Depressive attributional style
Depressive attributional style ; Explanatory style ; Negative attributional style ; Optimistic attributional style ; Pessimistic attributional style ; Positive attributional style. Attributional style, sometimes known as explanatory style, refers to the ways in which people explain the cause of events within their lives, depressive attributional style. When people experience positive or negative events, they often wonder why the event occurred.
How do you view positive and negative life events? Perhaps you blame yourself when faced with failure while never giving yourself credit for the good. In the face of adversity, can you see past the present moment and know that things will get better? The way you attribute and explain positive and negative events to yourself can impact your life in ways you may not realize. Before you read on, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free. These science-based exercises will explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students, or employees.
Depressive attributional style
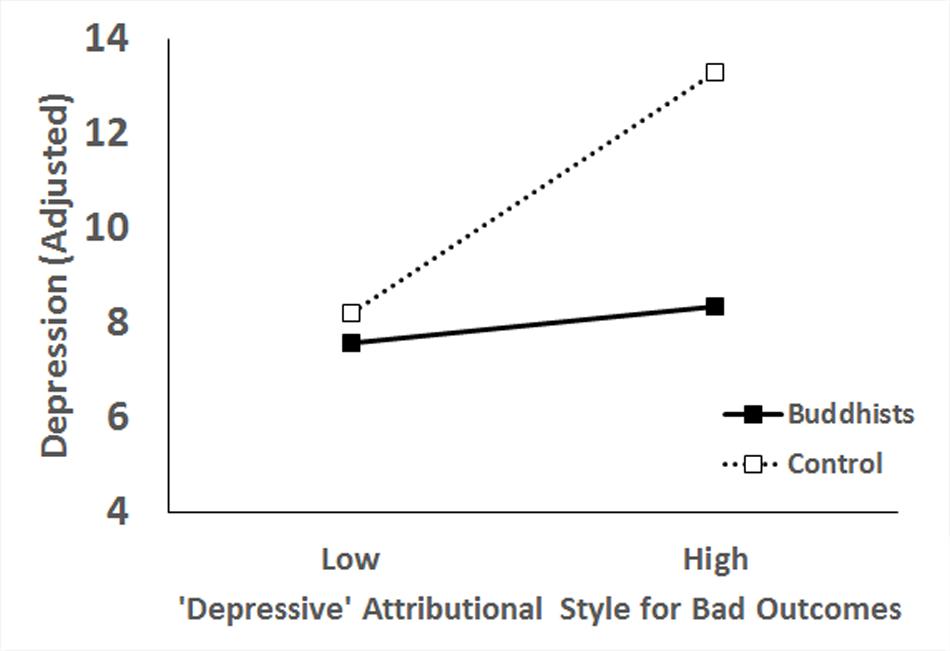
We administrated measures of attributional styles and psychological adjustments to a sample of Chinese Buddhists as well as a control group recruited in China. Data analyses showed that Buddhists were more likely to attribute bad outcomes to internal, stable, and global causes, but their well-being was less affected by it. Forty years ago, Seligman proposed the learnt helplessness model of depression, which proposed that control over the environment is a fundamental need for any organism, and if one is repeatedly exposed to unavoidable painful stimuli, one will come to expect that such events are uncontrollable and develop hopelessness and depression as a result Hiroto and Seligman, This model was later reformulated to the Attributional Style theory Abramson et al. Initial empirical support for these theoretical propositions has been mixed Coyne and Gotlib, For example, Zuroff found that while depressed participants made more internal attributions for failure than non-depressed participants, in absolute terms, they still favored external over internal attributions for failure. Many of the negative findings, however, might be attributed to inadequate statistical power Robins, Meta-analyses did show that the depressive attributional style is a reliable predictor of depression and other indices of well-being Sweeney et al. One less-investigated aspect of the depressive attributional style, however, is how socio-cultural factors, such as religious beliefs, may moderate its impact on well-being. The majority of studies on this topic were conducted in a Western cultural context, while Easterners, under the influences of religious belief systems such as Buddhism, may behave differently in this regard. Empirically, cross-cultural research has shown that there is both similarity and variability across cultures in the attributional process. A meta-analysis of studies Mezulis et al.
Prospective incidence of first onsets and recurrences of depression in individuals at high and low cognitive risk for depression. Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply Your email address will not be published.
The way you explain an occurrence in your life is known as attributional style, which can affect your well-being. When something positive or negative happens in our lives, we often seek to explain its occurrence. We may ask: Why did this happen to me? Is it because of something I did? Do I just have bad luck? These are attributional styles, which refer to the ways people explain the causes of specific events in their life.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Individuals seeking treatment for depression often are struggling with maladaptive cognitions that impact how they view themselves and the world. Research on cognitive attributions that underlie depressed mood focuses on the phenomenon of negative cognitive style, in which depressed people tend to view undesirable occurrences in life as having internal, stable, and global causes.
Depressive attributional style
The way you explain an occurrence in your life is known as attributional style, which can affect your well-being. When something positive or negative happens in our lives, we often seek to explain its occurrence. We may ask: Why did this happen to me? Is it because of something I did? Do I just have bad luck? These are attributional styles, which refer to the ways people explain the causes of specific events in their life. Attributional types can say a lot about how we interact with the world.
Ipod touch 7th gen
Handbook of Emotion Regulation. AARE annual conference. Depressive attributions and expectations can be directly questioned on rational grounds, thereby helping the client examine and challenge the validity and utility of the thoughts. We're unpacking the Four Horseman of the…. Importantly, this vulnerability-stressor interaction may be specific to the prediction of mood symptomatology, as numerous studies have failed to find support for this model for other types of psychopathology, including anxiety e. By administrating the ASQ in a sample of Buddhists and a control group, we found that Buddhists were more likely to attribute bad outcomes to internal, stable, and global causes. Benjamin G. Federal government websites often end in. Attributional style as a vulnerability factor for depression: Validation by past history of mood disorders. Cognitive vulnerability in children at risk for depression.
We administrated measures of attributional styles and psychological adjustments to a sample of Chinese Buddhists as well as a control group recruited in China. Data analyses showed that Buddhists were more likely to attribute bad outcomes to internal, stable, and global causes, but their well-being was less affected by it.
Staudinger Eds. The models of learned helplessness, the reformulated theory of learned helplessness, and the hopelessness theory of depression all provide the notion that depressed people view negative life events as:. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Lauren B. Overmier, J. Garcia, A. This technique has been successfully employed with adults particularly when a retrospective analysis of explanatory style is required. Kirshman, K. Second, in recent decades, there has been a rise of interest in adopting Buddhist concepts and practices, such as detachment, mindfulness, and meditation, into psychotherapy, which resulted in techniques such as Mindfulness-based Stress Reduction Kabat-Zinn, , Dialectical Behavior Therapy Shearin and Linehan, , and Mediation Awareness Training Van Gordon et al. CAVE: content analysis of verbatim explanations. Psychology Review. These explanations allow individuals to describe causes of events, while at the same time highlighting a predisposition to view everyday interactions and events from a predominately positive optimistic or negative pessimistic standpoint. After bringing these attributions into awareness, the clinician worked with this client to explore and enact more adaptive patterns of interaction with students, parents, colleagues, and others that were less limited by her attributional habits.

0 thoughts on “Depressive attributional style”