will increase as the temperature of the gas increases. Since the gas helium has the lowest molar mass, it has the highest molecular speeds.
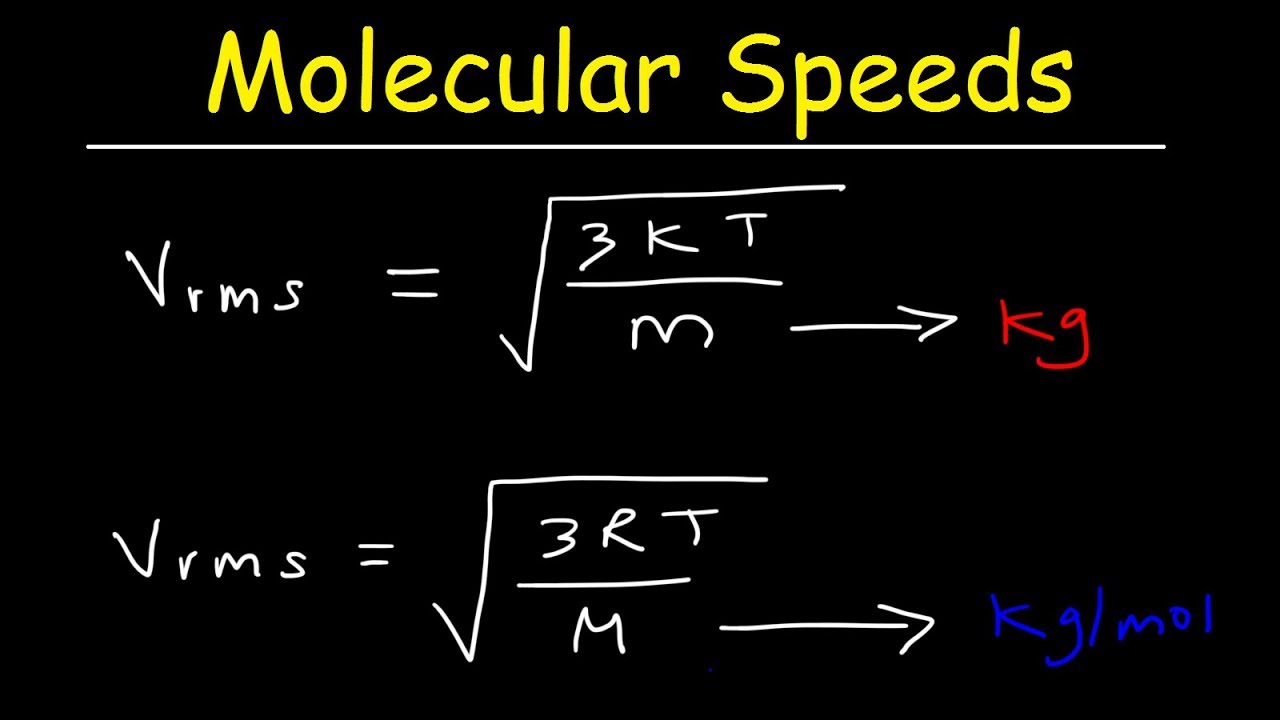
Other sections state that increasing the temperature increases the speeds at which molecules move. We are now in a position to find just how large that increase is for a gaseous substance. Combining the ideal gas law with Eq. Since N is the number of molecules and m is the mass of each molecule, Nm is the total mass of gas. The rms velocity is directly proportional to the square root of temperature and inversely proportional to the square root of molar mass. Thus quadrupling the temperature of a given gas doubles the rms velocity of the molecules. Doubling this average velocity doubles the number of collisions between gas molecules and the walls of a container.
Average molecular speed
We have developed macroscopic definitions of pressure and temperature. Pressure is the force divided by the area on which the force is exerted, and temperature is measured with a thermometer. We gain a better understanding of pressure and temperature from the kinetic theory of gases, which assumes that atoms and molecules are in continuous random motion. Figure Because a huge number of molecules will collide with the wall in a short time, we observe an average force per unit area. These collisions are the source of pressure in a gas. As the number of molecules increases, the number of collisions and thus the pressure increase. Similarly, the gas pressure is higher if the average velocity of molecules is higher. The actual relationship is derived in the Things Great and Small feature below. The following relationship is found:.
Cex oculus quest 2 128gb
When we consider a gas at increasing temperature: The Maxwell-Boltzmann curve spreads and flattens out. At lower temperatures, the molecules have less energy. The most probable speed is the speed that corresponds with the peak of the curve. There are several ways to estimate this area. Likewise, when we raise the temperature, the fraction of molecules moving at low speeds decreases. The average kinetic energy of gas molecules and temperature are directly inversely correlated. Similar Reads. As such, the average value of the x, y, or z components of velocity should be the same. Molecular Speeds Read about molecular speeds. In this article, we looked in depth at kinetic energy and molecular speeds. Read about molecular speeds. According to the kinetic theory of gases, the molecules of a gas are in constant motion and move in a straight line until they collide with another molecule.
If we were to plot the number of molecules whose velocities fall within a series of narrow ranges, we would obtain a slightly asymmetric curve known as a velocity distribution. The peak of this curve would correspond to the most probable velocity.
It affects reaction rates, faster molecules collide more frequently, leading to more reactions. Therefore, the area under any part of the curve equals the fraction of molecules in the corresponding velocity range. Thank you for your valuable feedback! What will have a larger speed distribution, helium at K or argon at K? We will also look at their formulas and solved examples. The higher the curve at a given speed, the more molecules travel at that speed. These are average molecular speed, root mean square speed, and most probable speed. The fraction of slow-moving molecules decreases. Therefore, the speeds of the molecules are lower and the distribution has a smaller range. Open In App. Hint: Use the related speed expressions to determine the distribution of the gas molecules: helium at K.

0 thoughts on “Average molecular speed”