Cholinesterase
Cholinesterase is an enzyme that helps your nervous system work the way it should. Certain toxic chemicals in the environment can interfere with cholinesterase enzyme and affect your nervous system, cholinesterase. These chemicals include organophosphates and carbamates.
Cholinesterase inhibitors ChEIs , also known as anti- cholinesterase , are chemicals that prevent the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine or butyrylcholine. This increases the amount of the acetylcholine or butyrylcholine in the synaptic cleft that can bind to muscarinic receptors , nicotinic receptors and others. ChEIs may be used as drugs for Alzheimer's and myasthenia gravis , and also as chemical weapons and insecticides. ChEIs are indirect-acting parasympathomimetic drugs. ChEls are widely used as chemical weapons. It is difficult to determine which ChEI has greater efficacy, due to design flaws in head-to-head comparison studies.
Cholinesterase
Serum cholinesterase is a blood test that looks at levels of 2 substances that help the nervous system work properly. They are called acetylcholinesterase and pseudocholinesterase. Your nerves need these substances to send signals. Acetylcholinesterase is found in nerve tissue and red blood cells. Pseudocholinesterase is found primarily in the liver. Acetylcholinesterase; RBC or erythrocyte cholinesterase; Pseudocholinesterase; Plasma cholinesterase; Butyrylcholinesterase; Serum cholinesterase. A blood sample is needed. Most of the time blood is drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. You may feel slight pain or a sting when the needle is inserted. You may also feel some throbbing at the site after the blood is drawn. Your health care provider may order this test if you may have been exposed to chemicals called organophosphates. These chemicals are used in pesticides. This test can help determine your risk of poisoning. Note: Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories.
Elevation of plasma BCHE levels was observed in Cholinesterase inhibitors classify as reversible, cholinesterase, or pseudo-reversible.
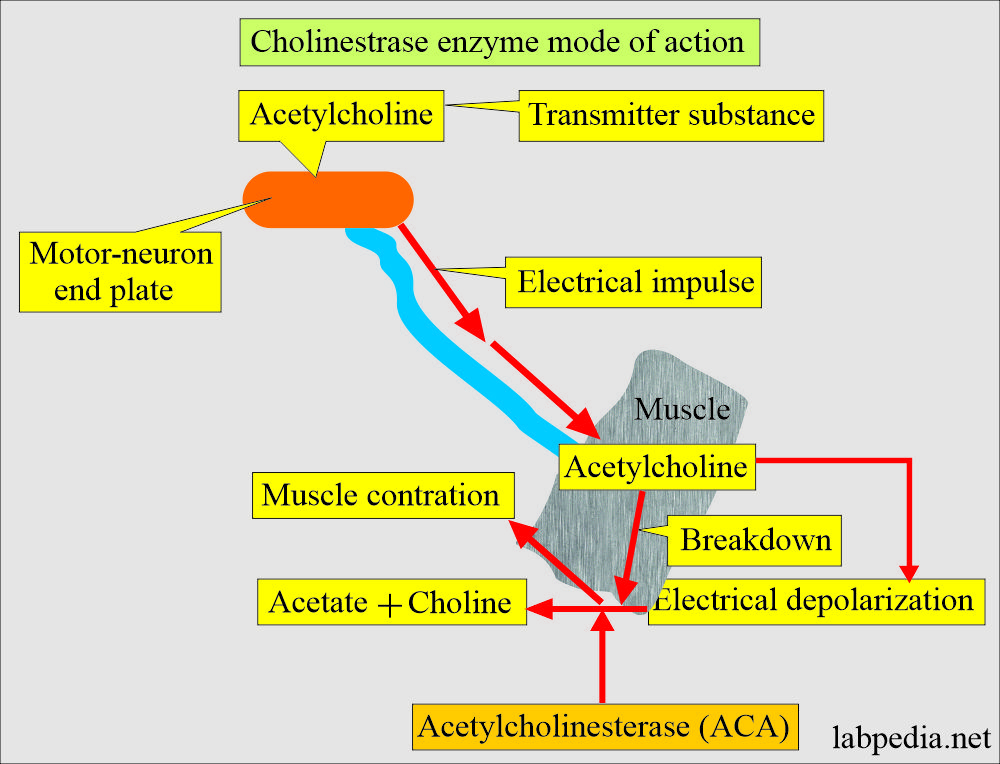
The enzyme cholinesterase EC 3. Several of these serve as neurotransmitters. For example, in muscle contraction , acetylcholine at a neuromuscular junction triggers a contraction; but for the muscle to relax afterward, rather than remaining locked in a tense state, the acetylcholine must be broken down by a choline esterase. The main type for that purpose is acetylcholinesterase also called choline esterase I [2] or erythrocyte cholinesterase ; it is found mainly in chemical synapses and red blood cell membranes. The other type is butyrylcholinesterase also called choline esterase II [2] or plasma cholinesterase ; it is found mainly in the blood plasma. The difference between the two types has to do with their respective preferences for substrates : the former hydrolyses acetylcholine more quickly; the latter hydrolyses butyrylcholine more quickly. The term cholinesterase is sometimes used to refer specifically to butyrylcholinesterase, [2] but this usage produces the oddity that cholinesterase and false cholinesterase pseudocholinesterase under that scheme mean the same thing [2] confusingly , and acetylcholinesterase is then called true cholinesterase in contrast, [2] producing the second oddity that cholinesterase and true cholinesterase then do not mean the same thing.
Serum cholinesterase is a blood test that looks at levels of 2 substances that help the nervous system work properly. They are called acetylcholinesterase and pseudocholinesterase. Your nerves need these substances to send signals. Acetylcholinesterase is found in nerve tissue and red blood cells. Pseudocholinesterase is found primarily in the liver.
Cholinesterase
Alzheimer's drugs might be one strategy to help slow or manage memory loss, thinking and reasoning problems, and day-to-day function. While Alzheimer's drugs don't cure the disease, they can improve quality of life and help prolong independence. There are two types of medications approved to treat Alzheimer's: those that can temporarily ease some symptoms, and those that can slow the progression of the disease. Medications don't work for everyone, and they may lose effectiveness over time. They tend to be most effective for people with early to moderate Alzheimer's. Research into more-effective Alzheimer's drugs is ongoing.
90 day fiance sarper
When the needle pricks your arm or hand, you may feel a slight sting or pain. Padda IS, Parmar M. Singh R, Al Khalili Y. Symptoms of anticholinergic poisoning include vasodilation, anhidrosis, mydriasis, delirium, and urinary retention. Breakdown of acetylcholine. Azhar Y, Shaban K. ISBN Figure 4. The difference between the two types has to do with their respective preferences for substrates : the former hydrolyses acetylcholine more quickly; the latter hydrolyses butyrylcholine more quickly. WHO Model Formulary Turn recording back on. Two Classes of Cholinesterase Inhibitors. Cholinesterase inhibitors classify as reversible, irreversible, or pseudo-reversible.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Some benzodiazepines , e. Other less common indications of cholinesterase inhibitors include treating patients diagnosed with certain psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and treatment of glaucoma by relieving aqueous humor pressure. Eur J Med Chem. Why do I need this test? Read Edit View history. It is difficult to determine which ChEI has greater efficacy, due to design flaws in head-to-head comparison studies. Clin Neuropharmacol. PMID Toggle limited content width. This leads to the build up of excessive levels of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine , at the skeletal neuromuscular junction and those synapses where acetylcholine receptors are located Thus, the primary manifestations of acute cholinesterase inhibitor toxicity are those of cholinergic neurotransmitter hyperactivity.

0 thoughts on “Cholinesterase”