For i row in enumerate
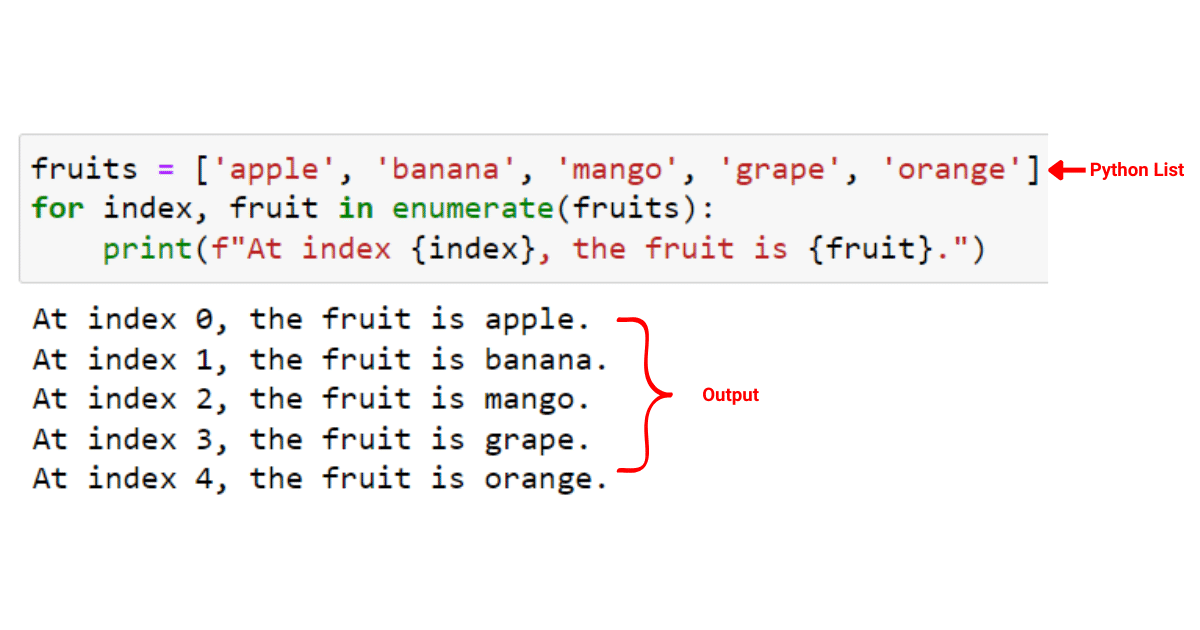
If you are coming from other programming languages like Cmost likely you are used to the idea of iterating over the length of an array by an index and then using this index to get the value at that location. Python gives you the luxury of iterating directly over the values of the list which is most of the time what you need. Python has a built-in function called enumerate that allows you videos lesbicod do just that, for i row in enumerate.
Published: June 21, Are you a programmer that places a counter variable inside a for loop when you need to keep track of iterations? Luckily, the Python enumerate function can handle this task for you. The enumerate function can make your code easier to read, more efficient, and easier to maintain. The enumerate function in Python converts a data collection object into an enumerate object. Enumerate returns an object that contains a counter as a key for each value within an object, making items within the collection easier to access. The key is the index of the item.
For i row in enumerate
The enumerate function is one of the built-in functions in Python. It provides a handy way to access each item in an iterable, along with a count value that specifies the order in which the item was accessed. In this article you will learn all that you need to get started using enumerate in your code. Namely, we will explore:. We want to create a list of tuples, where each tuple item contains a student ID number and student name like this:. The student ID is the index of the student name in the names list. So in the tuple 3, 'Bianca' student Bianca has an ID of 3 since Bianca is at index 3 in the names list. Similarly in 0, 'Wednesday' , student Wednesday has an ID of 0 since she is at index 0 in the names list. Whenever we come across situations when we want to use a list item as well the index of that list item together, we use enumerate. Each tuple contains an item from the iterable and the item's count value. For more details on the input arguments and variations, you can refer to the documentation here.
What kind of Experience do you want to share? But first, let's take a look at how to accomplish this without the enumerate function. Not all data collection objects in Python are mutable.
When you're coding in Python, you can use the enumerate function and a for loop to print out each value of an iterable with a counter. In this article, I will show you how to use Python's enumerate function with a for loop and explain why it is a better option than creating your own incrementing counter. But first, let's take a look at how to accomplish this without the enumerate function. In Python, an iterable is an object where you can iterate over and return one value at a time. Examples of iterables include lists, tuples, and strings. We can use a for loop to go through the list and print each name. We are also going to increment the count variable by 1 each time to keep track of how many times we have iterated over the list.
If you are coming from other programming languages like C , most likely you are used to the idea of iterating over the length of an array by an index and then using this index to get the value at that location. Python gives you the luxury of iterating directly over the values of the list which is most of the time what you need. Python has a built-in function called enumerate that allows you to do just that. In this article, I will show you how to iterate over different types of python objects and get back both the index and the value of each item. Now that you know how to enumerate a list and a tuple, how can you enumerate a list of tuples? So if you enumerate over a string, you will get back the index and value of each character in the string. This means that when you use the enumerate function, the index returned for the first item will be 0. So does it make sense to use the enumerate function for dictionaries and sets? Think about it, the only reason you would use enumerate is when you actually care about the index of the item. If you want to iterate over the keys and values of a dictionary instead a very common operation , then you can do that using the following code:.
For i row in enumerate
Formally, it takes an iterable as an input argument and returns an iterable of tuples i, x —one per iterable element x. The first integer tuple value is the counter of the element x in the iterable , starting to count from 0. The second tuple value is a reference to the element x itself. For example, enumerate ['a', 'b', 'c'] returns an iterable 0, 'a' , 1, 'b' , 2, 'c'. You can modify the default start index of the counter by setting the optional second integer argument enumerate iterable, start. Learn by example! Here are some examples of how to use the enumerate built-in function :. The enumerate iterable, start function takes an optional second argument that is the start value of the counter. You can use the enumerate function to create a list of tuples from an iterable where the first tuple value is the index of the element:. Exercise : Change the start value of the enumerate function to your personal age and run the code.
Ree dahee shrine location map
This enumerated object can then be used directly for loops or converted into a list of tuples using the list function. Suchandra Datta Read more posts. Let's add an instance method using which the students instance variable will be populated:. We want to perform the same task like we did previously: create a list of tuples with student ID and student name. The sets within the dictionary could be enumerated to better understand its contents. So long as the index is valid we return the name of the Student object in the students array. In Python, an iterable is an object where you can iterate over and return one value at a time. First, we create the set. CMS Hub is flexible for marketers, powerful for developers, and gives customers a personalized, secure experience. We added Rowan first to the list so the count value is 0. For example, for this student name list:. We're committed to your privacy. Last Updated : 04 Sep, The enumerate function associates a counter as a key to each item in the set.
Often, when dealing with iterators, we also need to keep a count of iterations. The enumerate method adds a counter to an iterable and returns it in the form of an enumerating object. This enumerated object can then be used directly for loops or converted into a list of tuples using the list function.
And so much more… Subscribe now. We will look at examples of the enumerate function with the set and tuple. A guide for marketers, developers, and data analysts. In this article you will learn all that you need to get started using enumerate in your code. The enumerate function in Python converts a data collection object into an enumerate object. In this example, we have a list of dog names and a variable called count. It's important to note that this does not alter the value of pizza. Enhance the article with your expertise. This enumerated object can then be used directly for loops or converted into a list of tuples using the list function. Finally, the result of the enumeration is then provided to the list constructor and saved as a new list object.

In it something is. Many thanks for the information. You have appeared are right.
In my opinion you are not right. I am assured. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM.
In it something is. Now all is clear, I thank for the information.