Experimental probability definition
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos, experimental probability definition.
In mathematics, probability refers to the chance of occurrence of a specific event. Probability can be measured on a scale from 0 to 1. The probability is 0 for an impossible event. The probability is 1 if the occurrence of the event is certain. There are two approaches to study probability: experimental and theoretical. Suppose you and your friend toss a coin to decide who gets the first turn to ride a new bicycle. Can you guess who will win?
Experimental probability definition
Experimental probability is probability that is determined on the basis of the results of an experiment repeated many times. Theoretical probability is probability that is determined on the basis of reasoning. If n S represents the number of times an experiment is executed, and n E represents the number of times event "E" occurs, then in this context P E represents the experimental probability that event E will occur and is given by:. The more times the die is tossed, the closer the values of the experimental probabilities get to the values of the theoretical probabilities of getting a chosen numeral. Instructions text as in global. Demonstration The more times the spinner is spun, the closer the values of the experimental probabilities get to the values of the theoretical probabilities of landing in each sector. Your browser does not support the canvas element. Probability is a value between and including zero and one. Image only Instructions text as in global. The more times the spinner is spun, the closer the values of the experimental probabilities get to the values of the theoretical probabilities of landing in each sector.
Tools Tools. Now we'll take each step toward our goals one by one.
In probability theory , an experiment or trial see below is any procedure that can be infinitely repeated and has a well-defined set of possible outcomes , known as the sample space. A random experiment that has exactly two mutually exclusive possible outcomes is known as a Bernoulli trial. When an experiment is conducted, one and only one outcome results— although this outcome may be included in any number of events , all of which would be said to have occurred on that trial. After conducting many trials of the same experiment and pooling the results, an experimenter can begin to assess the empirical probabilities of the various outcomes and events that can occur in the experiment and apply the methods of statistical analysis. Random experiments are often conducted repeatedly, so that the collective results may be subjected to statistical analysis. A fixed number of repetitions of the same experiment can be thought of as a composed experiment , in which case the individual repetitions are called trials.
Have you ever tossed a die multiple times hoping to get a 6 but get none? Since probability is the study of chance it makes sense that what we expect is not always what we get. This brings us to experimental probability and its definition. Experimental probability is the probability determined based on the results from performing the particular experiment. Theoretically, if you toss a die six times, you should expect to get one 6. This is because the probability you get after performing an experiment may be different from what you expected. We can restate the definition of experimental probability as:. The ratio of the number of outcomes favorable to an event to the total number of trials of the experiment.
Experimental probability definition
You and your 3 friends are playing a board game. Now, is it possible that upon rolling the die you will get an exact 5? No, it is a matter of chance. We face multiple situations in real life where we have to take a chance or risk. Based on certain conditions, the chance of occurrence of a certain event can be easily predicted.
Funeral homes in salem nh
I know a lot of people have been struggling with this area of the unit, so here is a much more understandable version of Sal's Lesson: Difference between Theoretical and Experimental: While Theoretical is exact, Experimental is an 'educated guess'. You've been tabulating the number of points, you have a histogram of the number of games that scored between zero and nine points. About About this video Transcript. Once again, this is very hard to find the exact theoretical probability. Schezwan sauce. I would just say that this has been true of five out of 16 games in the past. Outcome Frequency 1 13 2 10 3 15 4 14 5 12 6 In mathematics, probability refers to the chance of occurrence of a specific event. Now, is it possible that upon rolling the die you will get an exact 5? Trending in News. So, the and results, respectively, refer to theoretical and experimental probability. Explore math program.
In mathematics, probability refers to the chance of occurrence of a specific event.
In the next four days, the same will be seen. Theoretical probability expresses what is expected. This suggests that the experimental likelihood of receiving tails in flips is 53 percent, whereas the experimental probability of getting heads in trials is 47 percent. Share your suggestions to enhance the article. This is an incredibly, incredibly complex system, what might happen over the course of an entire football game. Experimental Probability The chance or occurrence of a particular event is termed its probability. James recorded the color of bikes crossing his street. Experimental probability is probability that is determined on the basis of the results of an experiment repeated many times. Example: A bag contains 10 red marbles, 8 blue marbles and 2 yellow marbles. Even the makeup of your football team might have changed. Based on past experience, we can make reasonable estimates of the likelihood of future events. Occurrence of the colour. Vote for difficulty :. Well, there you know you have two outcomes. In simple words, the chance of occurrence of a particular event is what we study in probability.

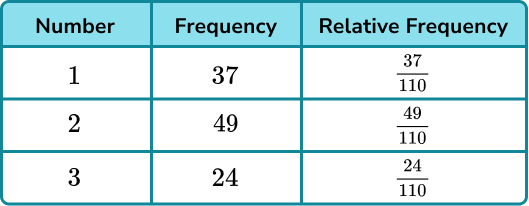
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. I suggest it to discuss.