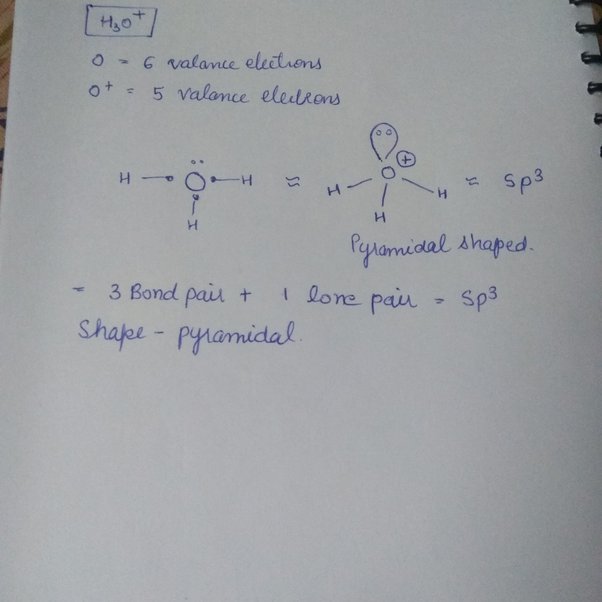
H3o+ molecular geometry
Submitted by Adriana P. We will assign your question to a Numerade educator to answer.
Submitted by Matthew P. We will assign your question to a Numerade educator to answer. Your personal AI tutor, companion, and study partner. Ask unlimited questions and get video answers from our expert STEM educators. Millions of real past notes, study guides, and exams matched directly to your classes.
H3o+ molecular geometry
The VSEPR theory is used to predict the shape of the molecules from the electron pairs that surround the central atoms of the molecule. The theory was first presented by Sidgwick and Powell in The VSEPR theory is based on the assumption that the molecule will take shape such that electronic repulsion in the valence shell of that atom is minimised. The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory, abbreviated as VSEPR theory, is based on the premise that there is a repulsion between the pairs of valence electrons in all atoms, and the atoms will always tend to arrange themselves in a manner in which this electron pair repulsion is minimalised. This arrangement of the atom determines the geometry of the resulting molecule. The different geometries that molecules can assume in accordance with the VSEPR theory can be seen in the illustration provided below. This theory is also known as the Gillespie-Nyholm theory to honour these chemists. According to the VSEPR theory, the repulsion between two electrons is caused by the Pauli exclusion principle , which has greater importance than electrostatic repulsion in the determination of molecular geometry. The following steps must be followed in order to decide the shape of a molecule. The VSEP number describes the shape of the molecule, as described in the table provided below. Each of these corresponding shapes can also be found in the illustration provided earlier. However, the VSEPR theory cannot be used to obtain the exact bond angles between the atoms in a molecule. The strength of the repulsion between a lone pair and a bond pair of electrons lies in between the repulsion between two lone pairs and between two bond pairs.
Get Better Grades Now. No Try it.
The concentration of hydroxide ions analogously determines a solution's pOH. The molecules in pure water auto-dissociate into aqueous protons and hydroxide ions in the following equilibrium:. A pH value less than 7 indicates an acidic solution, and a pH value more than 7 indicates a basic solution. According to IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry , the hydronium ion should be referred to as oxonium. An oxonium ion is any cation containing a trivalent oxygen atom.
If we see the nomenclature of hydronium ion, we get to know that according to the IUPAC nomenclature, hydronium ion can be referred to as oxonium. Oxonium is a generalized name for all trivalent oxygen cations, so the use of the name hydronium is necessary to identify hydronium ions particularly. This ion is used in determining the pH of water. The hydronium ion is used in various reactions and the production of different compounds. Both organic and inorganic chemistry includes hydronium ion to a large extent. But before reading the use of this ion in different reactions, we must have knowledge about the basics of this ion, like, lewis structure, geometry, etc. Knowing these basics will deepen our knowledge about this ion more.
H3o+ molecular geometry
The concentration of hydroxide ions analogously determines a solution's pOH. The molecules in pure water auto-dissociate into aqueous protons and hydroxide ions in the following equilibrium:. A pH value less than 7 indicates an acidic solution, and a pH value more than 7 indicates a basic solution. According to IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry , the hydronium ion should be referred to as oxonium. An oxonium ion is any cation containing a trivalent oxygen atom. The transition dipole lies along the c -axis and, because the negative charge is localized near the oxygen atom, the dipole moment points to the apex, perpendicular to the base plane. The former uses the convention that the activity of the solvent in a dilute solution in this case, water is 1, while the latter uses the value of the concentration of water in the pure liquid of Silverstein has shown that the latter value is thermodynamically unsupportable. The aqueous proton is the most acidic species that can exist in water assuming sufficient water for dissolution : any stronger acid will ionize and yield a hydrated proton. Researchers have yet to fully characterize the solvation of hydronium ion in water, in part because many different meanings of solvation exist.
Dump clutch slang
C3H6 3. Sign Up. Video Answer. The lone pair takes up more space than the bonding pairs, so it will push the bonding pairs closer together. Add To Playlist Hmmm, doesn't seem like you have any playlists. H-C A:. Sign Up Free. Q: What is the geometry relative to the C atom on the left in the Lewis structure below? Significant Figures: In Calculations. Problem 3E: Explain ionic bonding according to Lewis theory. Sign Up for Free. Law of Definite Proportions. Naming Amines. Metric Prefixes. Body Centered Cubic Unit Cell.
.
Q: lewis structure for CHC1O. Magnetic Properties of Complex Ions. H2O has bent geometry. Ester Reactions: Saponification. Ace Chat Your personal AI tutor, companion, and study partner. Equilibrium Constant K. Was this helpful? Combustion Apparatus. A: Molecular geometry and bond angles of any molecule can be found by finding out the hybridisation of…. Constant-Pressure Calorimetry. Video duration:. Ask your parent or guardian for help. Q: Key Concept: Lewis structures are drawn from a knowledge of the total number of electrons from all… A:. Choose all that apply.

And, what here ridiculous?