Gabaergic
Thank you for visiting nature, gabaergic. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you gabaergic a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Metrics details. GABAergic interneurons are inhibitory neurons of the nervous system that play a vital role in neural circuitry and activity. They are so named due to their release of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid GABA , and occupy different areas of the brain. This review will focus primarily on GABAergic interneurons of the mammalian cerebral cortex from a developmental standpoint. There is a diverse amount of cortical interneuronal subtypes that may be categorized by a number of characteristics; this review will classify them largely by the protein markers they express.
Gabaergic
Throughout early phases of brain development, the two main neural signaling mechanisms—excitation and inhibition—are dynamically sculpted in the neocortex to establish primary functions. Despite its relatively late formation and persistent developmental changes, the GABAergic system promotes the ordered shaping of neuronal circuits at the structural and functional levels. Within this frame, interneurons participate first in spontaneous and later in sensory-evoked activity patterns that precede cortical functions of the mature brain. Upon their subcortical generation, interneurons in the embryonic brain must first orderly migrate to and settle in respective target layers before they can actively engage in cortical network activity. During this process, changes at the molecular and synaptic level of interneurons allow not only their coordinated formation but also the pruning of connections as well as excitatory and inhibitory synapses. At the postsynaptic site, the shift of GABAergic signaling from an excitatory towards an inhibitory response is required to enable synchronization within cortical networks. Concomitantly, the progressive specification of different interneuron subtypes endows the neocortex with distinct local cortical circuits and region-specific modulation of neuronal firing. Finally, the apoptotic process further refines neuronal populations by constantly maintaining a controlled ratio of inhibitory and excitatory neurons. Interestingly, many of these fundamental and complex processes are influenced—if not directly controlled—by electrical activity. Interneurons on the subcellular, cellular, and network level are affected by high frequency patterns, such as spindle burst and gamma oscillations in rodents and delta brushes in humans. Conversely, the maturation of interneuron structure and function on each of these scales feeds back and contributes to the generation of cortical activity patterns that are essential for the proper peri- and postnatal development. Overall, a more precise description of the conducting role of interneurons in terms of how they contribute to specific activity patterns—as well as how specific activity patterns impinge on their maturation as orchestra members—will lead to a better understanding of the physiological and pathophysiological development and function of the nervous system.
Miller, M. Significant respiratory depression and obtundation are commonly seen. Cell Gabaergic.
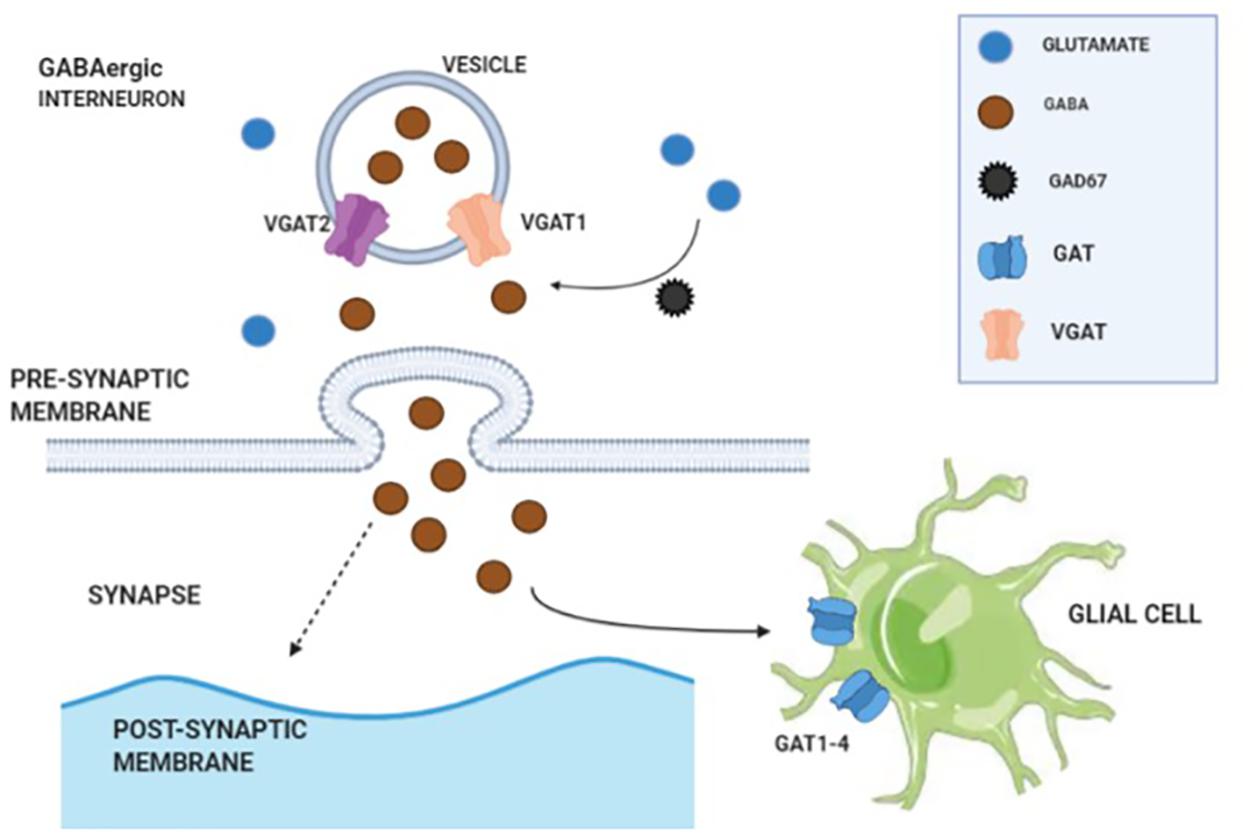
Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system. GABA is sold as a dietary supplement in many countries. It has been traditionally thought that exogenous GABA i. Two general classes of GABA receptor are known: [4]. Medium spiny cells are a typical example of inhibitory central nervous system GABAergic cells. In contrast, GABA exhibits both excitatory and inhibitory actions in insects , mediating muscle activation at synapses between nerves and muscle cells, and also the stimulation of certain glands. When the net flow of chloride is close to zero, the action of GABA is shunting.
Regardless of the pathological hallmarks, synaptic dysfunction is widely accepted as a causal event in AD. Of the two major types of synapses in the central nervous system CNS : glutamatergic and GABAergic, which provide excitatory and inhibitory outputs respectively, abundant data implicate an impaired glutamatergic system during disease progression. However, emerging evidence supports the notion that disrupted default neuronal network underlies impaired memory, and that alterations of GABAergic circuits, either plays a primary role or as a compensatory response to excitotoxicity, may also contribute to AD by disrupting the overall network function. Despite significant research and drug development effort in the past decades, currently there are no effective therapies that can prevent, delay or stop the progression of AD, causing a severe burden for the patients, their families and the society. The AICD tail released inside cytoplasm has been demonstrated to target the nucleus and regulate gene transcription activity Querfurth and LaFerla, The major component of AD hallmark NFTs was revealed to be abnormally hyperphosphorylated microtubule-associated protein tau MAPT , which is essential for assembly and stabilization of microtubules Spillantini and Goedert, ; Querfurth and LaFerla,
Gabaergic
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. GABAergic inhibition shapes the connectivity, activity and plasticity of the brain.
Nfscars
Tyzio, R. This population of interneurons possesses a fast-spiking pattern, and fire sustained high-frequency trains of brief action potentials [ 10 , 16 , 17 , 22 , 26 ]. GABA enhances the catabolism of serotonin into N -acetylserotonin the precursor of melatonin in rats. Chattopadhyaya, B. To date, the molecular mechanisms that regulate the termination of interneuron migration in the cortex are largely unknown. Communication in neural circuits: tools, opportunities, and challenges. Sandberg, M. Many psychiatric illnesses have been linked to low concentrations of GABA. Mitra for critical reading and comments of the manuscript. GABAb receptors are considered slow synaptic inhibitors. J Physiol Sci.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Liguz-Lecznar, M. Van der Kloot; J. Transcriptome alterations of prefrontal cortical parvalbumin neurons in schizophrenia. Graf, J. Schwarz, L. De novo synaptogenesis induced by GABA in the developing mouse cortex. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher. Golshani, P. Underlying this dynamic change in neuronal activity, among other developmental processes, is the structural and functional maturation of the two main signaling principles of neurons: excitation and inhibition Egorov and Draguhn, ; Luhmann et al. Findings from a subsequent study indicated that reduction in DTNBP1, frequently observed in schizophrenia, was linked to glutamatergic alterations in intrinsic hippocampal formation connections [ ]. Neuronal cell-type classification: challenges, opportunities and the path forward. Developmental diversification of cortical inhibitory interneurons. Behuet, S. Reh TA ed.

It was specially registered at a forum to tell to you thanks for council. How I can thank you?