Emt epithelial mesenchymal transition
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Cell Communication and Signaling volume 19 , Article number: 32 Cite this article. Metrics details. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition EMT is intrinsically linked to alterations of the intracellular cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix. Consequently, cells can deform and remodel the surrounding matrix in order to facilitate local invasion. In this review, we highlight recent bioengineering approaches to elucidate EMT and functional changes in the cytoskeleton. First, we review transitions between multicellular clusters and dispersed individuals on planar surfaces, which often exhibit coordinated behaviors driven by leader cells and EMT. Second, we consider the functional role of vimentin, which can be probed at subcellular length scales and within confined spaces.
Emt epithelial mesenchymal transition
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. An Author Correction to this article was published on 15 October Epithelial—mesenchymal transition EMT encompasses dynamic changes in cellular organization from epithelial to mesenchymal phenotypes, which leads to functional changes in cell migration and invasion. EMT occurs in a diverse range of physiological and pathological conditions and is driven by a conserved set of inducing signals, transcriptional regulators and downstream effectors. With over 5, publications indexed by Web of Science in alone, research on EMT is expanding rapidly. This growing interest warrants the need for a consensus among researchers when referring to and undertaking research on EMT. We trust that these guidelines will help to reduce misunderstanding and misinterpretation of research data generated in various experimental models and to promote cross-disciplinary collaboration to identify and address key open questions in this research field. While recognizing the importance of maintaining diversity in experimental approaches and conceptual frameworks, we emphasize that lasting contributions of EMT research to increasing our understanding of developmental processes and combatting cancer and other diseases depend on the adoption of a unified terminology to describe EMT. Arthur W.
Journal of Controlled Release. EMT plays a critical role in early developmental processes, such as gastrulation, leading to formation of mesoderm.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Some mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition EMT in normal development also facilitate disease progression e. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition EMT is a physiological process in which epithelial cells acquire the motile and invasive characteristics of mesenchymal cells. Although EMT in embryonic development is a coordinated, organized process involving interaction between many different cells and tissue types, aspects of the EMT program can be inappropriately activated in response to microenvironmental alterations and aberrant stimuli, and this can contribute to disease conditions including tissue fibrosis and cancer progression. Here we will outline how EMT functions in normal development, how it could be activated in pathologic conditions—especially by matrix metalloproteinases—and how it may be targeted for therapeutic benefit.
Review Series Free access Phone: ; Fax: ; E-mail: rkalluri bidmc. Find articles by Kalluri, R. Find articles by Weinberg, R. Published June 1, - More info.
Emt epithelial mesenchymal transition
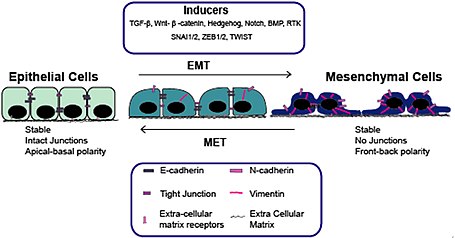
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition EMT comprises an essential biological process involving cancer progression as well as initiation. While the EMT has been regarded as a phenotypic conversion from epithelial to mesenchymal cells, recent evidence indicates that it plays a critical role in stemness, metabolic reprogramming, immune evasion and therapeutic resistance of cancer cells. Note that the dynamic conversion between EMT and epithelial reversion mesenchymal-epithelial transition, MET occurs through variable intermediate-hybrid states rather than being a binary process. Given the close connection between oncogenic signaling and EMT repressors, the EMT has emerged as a therapeutic target or goal in terms of MET reversion in cancer therapy. Here we review the critical role of EMT in therapeutic resistance and the importance of EMT as a therapeutic target for human cancer. Traditionally, the concept of epithelial to mesenchymal transition EMT was mainly restricted to the reversible phenotypic transformation of epithelial to mesenchymal cells seen during development, wound healing and various diseases Thiery et al. Reversible rounds of EMT and MET mesenchymal to epithelial transition; the reverse state of EMT constitute the physiologic stages of embryonic development with intense cell plasticity Kalluri and Neilson ; Thiery et al. Pathological hyperactivated EMT has been widely described in tumor progression as invasive and metastatic cellular dissemination in the altered epithelium Thiery ; Polyak and Weinberg After the single tumor cells are disseminated into the lymphatics or vasculature, MET is thought to be responsible for metastatic re-colonization in distant organs by regaining epithelial differentiation and proliferation ability Chaffer et al.
Hermanas durmiendo
TGF-beta signaling by Smad proteins. Cancer theory faces doubts. Cell swelling, softening and invasion in a three-dimensional breast cancer model. Leggett View author publications. Cancer Metastasis Rev. Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Cancer newsletter — what matters in cancer research, free to your inbox weekly. Also, craniofacial crest mesenchyme that forms the connective tissue forming the head and face, is formed by neural tube epithelium by EMT. It is still unclear what specific signals induce type 3 EMTs in carcinoma cells. CD44 splice isoform switching in human and mouse epithelium is essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer progression. Studies using fibrosis tissue from humans have also demonstrated EMT
Federal government websites often end in.
Similar to epithelial cells in EMT, endothelial cells that have activated EndoMT programmes exhibit a variety of intermediate or partial phenotypes, as discussed above for EMT. Thiery, J. Looking forward, to decipher the complexity and plasticity of the EMT programme, we propose that EMT research, while remaining anchored in traditional developmental, cell and cancer biology, should be explored within a broader conceptual context. Subsequently, Ray et al. Neural crest cells give rise to multiple cell types, including the neurons, glial cells, pigment cells, fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, odontoblasts and adipocytes. Copy Download. More recent work with cell monolayers in 2D culture showed that intermediate filaments can also sustain cell—cell contacts and bias cell—matrix adhesions [ 81 ]. Desmosomes interact with intermediate filaments intracellularly. Epithelial—mesenchymal transition EMT and metastasis: yes, no, maybe? Mol Cell Endocrinol. Cancer cells proceed through a gradation of phenotypic states, each associated with combinations of epithelial and mesenchymal markers 3 , 51 , Birchmeier W. Goossens, S.

0 thoughts on “Emt epithelial mesenchymal transition”