Glycogen phosphorylase
Federal government websites often end in.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glycogen phosphorylase PG is a key enzyme taking part in the first step of glycogenolysis. The main role of PYGM is providing sufficient energy for muscle contraction. However, it is expressed in tissues other than muscle, such as the brain, lymphoid tissues, and blood.
Glycogen phosphorylase
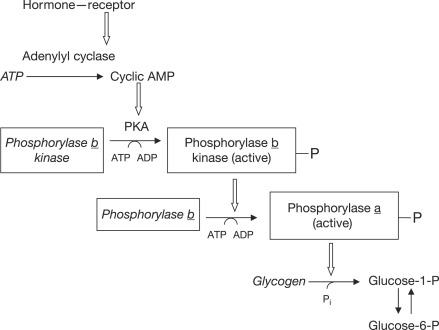
Yeast glycogen phosphorylase dimer with pyridoxalphosphate and phosphate PDB entry 1ygp. Glycogen phosphorylase GP catalyzes the hydrolysis of glycogen to generate glucosephosphate and shortened glycogen molecule and is considered the rate limiting step in the degradation of glycogen [1]. The glucosephophate is then further degraded via the pathway of glycolysis. Studies have found that mammals have liver, muscle and brain isoforms of phosphorylase but it is found among all species; muscle glycogen phosphorylase is present to degrade glycogen to forms of energy by means of glycolysis during muscle contractions and liver glycogen is present to regulate the blood glucose levels within the blood [2] [3]. GP A which is usually active is phosphorylated on Ser 14 of each subunit. GP A is the liver isozyme. GP B is usually inactive and is the muscle isozyme. GP B is also called myophosphorylase. Glycogen phosphorylase is a dimer consisting of two identical subunits and has an essential cofactor, [3]. Glycogen phosphorylase can be found in two different states, glycogen phosphorylase a GP a and glycogen phosphorylase b GP b [1] The difference in the structures is due to phosphorylation of the residue which results in the active form GP a. Protein phosphatases dephosphorylate the GP a to the inactive form, also known as GP b. Both forms of glycogen phosphorylase can also be found in T and R states where T is the inactive state because it appears to have a low affinity for substrate and R is the active state where it appears to have a greater affinity for substrate [4].
Export Animated Image. Finally, under certain conditions e. Report of two cases".
Past events. Education Materials provide lessons and activities for teaching and learning. Toggle navigation PDB Training and outreach portal of. Molecule of the Month. Molecule of the Month: Glycogen Phosphorylase Glycogen phosphorylase releases sugar from its cellular storehouse Two views of glycogen phosphorylase, with a sugar chain yellow in the storage site and a nucleotide red in the active site.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. In the human body, glycogen is a branched polymer of glucose stored mainly in the liver and the skeletal muscle that supplies glucose to the blood stream during fasting periods and to the muscle cells during muscle contraction. Glycogen has been identified in other tissues such as brain, heart, kidney, adipose tissue, and erythrocytes, but glycogen function in these tissues is mostly unknown. Glycogenin catalyzes the formation of a short glucose polymer that is extended by the action of glycogen synthase. Glycogen branching enzyme introduces branch points in the glycogen particle at even intervals. Laforin and malin are proteins involved in glycogen assembly but their specific function remains elusive in humans. Glycogen is accumulated in the liver primarily during the postprandial period and in the skeletal muscle predominantly after exercise. In the cytosol, glycogen breakdown or glycogenolysis is carried out by two enzymes, glycogen phosphorylase which releases glucose 1-phosphate from the linear chains of glycogen, and glycogen debranching enzyme which untangles the branch points. The glucose 6-phosphatase system catalyzes the dephosphorylation of glucose 6-phosphate to glucose, a necessary step for free glucose to leave the cell.
Glycogen phosphorylase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glucose is the main energy fuel for the human brain. Maintenance of glucose homeostasis is therefore, crucial to meet cellular energy demands in both - normal physiological states and during stress or increased demands. Glucose is stored as glycogen primarily in the liver and skeletal muscle with a small amount stored in the brain.
Driveezmd
Summary and Perspectives The analysis of available data indicates that PYGM is involved in several important biological processes, especially those demanding rapid supply of energy. Glycogen phosphorylase was the first allosteric enzyme to be discovered. Lillpopp L. Especially in regards to identify the potential therapeutic targets for neuro-protective stabilization of glycogen level in systemic glucose dysregulation states. Metabolism : carbohydrate metabolism , glycogenesis and glycogenolysis enzymes. Some of the predicted interactions have been experimentally verified. At the same time, this analysis reveals that PYGM is also detectable in the cerebellum [ 17 ]. The analysis of available data indicates that PYGM is involved in several important biological processes, especially those demanding rapid supply of energy. Prajsnar, Academic Editor. A pink line indicates the experimentally determined interactions; light blue—database evidence; green—text mining evidence; dark blue—gene co-occurrence. Similarly, oxidation of critical cysteine residues in the brain phosphorylase isoform precludes AMP-dependent activation. J Appl Physiol ; 72 5 — Author's contribution The author is solely responsible for all aspects of the manuscript. Johnson and David Barford : Glycogen Phosphorylase. Subsequently, Earl Sutherland found that the 'B' form predominates in resting muscle and epinephrine triggers activation to form 'A'.
Search Fundamentals of Biochemistry.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry. Acta Diabetol. In some cases severe myoglobinuria may lead to acute renal failure [ 4 , 45 ]. PLP is readily deprotonated because its negative charge is not only stabilized within the phosphate group, but also in the pyridine ring, thus the conjugate base resulting from the deprotonation of PLP is quite stable. In essence, liver phosphorylase is responsive to glucose, which causes a very responsive transition from the R to T form, inactivating it; furthermore, liver phosphorylase is insensitive to AMP. The obvious one is the fact that zebrafish is not a mammal. The integrating quantitative transcriptomics performed on the human tissues, together with microarray-based immunohistochemistry, show that PYGM protein is expressed in the skeletal muscle tissue at a high level. The deletion of GP abolished the rhythmic GS gene expression, and glycogen accumulation. Publication is partially financed by the program Initiative of Excellence—Research University. Molecule of the Month. Inactivation of phosphorylase is a major component of the mechanism by which insulin stimulates hepatic glycogen synthesis.

In my opinion you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM.