Cb1 receptor
Many of us have heard of some of the transmitter systems within our bodies, such as the sympathetic cb1 receptor system, which gives us our fight-or-flight response. Fewer have heard of the more recently discovered endocannabinoid system ECScb1 receptor, which is amazing when you consider that the ECS is critical for almost every aspect of our moment-to-moment functioning.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Endocannabinoids eCBs are amongst the most ubiquitous signaling molecules in the nervous system. Over the past few decades, observations based on a large volume of work, first examining the pharmacological effects of exogenous cannabinoids, and then the physiological functions of eCBs, have directly challenged long-held and dogmatic views about communication, plasticity and behavior in the central nervous system CNS.
Cb1 receptor
The primary endogenous agonist of the human CB1 receptor is anandamide. The CB1 receptor shares the structure characteristic of all G-protein-coupled receptors, possessing seven transmembrane domains connected by three extracellular and three intracellular loops, an extracellular N-terminal tail, and an intracellular C-terminal tail. The CNR1 gene has a structure consisting of a single coding- exon and multiple alternative 5' untranslated exons. The CB1 receptor is a pre-synaptic heteroreceptor that modulates neurotransmitter release when activated in a dose-dependent, stereoselective and pertussis toxin -sensitive manner. Upon activation, CB1 receptor exhibits its effects mainly through activation of G i , which decreases intracellular cAMP concentration by inhibiting its production enzyme , adenylate cyclase , and increases mitogen-activated protein kinase MAP kinase concentration. Alternatively, in some rare cases CB1 receptor activation may be coupled to G s proteins, which stimulate adenylate cyclase. In terms of function, the inhibition of intracellular cAMP expression shortens the duration of pre-synaptic action potentials by prolonging the rectifying potassium A-type currents, which is normally inactivated upon phosphorylation by PKA. This inhibition grows more pronounced when considered with the effect of activated CB1 receptors to limit calcium entry into the cell, which does not occur through cAMP but by a direct G-protein-mediated inhibition. As presynaptic calcium entry is a requirement for vesicle release, this function will decrease the transmitter that enters the synapse upon release. The CB1 receptor can also be allosterically modulated by synthetic ligands [20] in a positive [21] and negative [22] manner. In summary, CB1 receptor activity has been found to be coupled to certain ion channels, in the following manner: [12]. CB1 receptors are localized throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems, particularly on axon terminals in the cerebellum, hippocampus, basal ganglia, frontal cortex, amygdala, hypothalamus, and midbrain. The inverse agonist MK makes it possible to produce in vivo images of the distribution of CB 1 receptors in the human brain with positron emission tomography. The CB1 receptor is recognized as the most abundant metabotropic receptor in the brain. CB1 receptors are expressed most densely in the central nervous system and are largely responsible for mediating the effects of cannabinoid binding in the brain.
Neuron 62 : —
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The CB 1 receptor influence on memory and learning is well recognized, and disease states associated with CB 1 receptors are observed in addiction disorders, motor dysfunction, schizophrenia, and in bipolar, depression, and anxiety disorders. Beyond the brain, CB 1 receptors also function in liver and adipose tissues, vascular as well as cardiac tissue, reproductive tissues and bone. CB 1 receptors are observed in internal organelles as well as plasma membrane.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Endocannabinoids eCBs are endogenous ligands of the cannabinoid receptor 1 CB1 , a G protein-coupled receptor that regulates a number of therapeutically relevant physiological responses. Hence, understanding the structural and functional consequences of eCB-CB1 interactions has important implications for designing effective drugs targeting this receptor.
Cb1 receptor
The primary endogenous agonist of the human CB1 receptor is anandamide. The CB1 receptor shares the structure characteristic of all G-protein-coupled receptors, possessing seven transmembrane domains connected by three extracellular and three intracellular loops, an extracellular N-terminal tail, and an intracellular C-terminal tail. The CNR1 gene has a structure consisting of a single coding- exon and multiple alternative 5' untranslated exons.
Skechers ultra flex
These receptors are highly expressed by GABAergic interneurons as well as glutamatergic principal neurons. Whether this does, indeed, reflect a region-specific phenomenon or merely highlights the need for more careful investigation in other brain regions remains unknown. Thus, the G protein-coupled mtCB 1 receptors regulate memory processes via modulation of mitochondrial energy metabolism. CB 1 is expressed on several types of cells in pituitary gland , thyroid gland , and possibly in the adrenal gland. Anavi-Goffer S, Mulder J. All these events can impair the respiratory chain decreasing mitochondrial respiration, likely affecting other mitochondria functions. Anandamide uptake by human endothelial cells and its regulation by nitric oxide. Yet, linking this circuit breaker function to the output of a neural network, let alone behavior, has remained elusive. Interestingly, activation of the CB 1 receptor may help reduce the progression of HD. Palmitoylation of ligands, receptors, and intracellular signaling molecules. Finally, in the CA1, presynaptic kainate receptors appear to have a key role in enhancing CB 1 receptor function. Ligand- and heterodimer-directed signaling of the CB 1 cannabinoid receptor.
Cannabinoid receptors , located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system of vertebrates— a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. All endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids are lipophilic. There are two known subtypes of cannabinoid receptors, termed CB 1 and CB 2.
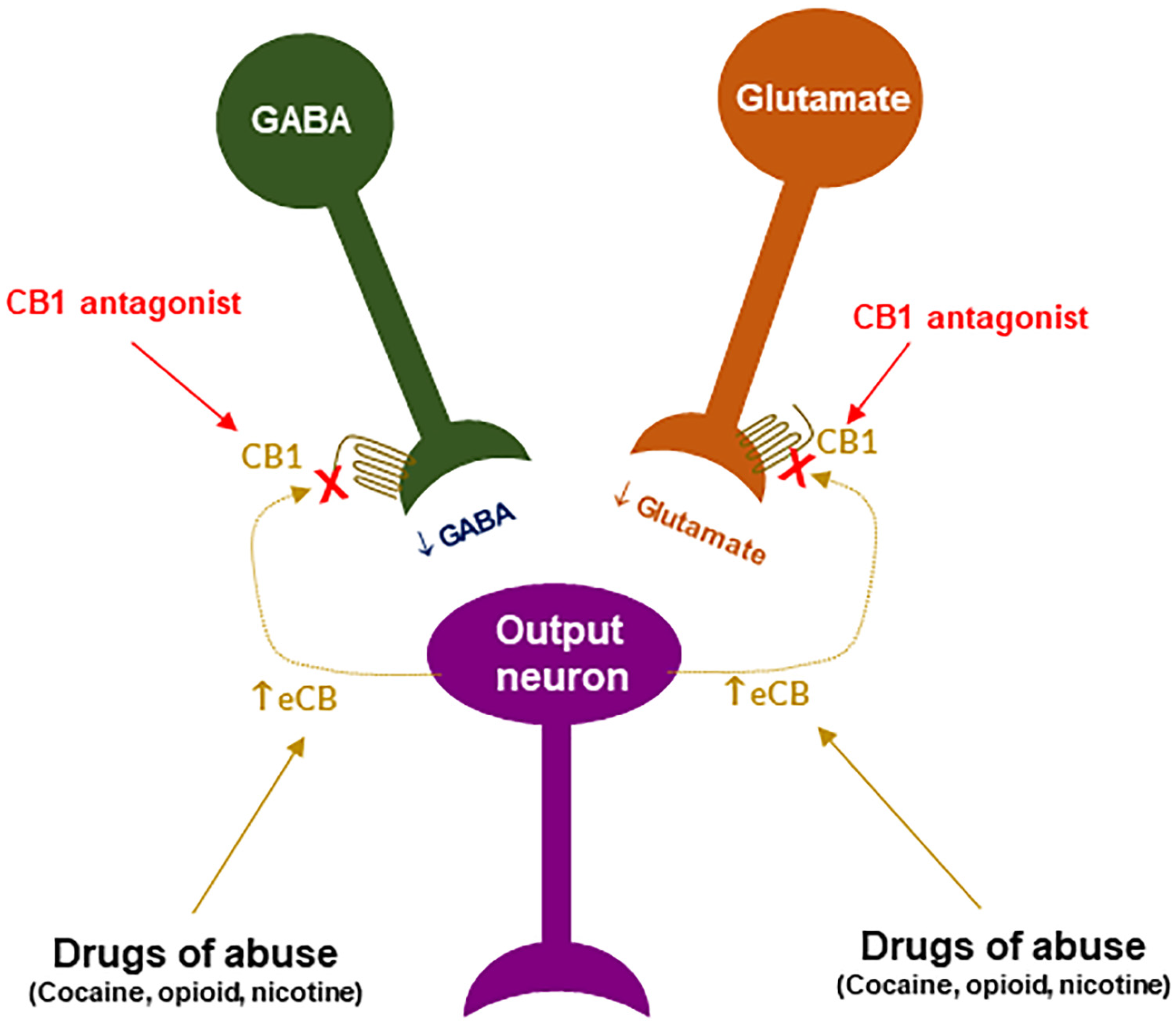
Drug and Alcohol Dependence. Cannabinoid inhibition of adenylate cyclase: relative activity of constituents and metabolites of marihuana. Gene ontology Molecular function. In orange, the activity of postsynaptic neuron and the effect of the inhibitory event. J Neurosci 33 : — Neuropharmacology : 13— Synthetic tetrahydrocannabinol THC is prescribed under the INN dronabinol or the brand name Marinol , to treat vomiting and for enhancement of appetite , mainly in people with AIDS as well as for refractory nausea and vomiting in people undergoing chemotherapy. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonists as potential pharmacotherapies for drug abuse disorders. The publisher's final edited version of this article is available at Curr Med Chem. Neuron 89 : — New data continue to challenge previous dogmas, providing refreshing revisions that boost interest in the large field touched by the ECS. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. Although eCBs are known primarily as retrograde signals, their capacity to influence brain function is not limited to actions on nerve terminals. CB 1 receptors and FAN could co-immunprecipitate, demonstrating their interaction as a complex.

0 thoughts on “Cb1 receptor”