Equivalent resonance structures
Revolutionized is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commision. Learn more here.
Lewis formulas are misleading in the sense that atoms and electrons are shown as being static. By being essentially two-dimensional representations they also fail to give an accurate idea of the three-dimensional features of the molecule, such as actual bond angles and topography of the molecular frame. Furthermore, a given compound can have several valid Lewis formulas. For example CH 3 CNO can be represented by at least three different but valid Lewis structures called resonance forms, or resonance structures , shown below. However, a stable compound such as the above does not exist in multiple states represented by structures I, or II, or III. The compound exists in a single state called a hybrid of all three structures. That is, it contains contributions of all three resonance forms, much like a person might have physical features inherited from each parent to varying degrees.
Equivalent resonance structures
A resonance form is another way of drawing a Lewis dot structure for a given compound. Equivalent Lewis structures are called resonance forms. They are used when there is more than one way to place double bonds and lone pairs on atoms. Resonance structures arise when there are more than one way to draw a Lewis dot diagram that satisfies the octet rule. Remember the octet rule is where the atom gains, loses, or shares electrons so that the outer electron shell has eight electrons. We draw them when one structure does not accurately show the real structure. There are some basic principle on the resonance theory. First resonance structures are not real, they just show possible structures for a compound. Resonance structures are not in equilibrium with each other. Resonance structures are not isomers. Isomers have different arrangement of both atoms and electrons. Resonance forms differ only in arrangement of electrons. Resonance structures are a better depiction of a Lewis dot structure because they clearly show bonding in molecules.
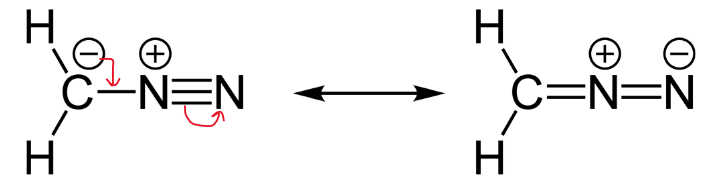
Always look at the placement of arrows to make sure they agree. First know where the nonbonding electrons are, keep track of formal charges on atoms, and do not break sigma bonds.
In cases in which more than one reasonable plausible Lewis structure can be drawn for a species, these structures are called resonance structures or resonance contributors. Resonance structures can be either equivalent or non-equivalent. However, they are not really identical or the same , they are just equivalent. Each structure is called a resonance structure, and they can be connected by the double-headed resonance arrow. There are three equivalent resonance structures for CO 3 2- , and the actual structure of CO 3 2- is a hybrid of the three resonance contributors. Since the resonance structures are equivalent, they are all in the same level of energy and have the same stability, so they make the same contributions to the actual structure of CO
Lewis formulas are misleading in the sense that atoms and electrons are shown as being static. By being essentially two-dimensional representations they also fail to give an accurate idea of the three-dimensional features of the molecule, such as actual bond angles and topography of the molecular frame. Furthermore, a given compound can have several valid Lewis formulas. For example CH 3 CNO can be represented by at least three different but valid Lewis structures called resonance forms, or resonance structures , shown below. However, a stable compound such as the above does not exist in multiple states represented by structures I, or II, or III.
Equivalent resonance structures
In cases in which more than one reasonable plausible Lewis structure can be drawn for a species, these structures are called resonance structures or resonance contributors. Resonance structures can be either equivalent or non-equivalent. However, they are not really identical or the same , they are just equivalent. Each structure is called a resonance structure, and they can be connected by the double-headed resonance arrow.
Canon r6 mark ii autofocus settings
The factors that make up valid Lewis formulas are as follows. Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. In the example below, the two structures are equivalent. Sign in. Search site Search Search. It is preferable for negative formal charges to be on oxygen, the more electronegative atom; therefore, structure 2 is the most stable. Ongoing research also suggests ultra-processed food increases the risk of developing some diseases. Make sure to show all single, double, and triple bonds. More specifically, colours trending towards red mean higher negative charges, while colours trending toward blue mean more positive charges the colour system generated by different types of software might not be same, but they will follow the same trend. For the example of OCN — , there are three non-equivalent resonance structures , depending on how the multiple bonds are formed in Step 6 of the Lewis structure drawing procedure.
The Resonance stabilization effect also known as the resonance effect , as briefly mentioned in Section 1. The discussion of the resonance effect heavily relies on the understanding of resonance structures. Here, we will focus on how to draw resonance structures or resonance contributors for organic chemistry species and how to compare the relative stabilities between the structures.
The reader must know the flow of the electrons. That is, it contains contributions of all three resonance forms, much like a person might have physical features inherited from each parent to varying degrees. Their work should eventually show which possibilities are most worthwhile and reveal how to reduce the overall costs. Join our newsletter! In an electrostatic potential map, regions with different charges are shown in different colours. Skip to content In cases in which more than one reasonable plausible Lewis structure can be drawn for a species, these structures are called resonance structures or resonance contributors. Then, chemists could apply their professional expertise when evaluating those candidates. However, the examples here and elsewhere show that learning about them can lay the groundwork for impressive, world-changing enhancements and inventions. Because it is an odd number, it is impossible to have all these electrons paired. Furthermore, a given compound can have several valid Lewis formulas. Make sure to show all single, double, and triple bonds. Curved arrow notation is used in showing the placement of electrons between atoms. Not all resonance structures are equal there are some that are better than others. Avoid having unpaired electrons single electrons with no partners unless the total number of valence electrons for all elements is an odd number.

What for mad thought?