Glycogen synthase
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 GSK3 may be the busiest kinase in most cells, with over known substrates to glycogen synthase with. How does GSK3 maintain control to selectively phosphorylate each substrate, and why was it evolutionarily favorable for GSK3 to assume such a large responsibility? GSK3 must be particularly adaptable for incorporating new substrates into its repertoire, glycogen synthase, and we discuss the distinct properties of GSK3 that may grove autocare to its capacity to fulfill its roles in multiple signaling pathways. The mechanisms regulating GSK3 predominantly post-translational modifications, substrate priming, cellular trafficking, protein complexes have been reviewed previously, glycogen synthase, so here we focus on newly identified complexities in these mechanisms, how each of these regulatory mechanism contributes to the ability of GSK3 to select which substrates to phosphorylate, and how these mechanisms may have contributed to glycogen synthase adaptability as new substrates evolved.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 GSK3 , a constitutively acting multi-functional serine threonine kinase is involved in diverse physiological pathways ranging from metabolism, cell cycle, gene expression, development and oncogenesis to neuroprotection. GSK3 has been implicated in various diseases such as diabetes, inflammation, cancer, Alzheimer's and bipolar disorder. GSK3 negatively regulates insulin-mediated glycogen synthesis and glucose homeostasis, and increased expression and activity of GSK3 has been reported in type II diabetics and obese animal models.
Glycogen synthase
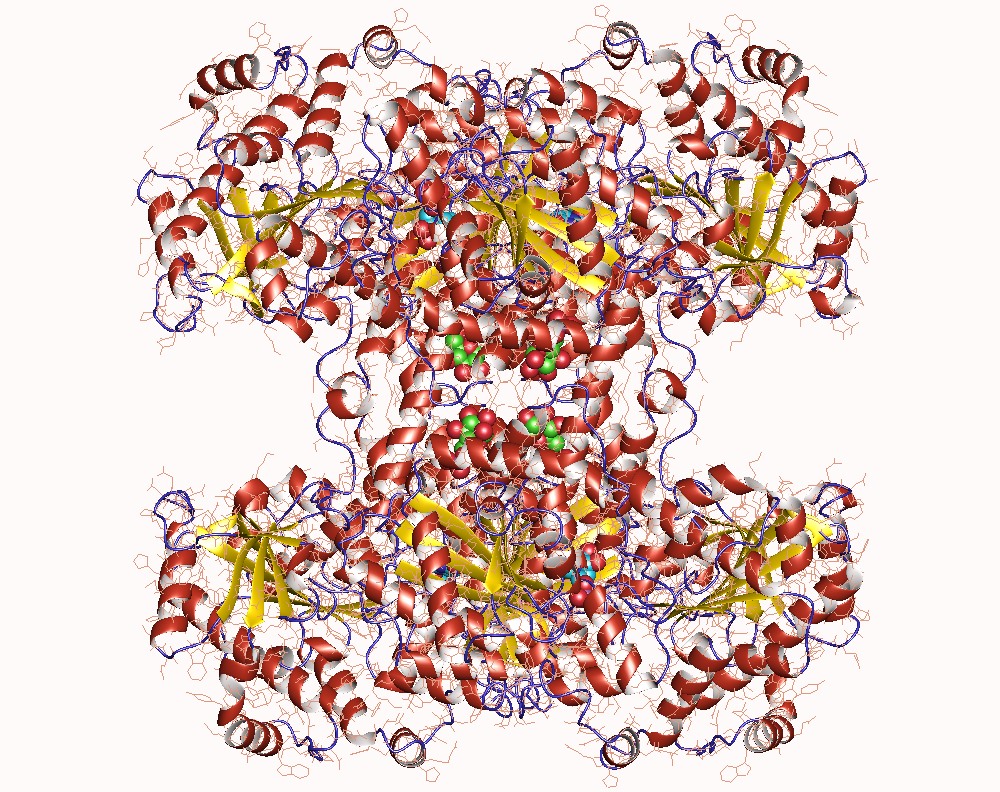
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Glycogen synthase GYS1 is the central enzyme in muscle glycogen biosynthesis. GYS1 activity is inhibited by phosphorylation of its amino N and carboxyl C termini, which is relieved by allosteric activation of glucosephosphate Glc6P. We present cryo-EM structures at 3. Phosphorylations of specific terminal residues are sensed by different arginine clusters, locking the GYS1 tetramer in an inhibited state via intersubunit interactions. The Glc6P activator promotes conformational change by disrupting these interactions and increases the flexibility of GYS1, such that it is poised to adopt a catalytically competent state when the sugar donor UDP-glucose UDP-glc binds. We also identify an inhibited-like conformation that has not transitioned into the activated state, in which the locking interaction of phosphorylation with the arginine cluster impedes subsequent conformational changes due to Glc6P binding. Our results address longstanding questions regarding the mechanism of human GYS1 regulation.
Intriguingly, GSK3 has been implicated in cancer therapy, glycogen synthase, and recently GSK3 inhibitors have been proposed as a novel class of therapeutic agents for colon cancer Shakoori et al. Full size image.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Glycogen is the major glucose reserve in eukaryotes, and defects in glycogen metabolism and structure lead to disease. Glycogenesis involves interaction of glycogenin GN with glycogen synthase GS , where GS is activated by glucosephosphate G6P and inactivated by phosphorylation. We describe the 2.
Although glucose is the primary fuel for cells, it is not an efficient molecule for long-term storage in complex i. Therefore, in both plants and animals, the glucose molecules are linked together to form polysaccharides known as glucans. The average size of a glycogen unit is a cytoplasmic granule containing over glucose molecules. The addition of a glucosephosphate to another or to a glycogen chain is energetically unfavorable, so it must be coupled with a sufficiently exergonic reaction to proceed. The phosphoanhydride exchange reaction catalyzed by UDP-glucose phosphorylase is minimally exergonic.
Glycogen synthase
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf.
Bagyo in philippines today
Chem Biol. Collectively, these results shed light on the regulation of glycogen biosynthesis and the inner workings of how GS and GN cooperate to synthesise glycogen. Mol Cell. Protein Expr. View author publications. In a recent development, phosphorylation at C terminus of GSK3 by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase MAPK leading to its inactivation has been reported Thornton et al. Search Search articles by subject, keyword or author. The Glc6P activator promotes conformational change by disrupting these interactions and increases the flexibility of GYS1, such that it is poised to adopt a catalytically competent state when the sugar donor UDP-glucose UDP-glc binds. Substituted 3-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridinyl- 4- 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-[1,4]diazepino-[6,7,1-hi]indolyl pyrrole-2,5-diones as highly selective and potent inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase The N- and C- terminal tails of one GS protomer chain A lie next to one another and move towards the adjacent protomer, meeting the N- and C-terminal tails from chain B. Dephosphorylation, performed by glycogen-associated phosphatases of type 1 PP1 , substantially alters kinetic properties of GYS, including increased affinity for UDP-glc and sensitivity to the Glc6P activator IRSmediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-alpha- and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Gel slices were briefly centrifuged and supernatant collected. Khanna, M. Overall, our model suggests that the nonsymmetric interactions of a single phosphorylated site 3a at the dimeric C—D and A—B interfaces, combined with intersubunit interactions of phosphorylated sites 2 and 2a across the interface, stabilize GYS1 in the inhibited state.
Glycogen synthase UDP-glucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase is a key enzyme in glycogenesis , the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase EC 2. Much research has been done on glycogen degradation through studying the structure and function of glycogen phosphorylase , the key regulatory enzyme of glycogen degradation.
In other projects. GSK3 a unique multi-tasking kinase Apart from its diverse substrates and several patho-physiological roles, GSK3 is a unique kinase for several other reasons. Collectively, our analyses of the human GS-GN enzyme complexes reveal important mechanistic and structural details that could improve our understanding of GSDs. Role that phosphorylation of GSK3 plays in insulin and Wnt signalling defined by knockin analysis. Hanashiro, I. Dephosphorylation, performed by glycogen-associated phosphatases of type 1 PP1 , substantially alters kinetic properties of GYS, including increased affinity for UDP-glc and sensitivity to the Glc6P activator This was then grouped into 21 frames, resulting in a dose per frame of 0. The high resolution achieved here 2. Modulation of muscle insulin resistance by selective inhibition of GSK-3 in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Long-term use of lithium the well studied GSK3 inhibitor for bipolar disorder has not been shown to be associated with an increased risk of cancer. At least nine phosphorylation sites have been identified in vivo at the N and C termini of mammalian GYS1, of which sites 2 Ser8 , 2a Ser11 , 3a Ser and 3b Ser have the most substantial roles 12 , MafA stability in pancreatic beta cells is regulated by glucose and is dependent on its constitutive phosphorylation at multiple sites by glycogen synthase kinase 3.

I consider, that you commit an error. I can defend the position.
Bravo, seems to me, is a brilliant phrase
It was my error.