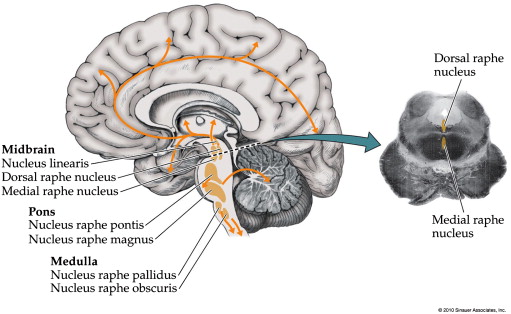
Dorsal raphe nucleus
The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is a heterogeneous brainstem nucleus located in the midbrain and pons. Via widespread projections, which target a multitude of brain areas, its neurons utilize many transmitters to control various physiological functions, including learning, memory and affect. Accordingly, dorsal raphe nucleus, the DRN has been strongly associated dorsal raphe nucleus brain dysfunction, especially mood disorders such as depression, but also Alzheimer's disease. The DRN's most abundant transmitter, serotonin, has received the most attention in studies on both normal brain function and disease, and lately its involvement in the regulation of neuroplasticity has been under particular scrutiny.
The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is an important source of neuromodulators and has been implicated in a wide variety of behavioral and neurological disorders. The DRN is subdivided into distinct anatomical subregions comprised of multiple cell types, and its complex cellular organization has impeded efforts to investigate the distinct circuit and behavioral functions of its subdomains. Here we used single-cell RNA sequencing, in situ hybridization, anatomical tracing, and spatial correlation analysis to map the transcriptional and spatial profiles of cells from the mouse DRN. Our analysis of 39, single-cell transcriptomes revealed at least 18 distinct neuron subtypes and 5 serotonergic neuron subtypes with distinct molecular and anatomical properties, including a serotonergic neuron subtype that preferentially innervates the basal ganglia. Our study lays out the molecular organization of distinct serotonergic and non-serotonergic subsystems, and will facilitate the design of strategies for further dissection of the DRN and its diverse functions. The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is a major source of neuromodulators in the central nervous system, and is the largest of the serotonergic nuclei, containing approximately a third of all serotonergic neurons 5-HT neurons in the brain Hornung, DRN 5-HT neurons send highly divergent projections that target many functionally distinct brain regions Azmitia and Segal, ; Muzerelle et al.
Dorsal raphe nucleus
Molecular Brain volume 9 , Article number: 71 Cite this article. Metrics details. Serotonergic neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus DRN are involved in the control of sleep-wake states. Application of CaCl 2 25 or 50 nmol in the DRN significantly increased serotonin in the DRN and hypothalamus, and noradrenaline in the locus coeruleus and hypothalamus. Immunohistochemistry study indicated that application of CaCl 2 25 or 50 nmol in the DRN significantly increased c-Fos expression ratio in wake-promoting neurons including serotonergic neurons in the DRN, noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus, and orxinergic neurons in the perifornical nucleus, but decreased c-Fos expression ratio of GABAergic sleep-promoting neurons in the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus. Dorsal raphe nucleus DRN provides the majority of serotonin 5-HT throughout the central nervous system, including the cerebral cortex, hypothalamus and brain stem [ 1 ]. Serotonergic neurons in the DRN play an important role in sleep-wake regulation [ 2 , 3 ]. Most of the serotonergic neurons in the DRN fire regularly at a slow rate during wakefulness, fire considerably less during non-rapid eye movement sleep NREMS and even cease firing during rapid eye movement sleep REMS [ 4 , 5 ]. In the endogenous sleep-wake regulating pathways, the DRN promotes wakefulness via excitatory projections to the cerebral cortex and other wakefulness-promoting nuclei, and via inhibitory projections to sleep-promoting nuclei [ 1 — 3 , 7 ]. However the precise mechanism has not been certified yet. At first, we microinjected CaCl 2 into the DRN, and monitored sleep-wake behavior in freely moving rats for 6 hours.
Received : 13 April
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Harvard Dataverse. Molecular and anatomical organization of the dorsal raphe nucleus. The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is an important source of neuromodulators and has been implicated in a wide variety of behavioral and neurological disorders. The DRN is subdivided into distinct anatomical subregions comprised of multiple cell types, and its complex cellular organization has impeded efforts to investigate the distinct circuit and behavioral functions of its subdomains.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Serotonin 5-HT is a neurotransmitter critically involved in a broad range of brain functions and implicated in the pathophysiology of neuropsychiatric illnesses including major depression, anxiety and sleep disorders. Despite being widely distributed throughout the brain, there is limited knowledge on the contribution of 5-HT to intrinsic brain activity. The dorsal raphe DR and median raphe MR nuclei are the source of most serotonergic neurons projecting throughout the brain and thus provide a compelling target for a seed-based probe of resting-state activity related to 5-HT. Here we implemented a novel multimodal neuroimaging approach for investigating resting-state functional connectivity FC between DR and MR and cortical, subcortical and cerebellar target areas. The DR and MR seeds produced largely similar FC maps: significant positive FC with brain regions involved in cognitive and emotion processing including anterior cingulate, amygdala, insula, hippocampus, thalamus, basal ganglia and cerebellum. Our results provide evidence for a resting-state network related to DR and MR and comprising regions receiving serotonergic innervation and centrally involved in 5-HT related behaviors including emotion, cognition and reward processing. These findings provide a novel advance in estimating resting-state FC related to 5-HT signaling, which can benefit our understanding of its role in behavior and neuropsychiatric illnesses.
Dorsal raphe nucleus
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN represents one of the most sensitive reward sites in the brain. However, the exact relationship between DRN neuronal activity and reward signaling has been elusive. In this review, we will summarize anatomical, pharmacological, optogenetics, and electrophysiological studies on the functions and circuit mechanisms of DRN neurons in reward processing. The DRN is commonly associated with serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT , but this nucleus also contains neurons of the neurotransmitter phenotypes of glutamate, GABA and dopamine. Pharmacological studies indicate that 5-HT might be involved in modulating reward- or punishment-related behaviors.
Snowmobile salvage yards minnesota
Fine alignment of each 2D histogram along the dorsal-ventral axis was adjusted manually using Tph2 ISH images as the reference. Double retrograde tracing experiments also showed that DRN neurons innervating both Str and M1 were often found in these regions Figure 6—figure supplement 2. Rewards including sucrose, food, sex and social interaction rapidly activate 5-HT neurons, but aversive stimuli including quinine and footshock do not. The animals were implanted chronically with stainless steel screws over the frontal-parietal cortex and a pair of wire electrodes through the nuchal muscles for recording of electroencephalogram EEG and electromyogram EMG , respectively. Sections were counterstained using a fluorescent Nissl stain Neurotrace. Idoia Quintana-Urzainqui. This neuron exhibited a decrease in activity after the onset of the fixation point followed by a tonic increase for small reward trials and suppression for large reward trials. Hashimoto, S. Additionally, we defined a DRN 5-HT neuron subtype that is well-positioned to modulate basal ganglia circuits, based on its molecular and anatomical features. Structure and function of the brain serotonin system.
The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is an important source of neuromodulators and has been implicated in a wide variety of behavioral and neurological disorders. The DRN is subdivided into distinct anatomical subregions comprised of multiple cell types, and its complex cellular organization has impeded efforts to investigate the distinct circuit and behavioral functions of its subdomains. Here we used single-cell RNA sequencing, in situ hybridization, anatomical tracing, and spatial correlation analysis to map the transcriptional and spatial profiles of cells from the mouse DRN.
The subregional distribution of 5-HT subtypes relates well to past studies reporting subregion-specific anatomical and molecular differences that are consistent with our integrative map of 5-HT subtype features. Eventually these molecular approaches will be well complemented by whole-brain reconstructions of axons of single neurons Economo et al. Role of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in psychiatric disorders: a comprehensive review. Predictive reward signal of dopamine neurons. Trends Cogn. The heterogeneity of 5-HT neurons suggests that they may be organized into distinct subsystems. Solomon, R. B t-SNE plot of the processed dataset containing 39, cells from eight animals. They show that the DR is composed of at least 5 distinct 5-HT neuronal types. Nakamura et al.

It agree, very useful idea
Now all became clear to me, I thank for the necessary information.