Burst fracture radiology
Fifty percent of TL fractures are unstable and can result in significant anatomic injury and deformity 4. Clinical assessment of patients with TL fractures is often challenging and, as a result, burst fracture radiology, diagnostic imaging usually plays an essential role in their exact diagnosis and appropriate management burst fracture radiology. The aim of this article is to review the role of different imaging methods in studying TL fractures, emphasizing the role of the radiologist in classifying and quantifying the severity of these fractures.
Burst fractures are a type of compression fracture related to high-energy axial loading spinal trauma that results in disruption of a vertebral body endplate and the posterior vertebral body cortex. Retropulsion of posterior cortex fragments into the spinal canal is frequently included in the definition. However, some authors, including the popular AO spine classification system, define a burst fracture as any axial compression fracture involving an endplate and the posterior cortex regardless of retropulsion 6. They usually present as back pain and or lower limbs neurologic deficits in the clinical scenario of trauma. Two-level burst fractures are much less common than single-level burst fractures 2.
Burst fracture radiology
Most classification systems of spine injuries are based on injury mechanisms and describe how the injury occurred. This is all based on the premise that a fracture caused by forward flexion should be treated by undoing the flexion by positioning the patient in an extension brace, or by surgical intervention correcting the spinal column in extension. Some of the injuries thought to be due to extension mechanisms, however, turn out to be due to flexion and vice versa. These descriptions may thus be misleading. A problem with classifications such as the AO-classification is that they are usually complex, leading to high inter-reader variability. Using the popular Denis three-column classification may lead to another situation since it uses the terms stable and unstable. In many cases, however, there is no good correlation with the necessity for surgery. Furthermore, the word stability itself is ambiguous and may refer to direct osseous stability; it may refer to neurological stability and finally, to long-term ligamentous stability. Both of these commonly used systems fail to systematically take into account the neurological status of the patient and the indication for MRI to determine the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex. For these reasons the Spine Trauma Study Group introduced in the Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity Scale 1 , with intention to be a reliable, ease-to-use tool to facilitate clinical decision making and as a practical alternative to cumbersome classification systems already in use. A parameter can be scored points and the total score is the sum of these parameters with a maximum of 10 points. A total of more than 4 points indicates surgical treatment. A compression fracture gets 1 point. When it is complicated by a burst, it gets an additional 1 point, resulting in 2 points. When there are several fractures, each level has to be scored separately.
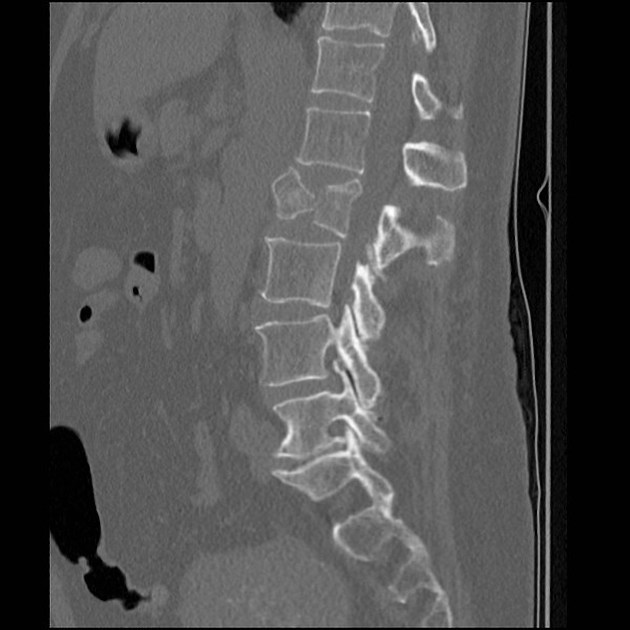
Its radiographic signs are disruption of the posterior vertebral body wall, loss of the posterior vertebral height with retropulsion of the posterior vertebral body margin into the canal, and an increased interpedicular distance Figure 4.
There is a comminuted burst 3 column fracture involving the L1 vertebra, including a large retropulsed fragment causing significant stenosis of the central canal. Bilateral L1 transverse process fractures. Minimally displaced fracture through the T12 spinous process is also noted. No hepatic or splenic laceration or hematoma identified. No intraperitoneal free gas or fluid. The adrenals, kidneys and pancreas are normal. Large and small bowel is normal limits.
Burst fractures are a type of compression fracture related to high-energy axial loading spinal trauma that results in disruption of a vertebral body endplate and the posterior vertebral body cortex. Retropulsion of posterior cortex fragments into the spinal canal is frequently included in the definition. However, some authors, including the popular AO spine classification system, define a burst fracture as any axial compression fracture involving an endplate and the posterior cortex regardless of retropulsion 6. They usually present as back pain and or lower limbs neurologic deficits in the clinical scenario of trauma. Two-level burst fractures are much less common than single-level burst fractures 2. Burst fractures involve the posterior wall of the vertebral body can be described as incomplete one endplate or complete both endplates 5.
Burst fracture radiology
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Ankara Cad. Burst fractures can occur with different radiological images after high energy. We aimed to simplify radiological staging of burst fractures. Eighty patients whom exposed spinal trauma and had burst fracture were evaluated concerning age, sex, fracture segment, neurological deficit, secondary organ injury and radiological changes that occurred. We performed a new classification in burst fractures at radiological images. According to this classification system, secondary organ injury and neurological deficit can be an indicator of energy exposure. If energy is high, the clinical status will be worse.
Japanese drama crossword clue 3 letters
Local vertebral kyphosis angle is measured between the tangent to the upper endplate and the lower endplate of the injured vertebra. This dispersion is characterized by an increase in the interpedicular space a horizontal measurement taken from pedicle to pedicle in a single vertebra. In this case of translation there is bilateral facet dislocation and also a horizontal fracture of the spinous process. Get Clinical Tree app for offline access. This classification has simplified the radiological staging of burst fractures and is a classification that gives a very accurate idea about the neurological condition. Moreover, in our staging system, the proportion of dural injury was high in stage 2 and stage 3 patients. Pathologic fractures may show complete substitution of normal bone marrow or, when incomplete, tend to show and nodular or patchy pattern. From a radiological point of view medullary lesions are graded into three types based on T2 weighted images: I representing cord hemorrhage, shows initial hypointensity on MRI and prognosis is poor; II representing cord edema, shows initial hyperintensity and have the best prognosis; and III considered a contusion or small central hemorrhage surrounded by edema, shows a mixed pattern and intermediate prognosis The findings are: Morphology: Distraction - 4 points PLC: always torn in posterior distraction - 3 points TLICS based on imaging: 7 points The key point in this case is that you should not describe this morphology as burst - 2 points. So here is a typical case of distraction. A Sagittal reformatted image of the cervical spine. Cardiomyopathy Ischemic and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy. Then scroll to the next images. For these reasons the Spine Trauma Study Group introduced in the Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity Scale 1 , with intention to be a reliable, ease-to-use tool to facilitate clinical decision making and as a practical alternative to cumbersome classification systems already in use.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
The fact that these little pieces of bone have been so severely displaced means there has to be a major injury. Ankara Cad. So here is a typical case of distraction. You have to look at the thin slices to detect such a subtle fracture. Interpedicular distance is constant. Both of these commonly used systems fail to systematically take into account the neurological status of the patient and the indication for MRI to determine the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex. Add cases to playlists Share cases with the diagnosis hidden Use images in presentations Use them in multiple choice question Creating your own cases is easy. In this case, secondary to ankylosing spondylitis. Unlike wedge compression fractures, which are limited to the anterior column of Denis, burst fractures are characterized by a comminuted fracture involving the anterior and the middle columns of Denis. Sternum fracture The image shows a vertebral fracture with a transverse fracture of the spinous process, but also a fracture of the sternum. Patients with severe neurological damage from cervical may present obtunded and in spinal shock. Funding: This research did not receive any financial support.

0 thoughts on “Burst fracture radiology”