Findpeaks in matlab
Help Center Help Center. Use the findpeaks function to find values and locations of local maxima in a set of data. Find the maxima and their years of occurrence.
Help Center Help Center. A local peak is a data sample that is either larger than its two neighboring samples or is equal to Inf. The peaks are output in order of occurrence. Non- Inf signal endpoints are excluded. If a peak is flat, the function returns only the point with the lowest index. The first sample of data is assumed to have been taken at time zero.
Findpeaks in matlab
.
Data Types: double single duration.
.
Help Center Help Center. A local peak is a data sample that is either larger than its two neighboring samples or is equal to Inf. The peaks are output in order of occurrence. Non- Inf signal endpoints are excluded. If a peak is flat, the function returns only the point with the lowest index. The first sample of data is assumed to have been taken at time zero. Find the local maxima. The first sample is not included despite being the maximum.
Findpeaks in matlab
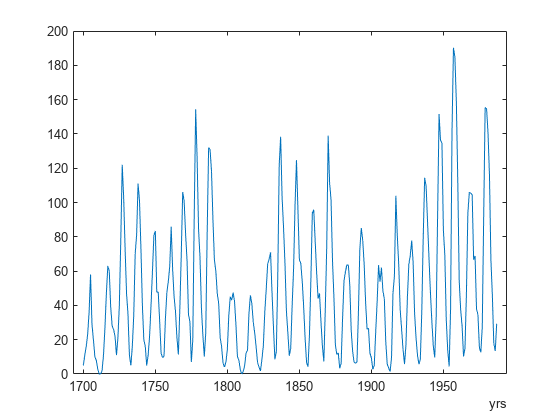
Help Center Help Center. This example shows how to perform basic peak analysis. It will help you answer questions such as: How do I find peaks in my signal? How do I measure distance between peaks? How do I measure the amplitude of peaks of a signal which is affected by a trend? How do I find peaks in a noisy signal? How do I find local minima? The Zurich sunspot relative number measures both the number and size of sunspots. Use the findpeaks function to find the locations and the value of the peaks. The above plot shows sunspot numbers tabulated over years and labels the detected peaks.
Calella train
Do you want to open this example with your edits? Use the years function to specify the minimum peak separation as a duration. Simulate a saturated measurement by truncating every reading that is greater than a specified bound of 0. Create a timetable with the data. To apply this constraint, findpeaks chooses the tallest peak in the signal and eliminates all peaks within 5 ms of it. Peak widths, returned as a vector of real numbers. The ones that are not recur at regular intervals. Minimum peak width, specified as a positive real scalar. Peak sorting, specified as one of these values: 'none' returns the peaks in the order in which they occur in the input data. If you specify a location vector, x , then the widths are expressed in terms of x. Load the file sunspot. Extend a horizontal line from the peak to the left and right until the line does one of the following: Crosses the signal because there is a higher peak Reaches the left or right end of the signal.
File Exchange. Retrieved March 8,
Their number is known to peak roughly every 11 years. Maximum number of peaks to return, specified as a positive integer scalar. SortStr — Peak sorting 'none' default 'ascend' 'descend'. Specifying a minimum peak height can reduce processing time. Select a Web Site Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Peaks with height less than zero are discarded. Input data, specified as a vector. You have a modified version of this example. Search MathWorks. Peak Prominences.

The authoritative point of view, curiously..