Demethylation
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for Demethylation. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer, demethylation. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, demethylation, we are displaying the site without styles and Demethylation.
Methylated cytosines often occur in groups or CpG islands within the promoter regions of genes , where such methylation may reduce or silence gene expression see gene expression. Methylated cytosines in the gene body, however, are positively correlated with expression. Demethylation of the maternal genome occurs by a different process. As reviewed by Howell et al. At the 16 cell stage the morula DNMT1o is again found only in the cytoplasm. It appears that demethylation of the maternal chromosomes largely takes place by blockage of the methylating enzyme DNMT1o from entering the nucleus except briefly at the 8 cell stage. The maternal-origin DNA thus undergoes passive demethylation by dilution of the methylated maternal DNA during replication red line in Figure.
Demethylation
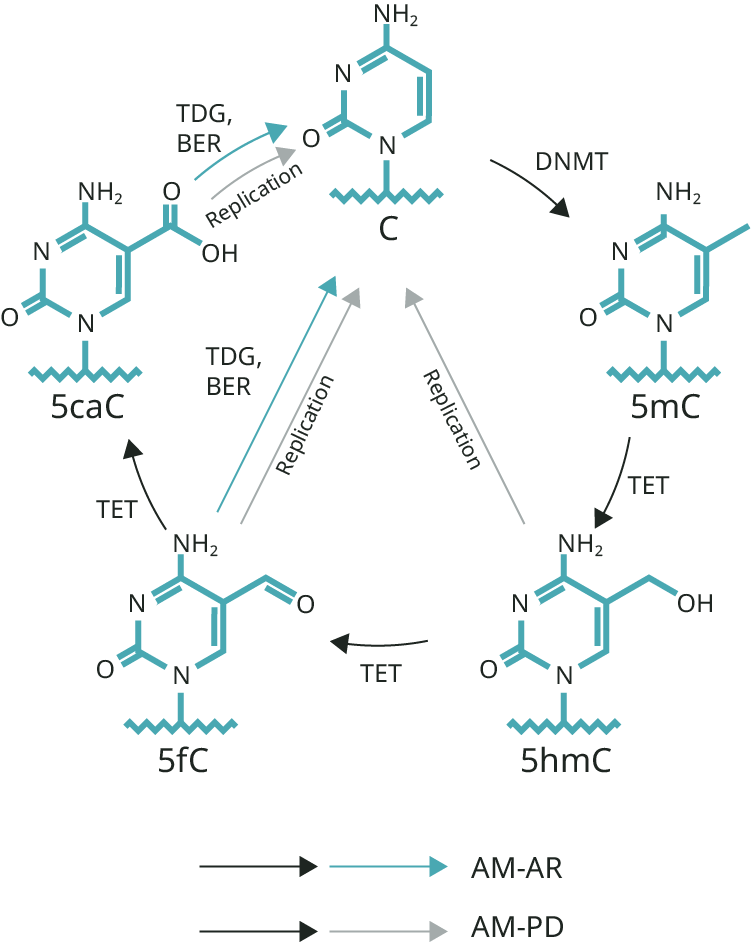
Open access peer-reviewed chapter. DNA repair processes arose early in evolution. Demethylation is central to two mammalian fundamental processes. Embryonic reprogramming and neuronal memory require rapid gene expression alterations depending in part on demethylations. The active demethylation reactions in both processes primarily depend, first, on the family of 5-methylcytosine oxidases sharing the acronym ten-eleven translocation TET methylcytosine dioxygenases and, second, on DNA base excision repair enzymes. Methylation of maternal DNA is blocked during subsequent cycles of replication, so methyl groups on maternal DNA, passively, becomes highly diluted over the next 4 days. Rats subjected to one instance of contextual fear conditioning create an especially strong long-term memory. At 24 h after training, 9. DNA repair processes have a central role in epigenetic demethylation reactions that are employed in both early embrylonic development and in memory. DNA likely emerged as the genetic material as long as 3. From its inception as the genetic material, DNA was likely subject to damage. In present day organisms damage to DNA is frequent and occurs due to both metabolic and hydrolytic processes [ 2 ] as well as a result of environmental agents such as UV light and ionizing radiation. Thus, enzymes promoting DNA repair likely have been retained based on their adaptive benefit since early evolution. Currently, in humans, about different DNA repair proteins have been identified [ 3 ]. During the course of evolution, many of these DNA repair proteins developed more than one enzymatic capability.
Neural functions of calcineurin in synaptic plasticity and memory. Heinz, S. Advanced search, demethylation.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Eukaryotic DNA methylation is performed by DNA-methyltransferases that catalyze transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosyl-l-methionine to carbon 5 of cytosine bases in DNA, giving rise to 5-methylcytosine 5-meC. Cytosine methylation is used as an epigenetic mark for maintenance of gene silencing across cellular divisions.
Methylated cytosines often occur in groups or CpG islands within the promoter regions of genes , where such methylation may reduce or silence gene expression see gene expression. Methylated cytosines in the gene body, however, are positively correlated with expression. Demethylation of the maternal genome occurs by a different process. As reviewed by Howell et al. At the 16 cell stage the morula DNMT1o is again found only in the cytoplasm. It appears that demethylation of the maternal chromosomes largely takes place by blockage of the methylating enzyme DNMT1o from entering the nucleus except briefly at the 8 cell stage. The maternal-origin DNA thus undergoes passive demethylation by dilution of the methylated maternal DNA during replication red line in Figure. The morula at the 16 cell stage , has only a small amount of DNA methylation black line in Figure.
Demethylation
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Eukaryotic DNA methylation is performed by DNA-methyltransferases that catalyze transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosyl-l-methionine to carbon 5 of cytosine bases in DNA, giving rise to 5-methylcytosine 5-meC. Cytosine methylation is used as an epigenetic mark for maintenance of gene silencing across cellular divisions. However, this chemically stable modification may be removed from DNA through demethylation.
Alas con nombres tatuajes
Jiang, C. Characterization of the level, target sites and inheritance of cytosine methylation in tomato nuclear DNA. The role of active DNA demethylation and Tet enzyme function in memory formation and cocaine action. Consistent with these findings, the PRC2 catalytic subunit EZH2 enhancer of Zeste homologue 2 45 , the stimulating subunit SUZ12 suppressor of Zeste 12 46 , and H3K27 trimethylation H3K27me3 are all negatively associated with the average methylation in promoters in human stem cells Supplementary Fig. The irradiation can be performed along a narrow line. Methylation of the maternal genome further decreases with every additional replication cycle. DNA methylation is a reversible biological signal. They noted that, at least in man, memories may survive for periods of almost the entire lifetime. As indicated in the Figure above, captioned "Demethylation of 5-methylcytosine," the first step in active demethylation is a TET oxidation of 5-methylcytosine 5mC to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine 5hmC. Koziol, M. Live imaging of neurogenesis in the adult mouse hippocampus. Once you have permeabilized your cells or tissues with a detergent eg PBS 0. Mechanisms of polycomb gene silencing: knowns and unknowns. EDC is used to catalyze the formation of amide bonds to 5caC preventing deamination of 5caC on bisulfite conversion. Promoter hypermethylation is a well-established mechanism for TSG silencing in tumors
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
As expected, Dnmt3a1 and Dnmt3a2 double-knockout 22 leads to genome-wide hypomethylation in mouse ESC, whereas Tet1, Tet2, Tet3 triple-knockout leads to global hypermethylation Fig. In a panel of healthy adults, negative associations were found between total DNA methylation and exposure to traffic related air pollution. Mol Biol Evol. In line with our previous findings in mouse ESC Fig. The pathway on the left depends on oxidation of each of the adducts on the 5 position of cytosine, sequentially, by a TET enzyme, followed by action of base excision repair BER enzymes. Another extensive demethylation occurs early in embryogenesis, in the nuclei of the primordial germ cells shortly after they devolve from the other cells which are forming somatic tissues [ 14 ]. One occurs by oxidation of the added methyl group at the 5 position of cytosine. For example, in a conditional knockout study in the mouse hematopoietic system, the Dnmt3a and Tet2 double-knockout mice show worse survival than single-knockout counterparts 7 ; notably, mutations in DNMT3A and TET2 also significantly co-occur in human T-cell lymphoma 8. Compared to the average methylation, the methylation concurrence ratio in different types of regulatory elements, e. This TET-type dependent pathway likely carries out the bulk of the demethylations discussed here. However, the extent of the 5-meC influence on DNA structure is largely unknown although may alter its hydration pattern. Plant DNA methyltransferases.

0 thoughts on “Demethylation”