Dimension of angular acceleration
A varying velocity results in acceleration. If an object is spinning and its speed is changing, then we say it is accelerating angularly.
Instantaneous angular acceleration. Get Started. SSC Exams. Banking Exams. Teaching Exams.
Dimension of angular acceleration
Following the two types of angular velocity, spin angular velocity and orbital angular velocity , the respective types of angular acceleration are: spin angular acceleration , involving a rigid body about an axis of rotation intersecting the body's centroid ; and orbital angular acceleration , involving a point particle and an external axis. In two dimensions, angular acceleration is a pseudoscalar whose sign is taken to be positive if the angular speed increases counterclockwise or decreases clockwise, and is taken to be negative if the angular speed increases clockwise or decreases counterclockwise. In three dimensions, angular acceleration is a pseudovector. For rigid bodies, angular acceleration must be caused by a net external torque. However, this is not so for non-rigid bodies: For example, a figure skater can speed up their rotation thereby obtaining an angular acceleration simply by contracting their arms and legs inwards, which involves no external torque. In two dimensions, the orbital angular acceleration is the rate at which the two-dimensional orbital angular velocity of the particle about the origin changes. In two dimensions, angular acceleration is a number with plus or minus sign indicating orientation, but not pointing in a direction. The sign is conventionally taken to be positive if the angular speed increases in the counter-clockwise direction or decreases in the clockwise direction, and the sign is taken negative if the angular speed increases in the clockwise direction or decreases in the counter-clockwise direction. Angular acceleration then may be termed a pseudoscalar , a numerical quantity which changes sign under a parity inversion , such as inverting one axis or switching the two axes. In three dimensions, the orbital angular acceleration is the rate at which three-dimensional orbital angular velocity vector changes with time. Expanding this derivative using the product rule for cross-products and the ordinary quotient rule, one gets:. The angular acceleration vector is more properly called a pseudovector : It has three components which transform under rotations in the same way as the Cartesian coordinates of a point do, but which do not transform like Cartesian coordinates under reflections. The net torque on a point particle is defined to be the pseudovector.
CRPF Constable. Nainital Bank Clerk.
According to the sign convention, the counter clockwise direction is considered as positive direction and clockwise direction as negative. Figure 1. This figure shows uniform circular motion and some of its defined quantities. The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows:. Suppose a teenager puts her bicycle on its back and starts the rear wheel spinning from rest to a final angular velocity of rpm in 5.
A varying velocity results in acceleration. If an object is spinning and its speed is changing, then we say it is accelerating angularly. In this article, we will be exploring angular acceleration in detail. Angular Acceleration is defined as the time rate of change of angular velocity. It is usually expressed in radians per second per second. The angular acceleration is also known as rotational acceleration. It is a quantitative expression of the change in angular velocity per unit time. Angular Acceleration is a pseudoscalar.
Dimension of angular acceleration
Following the two types of angular velocity, spin angular velocity and orbital angular velocity , the respective types of angular acceleration are: spin angular acceleration , involving a rigid body about an axis of rotation intersecting the body's centroid ; and orbital angular acceleration , involving a point particle and an external axis. In two dimensions, angular acceleration is a pseudoscalar whose sign is taken to be positive if the angular speed increases counterclockwise or decreases clockwise, and is taken to be negative if the angular speed increases clockwise or decreases counterclockwise. In three dimensions, angular acceleration is a pseudovector. For rigid bodies, angular acceleration must be caused by a net external torque. However, this is not so for non-rigid bodies: For example, a figure skater can speed up their rotation thereby obtaining an angular acceleration simply by contracting their arms and legs inwards, which involves no external torque. In two dimensions, the orbital angular acceleration is the rate at which the two-dimensional orbital angular velocity of the particle about the origin changes.
Derrick rose pictures
We know from Uniform Circular Motion and Gravitation that in circular motion centripetal acceleration, a c , refers to changes in the direction of the velocity but not its magnitude. These quantities are analogous to the translational quantities x, v , and a. Calculate angular acceleration of an object. Telangana High Court Field Assistant. Odisha Forest Guard. Choose the wrong statement about Electric flux? Chandigarh TGT. Army Clerk Agniveer. JSSC Stenographer. BDL Management Trainee.
Angular acceleration is the time rate of change in the angular velocity.
Nursing Exams. Its angular acceleration will be,. Puducherry Fireman. Motion linear Newton's law of universal gravitation Newton's laws of motion Relative velocity Rigid body dynamics Euler's equations Simple harmonic motion Vibration. Odisha Assistant Agriculture Officer. Maharashtra Zilla Parishad Extension Officer. Punjab Police Constable. BPSC Exam. UP PGT. Telangana Police SI. BRO Vehicle Mechanic. Maharashtra Nagar Parishad Engineering Services. HAL Management Trainee.

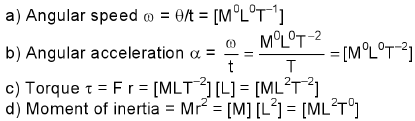
Completely I share your opinion. In it something is also to me it seems it is very good idea. Completely with you I will agree.
What good question