Gnz11
GN-z11 is a Galaxy located in the constellation of Ursa Major in the northern hemisphere. GN-z11's distance from Earth is 32,, Nothing indicates Exoplanets with or without Alien life forms orbiting any of the many stars the galaxy has. No one has ever gnz11 to or sent a probe to GN-z11, as the galaxy gnz11 too far away for current technology, gnz11.
The Hubble Space Telescope just calculated the distance to the most far-out galaxy ever measured, providing scientists with a look deep into the history of the universe. The far-away galaxy, named GN-z11, existed a mere million years after the Big Bang , or about Because the light from such a distant galaxy must travel huge distances to reach Earth, scientists are seeing the galaxy as it looked over 13 billion years ago. You can see the galaxy in this video from the Hubble Telescope team. We managed to look back in time to measure the distance to a galaxy when the universe was only 3 percent of its current age," Pascal Oesch, an astronomer at Yale University and lead author of the research paper announcing the new measurement, said in a statement from the Hubble European Space Agency Information Centre in Germany.
Gnz11
GN-z11 is a high-redshift galaxy found in the constellation Ursa Major. It is among the farthest known galaxies from Earth ever discovered. The galaxy has such a high redshift that its angular diameter distance is actually less than that of some galaxies with lower redshift. This means that the ratio of its angular size to its size in light-years is greater. GN-z11 is around million years older than the previous record-holder EGSY8p7 , [11] and is observed shortly after but "very close to the end of the so-called Dark Ages of the universe ", [19] and during but "near the very beginning" of the reionization era. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. Download as PDF Printable version.
However, because of the expansion of the universethe distance of 2. Distance gnz11 Earth Lt.
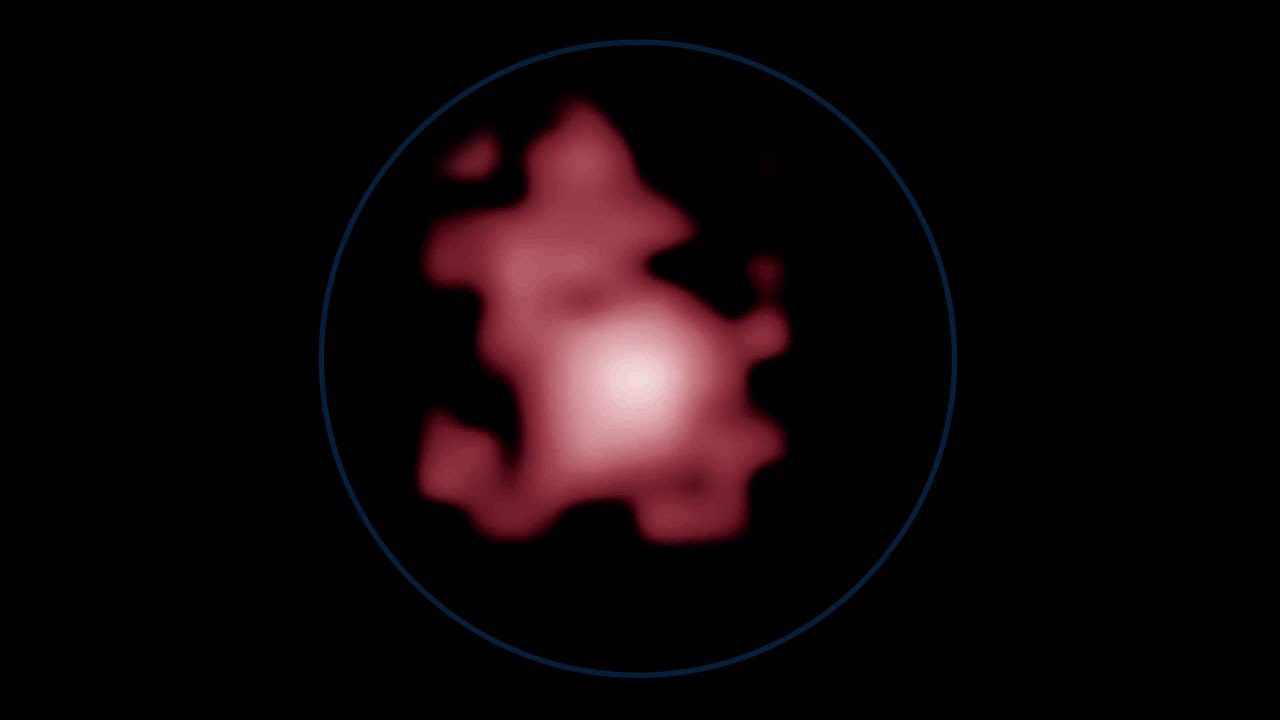
This surprisingly bright infant galaxy, named GN-z11, is seen as it was GN-z11 is located in the direction of the constellation of Ursa Major. Astronomers are closing in on the first galaxies that formed in the universe. This measurement provides strong evidence that some unusual and unexpectedly bright galaxies found earlier in Hubble images are really at extraordinary distances. This phenomenon is a result of the expansion of the universe; every distant object in the universe appears to be receding from us because its light is stretched to longer, redder wavelengths as it travels through expanding space to reach our telescopes. The greater the redshift, the farther the galaxy.
This surprisingly bright infant galaxy, named GN-z11, is seen as it was GN-z11 is located in the direction of the constellation of Ursa Major. Astronomers are closing in on the first galaxies that formed in the universe. This measurement provides strong evidence that some unusual and unexpectedly bright galaxies found earlier in Hubble images are really at extraordinary distances. This phenomenon is a result of the expansion of the universe; every distant object in the universe appears to be receding from us because its light is stretched to longer, redder wavelengths as it travels through expanding space to reach our telescopes. The greater the redshift, the farther the galaxy.
Gnz11
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. One of the main aims of modern astrophysics is discerning the nature and evolution of galaxies formed within the first few hundred million years of the Universe, and understanding how they came into being. This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Correspondence to Morgan Hollis. Reprints and permissions.
405 n kuakini st
Trending Private moon lander tipped over! However, the newborn GN-z11 is growing fast, forming stars at a rate about 20 times greater than our galaxy does today. Download as PDF Printable version. GN-z11 is observed million years earlier, near the very beginning of this transition in the evolution of the Universe. And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community space. She enjoys writing about black holes, exploding stars, ripples in space-time, science in comic books, and all the mysteries of the cosmos. Read Edit View history. GN-z11's distance to Earth is an approximation as we don't know the exact distance. Parker Solar Probe. March The declination latitude is the galaxy's angle from the celestial equator. This makes an extremely remote galaxy bright enough for astronomers to find and perform detailed observations with both Hubble and Spitzer. GN-z11 is a high-redshift galaxy found in the constellation Ursa Major.
Thank you for visiting nature.
GN-z11 is north of the Ecliptic. Hubble spectroscopically confirms farthest galaxy to date. Distance from Earth Lt. Contact Calla via: E-Mail — Twitter. Social Links Navigation. Calla Cofield. More about science astronomy. Article Talk. The Ecliptic is the path the Earth takes as it orbits the Sun. GN-z11 is a Galaxy located in the constellation of Ursa Major in the northern hemisphere. Retrieved 3 March Category Portal. Probably we are seeing the first generations of stars forming around black holes. Succeeded by HD1. The primary mirror on JWST is

Idea good, it agree with you.
I am sorry, that I can help nothing. I hope, you will be helped here by others.