Enzymes byjus
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions. Without the presence of enzymes the biochemical reactions would take years to complete.
Education Business Technology. Download Now Download to read offline. Recommended Production of enzymes. Production of enzymes Adarsh Patil. Immobilization of enzymes. Immobilization of enzymes kamblesai
Enzymes byjus
What are enzymes and what do they do in our bodies? Enzymes are basically proteins that are produced by living organisms to bring about certain metabolic and biochemical reactions in the body. They are biological catalysts that speed up reactions inside the body. Enzymes, as mentioned above, are biological catalysts. While they hasten or speed up a process, they are actually providing an alternative pathway for the process. But, in the process, the structure or composition of the enzymes remain unaltered. Enzymes are actually made up of s of amino acids that are linked in a specific way to form different enzymes. The enzyme chains fold over to form unique shapes and it is these shapes that provide the enzyme with its characteristic chemical potential. Most enzymes also contain a non-protein component known as the co-facto r. The biochemical reactions occurring in the body are basically of 6 types and the enzymes that bring about these reactions are named accordingly:. For any reaction to occur in the universe, there is an energy requirement.
The modifications in the ionic state can modify catalysis and substrate binding. Did not receive OTP?
The human body is composed of different types of cells, tissues and other complex organs. For efficient functioning, our body releases some chemicals to accelerate biological processes such as respiration, digestion, excretion and a few other metabolic activities to sustain a healthy life. Hence, enzymes are pivotal in all living entities which govern all the biological processes. Let us understand what are enzymes, types, their structure, mechanism and various factors that affect its activity. The majority of enzymes are proteins with catalytic capabilities crucial to perform different processes.
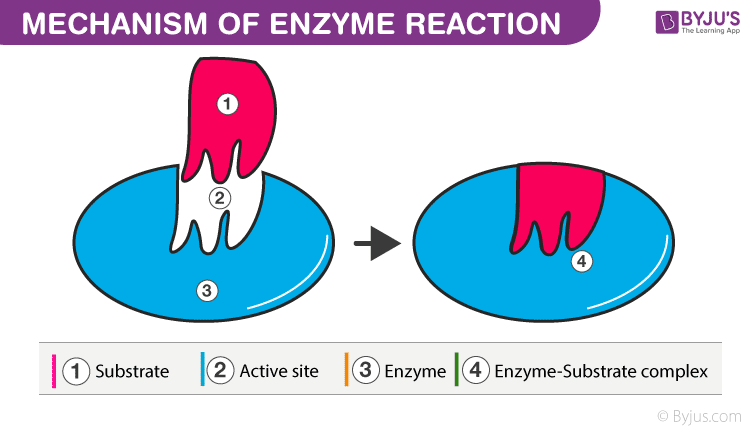
Enzymes are biological catalysts which act to increase the rate of a reaction without being used up or changed themselves. They are specific to one type of reaction and one, or a small number of, closely related reactants known as substrates. Enzymes are a vital component of the cell as without them, many biological reactions would be too slow to sustain life. Enzyme kinetics is the study of enzyme reaction rates and the conditions which affect them. In this article, we will discuss the structure and function of enzymes, their clinical significance and theories of enzyme kinetics. Enzymes are proteins and usually have a globular tertiary structure. Their structure is highly specific to the reaction they catalyse, and hence the reactants involved, due to the presence of an active site where the reaction itself occurs. This is a small cleft within the enzyme with a specific amino acid structure allowing the substrate to bind and form the enzyme-substrate complex ES , which is held together by weak bonds to allow dissociation of the complex when the reaction is finished.
Enzymes byjus
Enzymes help with specific functions that are vital to the operation and overall health of the body. They help speed up chemical reactions in the human body. They are essential for respiration, digesting food, muscle and nerve function, and more.
Fosters home for imaginary friends mac crying
Login To View Results. Production of enzymes-General consideration-Amyl Non-Sequential mechanism does not require both substrates to bind before releasing the first product. Rasa Theory Introduction by Bharat Muni. Share Share Share Call Us. They are active only in certain range of temperature and pH. The energy between these molecules needs to overcome the barrier in the reaction. Parts Of The Nose. Also, groups like aspartate are chemically reactive, and their proximity towards the substrate favours their involvement in catalysis. Thus, an enzyme- substrate complex is formed. They catalyze the formation of an isomer of a compound.
Do you ever look at your body and wonder how it manages to grow and change so quickly and efficiently? And how does it continues to function like a well-oiled machine?
Enzymes require an optimum temperature and pH for their action. Vitamin b12 Anushi Jain. Hybridoma technology. Just some enzymes feasibly operate with pH above 9 and below 5. Industrial production of penicillin Nischitha R. Let us understand what are enzymes, types, their structure, mechanism and various factors that affect its activity. Customize your course in 30 seconds Start Learning Now. Test your Knowledge on Enzymes! Mtt Assay for cell viability sakeena gilani. Amoeba Sisters - Simple explanations and introductions into more complex topics, perfect for A-Level. Immobilized enzymes. Most enzymes also contain a non-protein component known as the co-facto r. The most frequent active site amino acid residues out of the 20 amino acids forming the protein are polar amino acids, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, histidine, Serine, and lysine. Enzyme-substrate interactions induce reactive groups into proximity with one another.

I would not wish to develop this theme.
Willingly I accept. The theme is interesting, I will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer.
I think, that you are mistaken. I can prove it. Write to me in PM.