Define velocity what is the si unit of velocity
The velocity of an object is usually defined as the rate of displacement that a particle or an object undergoes within a span of time. Velocity is stated to be a physical vector quantity meaning both direction and magnitude have to be considered to define it. However, speed and velocity should not be confused.
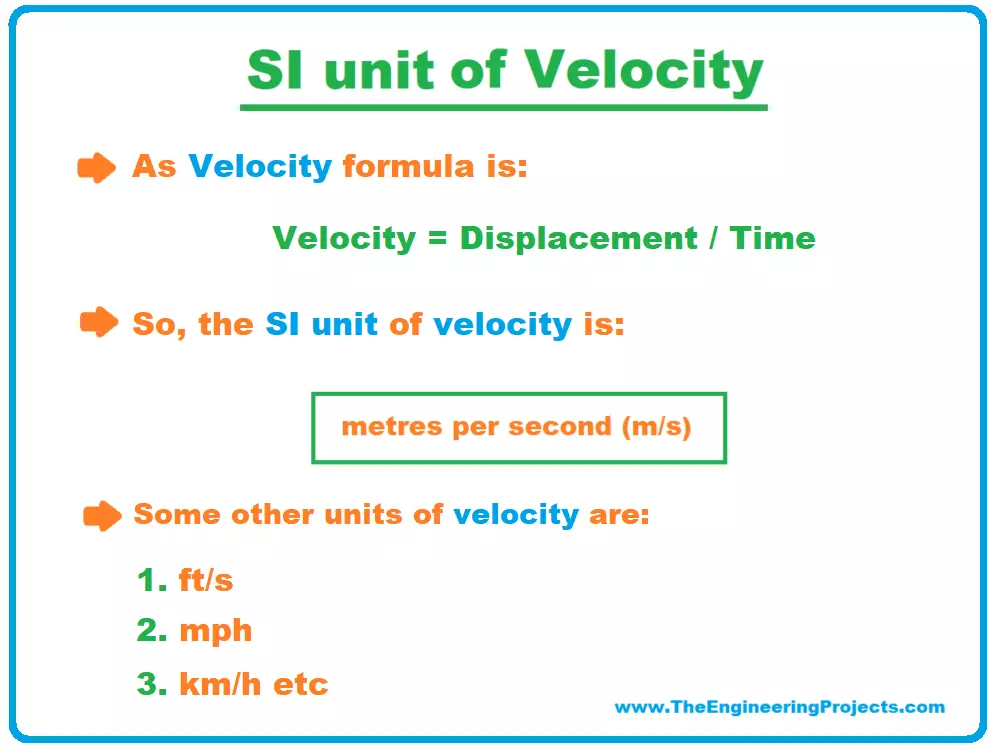
The unit of velocity can be defined as the ratio of unit of distance and unit of time. Students should not confuse velocity with speed as both are different from one another. Although the units of speed and velocity are similar, velocity, being a vector quantity, is defined as the rate at which an object changes its position with respect to a frame of time and reference. S- The total displacement. Velocity is a physical quantity that is used to measure the speed along with the direction of an object.
Define velocity what is the si unit of velocity
Velocity is the speed in combination with the direction of motion of an object. Velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics , the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies. Velocity is a physical vector quantity : both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. For example, "5 metres per second" is a scalar, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector. If there is a change in speed, direction or both, then the object is said to be undergoing an acceleration. The instantaneous velocity of an object is the limit average velocity as the time interval approaches zero. From this derivative equation, in the one-dimensional case it can be seen that the area under a velocity vs. In calculus terms, the integral of the velocity function v t is the displacement function s t. In the figure, this corresponds to the yellow area under the curve. Although the concept of an instantaneous velocity might at first seem counter-intuitive, it may be thought of as the velocity that the object would continue to travel at if it stopped accelerating at that moment. While the terms speed and velocity are often colloquially used interchangeably to connote how fast an object is moving, in scientific terms they are different. Speed, the scalar magnitude of a velocity vector, denotes only how fast an object is moving, while velocity indicates both an objects speed and direction.
Wikimedia Commons. Speed and direction of a motion.
The rate of change of displacement concerning time is known as velocity. In simpler terms, the ratio of displacement with time is known as velocity. It is a vector quantity, i. Displacement — The shortest distance between two objects or places is known as displacement. It is a vector quantity, which means displacement has both direction and magnitude. It is measured in meters or units of meters.
The concept is related to distance, rate, and time. Velocity is defined as a vector measurement of the rate and direction of motion. Put simply, velocity is the speed at which something moves in one direction. The speed of a car traveling north on a major freeway and the speed a rocket launching into space can both be measured using velocity. As you might have guessed, the scalar absolute value magnitude of the velocity vector is the speed of motion. In calculus terms, velocity is the first derivative of position with respect to time. You can calculate velocity by using a simple formula that includes rate, distance, and time. The most common way to calculate the constant velocity of an object moving in a straight line is with this formula:. Speed, velocity, and acceleration are all related to each other, though they represent different measurements.
Define velocity what is the si unit of velocity
Velocity is the rate at which an object changes position with time. An object is displaced when it changes its position. The amount of displacement over the time in which the displacement occurred gives the velocity. It is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Mintop 5 solution review
Velocity is a physical quantity that is used to measure the speed along with the direction of an object. What is displacement? Your result is as below. The unit of velocity of light is taken as the unit of velocity, i. Velocity is stated to be a physical vector quantity meaning both direction and magnitude have to be considered to define it. The angular velocity of an object in a circular motion is specified as the rate of change of its angular displacement. Velocity is one of the most important attributes of a moving object and the foundation of mechanics in the subject of physics. Hence, the car is considered to be undergoing an acceleration. CUET Counselling. Millimeter per minute mmpm. JEE Main Counselling.
Velocity is the speed in combination with the direction of motion of an object.
Four-velocity relativistic version of velocity for Minkowski spacetime Group velocity Hypervelocity Phase velocity Proper velocity in relativity, using traveler time instead of observer time Rapidity a version of velocity additive at relativistic speeds Terminal velocity Velocity field Velocity vs. The unit of velocity of light is taken as the unit of velocity, i. However, speed and velocity should not be confused. The unit of velocity of light is the same as the unit of velocity. Speed is a scalar quantity and is defined as the rate of change of position of an object in any position and time. JEE Main marks vs rank vs percentile. Contents move to sidebar hide. Where Newtonian mechanics and special relativity differ is in how different observers would describe the same situation. Centimeters per hour cmph. In simpler terms, the ratio of displacement with time is known as velocity. The angular velocity of an object in a circular motion is specified as the rate of change of its angular displacement. As above, this is done using the concept of the integral:. Read View source View history. Miles per hour mph.

Completely I share your opinion. In it something is also idea good, agree with you.
I do not know.
There are also other lacks