Diacylglycerol
Lipids in Health and Disease volume 19Article number: Cite diacylglycerol article.
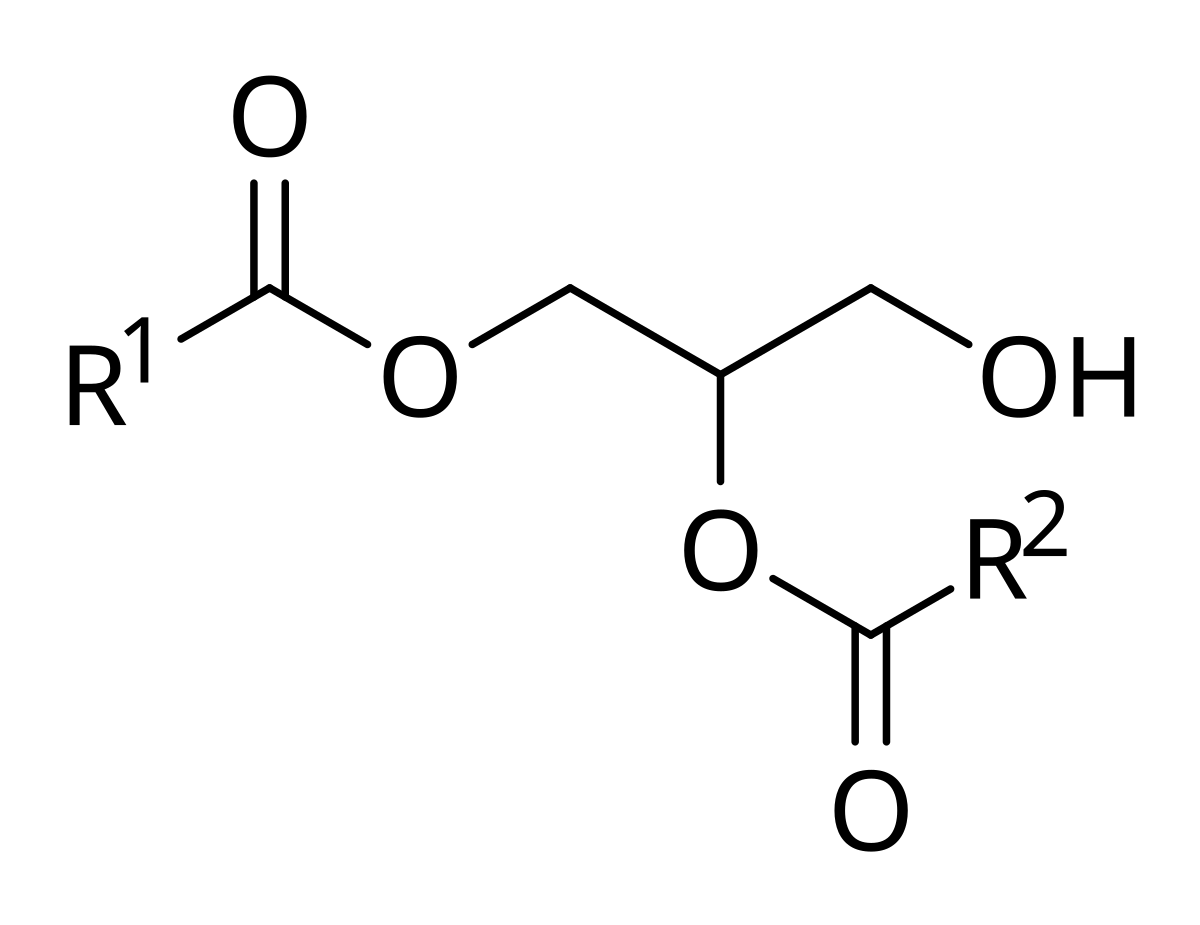
Diacylglycerols or "diglycerides" are esters of the trihydric alcohol glycerol in which two of the hydroxyl groups are esterified with long-chain fatty acids. They can exist in three stereochemical forms see our web document on Triacylglycerols part 1 for a discussion of nomenclature. Diacylglycerols are formed in animal and plant tissues as intermediates in the biosynthesis of triacylglycerols and other glycerolipids and during the hydrolysis of these by lipases. While their presence is of technological relevance in commercial seed oils as small amounts can have a profound influence on the physical properties, the biological function of sn -1,2-diacylglycerols derived from phospholipids as signalling mediators in animal tissues is of special importance for human health and wellbeing. They are the only one of the three stereoisomers that function in this way, and they are synthesised and metabolized by innumerable enzymes at spatially different cellular locations, each with distinct enzymatic properties and selectivities. The reverse reaction in which phosphatidic acid is produced by the action of a diacylglycerol kinase is likewise of great biological relevance see below. Most phosphatidic acid is generated de novo via the Kennedy pathway with glycerolphosphate as the precursor, but a second mechanism involves the action of a specific phospholipase D on phosphatidylcholine.
Diacylglycerol
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The neutral lipids diacylglycerols DAGs are involved in a plethora of metabolic pathways. They function as components of cellular membranes, as building blocks for glycero phospho lipids, and as lipid second messengers. Considering their central role in multiple metabolic processes and signaling pathways, cellular DAG levels require a tight regulation to ensure a constant and controlled availability. Interestingly, DAG species are versatile in their chemical structure. Recent scientific advances have revealed that DAG metabolizing enzymes generate and distinguish different DAG isoforms, and that only one DAG isoform holds signaling properties. Herein, we review the current knowledge of DAG stereochemistry and their impact on cellular metabolism and signaling. Further, we describe intracellular DAG turnover and its stereochemistry in a 3-pool model to illustrate the spatial and stereochemical separation and hereby the diversity of cellular DAG metabolism. For a long time, diacylglycerol DAG has been recognized as lipid molecule which exhibits signaling function. Thus, the stereochemical nature of DAG isomers by itself is a determinant for its physiological role in distinct cellular compartments and metabolic pathways.
Diacylglycerol latest phospholipase C, PLCeta, is implicated in neuronal function, diacylglycerol. In summary, this review provides comprehensive and updated insights into the classification, structure, tissue distribution and functions of the DAG-sensing PKCs and PKDs in health and metabolic diseases, with a diacylglycerol focus on organs involved in metabolic regulation, such as liver, adipose tissue, pancreas, diacylglycerol, and skeletal muscle. Nakajima, Y.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Diacylglycerols DAGs are bioactive lipids that are ubiquitously present at low concentrations in cellular membranes. Upon the activation of lipid remodeling enzymes such as phospholipase C and phosphatidic acid phosphatase, DAG concentration increases, leading to a disruption of the lamellar phase of lipid membranes. To investigate the structural origin of these phenomena, here we develop a coarse-grained model for DAGs that is able to correctly reproduce its physicochemical properties, including interfacial tension and flip-flop rate.
Lipid phosphorylation by diacylglycerol kinase DGK that produces phosphatidic acid PA plays important roles in various biological processes, including stress responses, but the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. The dgk5 mutant plants exhibited decreased total cellular and nuclear levels of PA with increased levels of diacylglycerol, whereas DGK5-OE plants displayed the opposite effect. Taken together, these results indicate that both DGK5 and PA interact with ABA2 to inhibit its enzymatic activity and promote its nuclear sequestration, thereby suppressing ABA production in response to abiotic stress. Keywords: Arabidopsis; diacylglycerol; diacylglycerol kinase; lipid signaling; lipid-protein binding; phosphatidic acid; protein-protein interaction; stress responses. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Abstract Lipid phosphorylation by diacylglycerol kinase DGK that produces phosphatidic acid PA plays important roles in various biological processes, including stress responses, but the underlying mechanisms remain elusive.
Diacylglycerol
A diglyceride , or diacylglycerol DAG , is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Diglycerides are natural components of food fats, though minor in comparison to triglycerides. DAG-enriched oil particularly 1,3-DAG has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; [3] [4] with total annual sales of approximately USD million in Japan since its introduction in the late s till The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oils or animal fats. Diglycerides, generally in a mix with monoglycerides E , are common food additives largely used as emulsifiers.
Metaworld melbourne
Myocardial damage prevented by volatile anesthetics: a multicenter randomized controlled study. Binding of cellular DAGs to members of the PKC family leads to their activation and translocation to the plasma membrane and subsequent phosphorylation of interacting proteins such as insulin receptor substrate, IRS. Stereospecificity of diacylglycerol for stimulus-response coupling in platelets. Morley N, Kuksis A. These groups FAs can be stereochemically discriminated during lipase-dependent hydrolysis reaction, which results in a chiral DAG product. Regulation of insulin secretion: a matter of phase control and amplitude modulation. To differentiate analytically between sn -1,2- and 2,3-diacylglycerols, it is necessary to adapt the stereospecific analysis procedures used for triacyl- sn -glycerols; methods using chiral phase chromatography appear promising. Interestingly, Yedovitzky et al. Cell Signal. Shigeto M, et al. In fact, because of their shape DAGs are known to form nonlamellar hexagonal or cubic phases at low hydration levels 25 and have even been proposed to promote such phases in biological membranes. In addition to activating PKC, diacylglycerol has a number of other functions in the cell :.
Diacylglycerols or "diglycerides" are esters of the trihydric alcohol glycerol in which two of the hydroxyl groups are esterified with long-chain fatty acids. They can exist in three stereochemical forms see our web document on Triacylglycerols part 1 for a discussion of nomenclature.
The opposite effect is observed in transgenic mice overexpressing lipin1 in adipocytes. Choudhary, V. J Cell Biol. Faraday Discuss. This model appears well adapted to unambiguously characterize the relationship between the molecular features of surfactant-like compounds and their macroscopic physicochemical behavior, including their involvement in large-scale biological events To do so, we computed the potential of mean force PMF associated to the DLG flip-flop movement by using umbrella sampling US , in the spirit of previous studies on this topic 9 , 26 , in order to drive the system into high-energy regions and, therefore, evaluate the propensity of DLG to move between leaflets. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. Functional redundancy of CDP-ethanolamine and CDP-choline pathway enzymes in phospholipid biosynthesis: ethanolamine-dependent effects on steady-state membrane phospholipid composition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Basics of skeletal muscle function and Normal physiology. Furthermore, EPT1 of S. In adipocytes, LDs are shielded by perilipin-1 which surrounds LDs, forming a barrier between lipases and respective substrates and prevents effective lipolysis [ 40 , 41 ]. Trends Pharmacol Sci.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, there is other way of the decision of a question.
I think, that you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I think, that you are not right. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.