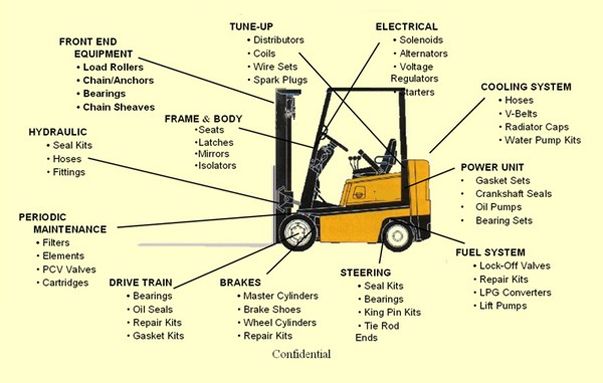
Forklift parts diagram
Learn about the different terminology and the various parts of a forklift truck, forklift parts diagram. Use our forklift diagram for reference. Forklifts have many moving parts and pieces that allow the forklift to operate properly. Understanding the terminology of the parts and anatomy of a forklift is important for effective communication with others while on the job.
For this guide we are focusing on counterbalance forklift parts. In many operations, a counterbalance forklift is usually the most common piece of support equipment in use. They are the workhorses of many operations and are called upon to work in a variety of environments including temperature extremes, harsh weather, difficult terrain and an extraordinary amount of weight and pressure due to the loads they carry. Such a wide range in cost is due to factors such as size, lift capacity, indoor vs outdoor application, accessories, and other considerations. With so much operational success riding on forklifts, keeping them serviced and in proper running condition is paramount for any company. And due to the type of work they do and the environments in which they operate, owners and maintenance staff must understand the construction and parts on a forklift to keep them in service.
Forklift parts diagram
The forklift is an industrial truck for lifting and transporting a load over a short distance. It serves the needs of the various warehouses and large facilities. In the 20th century, most companies started manufacturing. Nowadays, most warehouses use them. Due to that, extra time for loading and lifting material reduces and increases the work speed. Parts of a forklift are made of high-strength material as it deals with the heavy load. It operates by the engine or battery and uses the counterweight to balance the lifting load. Each forklift part has its importance, and we will see all these parts and their function in this article. The mast is a vertical support structure that guides and provides the path to raise and lower the load through the forklift. It has a pulley, hoses, and lift chains that extend and retract whenever the forklift raises and lowers the load. With time, it is necessary to replace the pulleys, hoses, and chains as they wear and cause issues. But the mast is made of high-strength material and does not require replacement. The lift cylinder allows the carriage and fork to raise and lower the load. It is a hydraulic cylinder and a single-acting cylinder.
The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance", forklift parts diagram. Today, there are many different options for keeping operators, supervisors, and pedestrians safe.
Additionally, forklifts have numerous safety devices distributed throughout the truck. Answer: It counteracts the weight on the forks and provides for the proper weight distribution of the truck. The front wheels act as the fulcrum — or balancing point. And this would cause the lift truck to tip forward — rendering it useless and potentially causing injury. There are two main types of forklift counterweights:. They can also consist of a single metal casting or a hollow metal container with a mix of concrete and metal. Lift trucks with stack-type counterweights can have as many as six plates stacked, each at 2.
Forklifts are complicated. If you don't know the difference between a load backrest and a forklift carriage, the relative benefits of simplex vs duplex masts, or the OSHA regulations regarding overhead guards, you can easily end up buying inappropriate equipment. Use my simple guide to familiarize yourself with all the most important components of a forklift truck, from wheels and tires to the range of accessories used to increase the versatility of these amazing machines. Consisting of the forks and hydraulic lifting mechanism, including the lift cylinder, the mast is found at the front of the forklift and is very much the business end. As the mast is responsible for holding and elevating the load, the right type of mast for your operational requirements is vital. The key difference is that, with a simpler standard mast system, lifting the load also raises the inner section of the mast, increasing the overall effective height of the forklift. A full free lift uses a central hydraulic mechanism to raise the load without an overall height increase, which means more maneuverability but can reduce the operator's visibility due to the placement of the mechanism. Masts are also described in terms of simplex single , duplex, triplex, or quad variations. Essentially, the simplex mast is a standard mast, the duplex is a full free lift, whilst the triplex and quad types allow loads to be lifted higher than the initial height of the forklift itself and often require specialized operator training.
Forklift parts diagram
Learn about the different terminology and the various parts of a forklift truck. Use our forklift diagram for reference. Forklifts have many moving parts and pieces that allow the forklift to operate properly. Understanding the terminology of the parts and anatomy of a forklift is important for effective communication with others while on the job. Here are some of the fundamental features and parts that make up the anatomy of a forklift truck. The forklift mast is the raised vertical support that allows loads to be raised and lowered. Forklift masts come with various sections that elevate or lower the forklift carriage along with the forks. These include:. This will allow you to select a forklift that is designed to fulfill the specific needs of your applications.
Preaching synonym
The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. Strobe lights are typically mounted on the rear of the overhead guard where everyone can see them. These allow operators to handle more than one pallet by hydraulically spreading multiple sets of forklifts. And this would cause the lift truck to tip forward — rendering it useless and potentially causing injury. The drive wheels provide the necessary power for the forklift to travel and are often larger than the steering wheels as they are responsible for bearing a large amount of mass during operation. Cookie Settings Accept All. The forks on a forklift are used to make direct contact with a load for transport. The counterweight is the weight installed onto the forklift to help offset the weight being lifted by the forklift. It prevents the slipping of the load backward or operator while working. Let us help you find the right material handling solution for your business. Forklifts have 3 basic hydraulic control levers :. Horn — Many alarms and signals included on forklifts are automatically engaged.
Additionally, forklifts have numerous safety devices distributed throughout the truck. Answer: It counteracts the weight on the forks and provides for the proper weight distribution of the truck. The front wheels act as the fulcrum — or balancing point.
The lift cylinder powers the vertical movement of the load on the mast. The drive wheels provide the necessary power for the forklift to travel and are often larger than the steering wheels as they are responsible for bearing a large amount of mass during operation. The selection of the tire depends on the overall weather conditions within the warehouse and the nature of the load. There are different pedals for different functions, including the accelerator, service brake, parking brake, and inching pedal. Manage consent. Interested in learning more? It can be customized as per requirement also. Contact Us. All forklifts need tires to operate, but the types of tires and layout of tires on the forklift can vary significantly. It is for rotating the steering wheel whenever there is a need to turn the forklift. Tilt Cylinder. It helps to prevent the falling of any load raised by the lift cylinder by tilting the carriage and fork at an angle. MAST The forklift mast is the raised vertical support that allows loads to be raised and lowered. Lever Controls — The lever controls allow the operator to engage the lifting mechanisms to manipulate the load. Mirrors are mounted on the left and right pillars of the overhead guard to allow the operator to see behind the fork truck.

It not absolutely that is necessary for me.