How many covalent bonds can carbon form
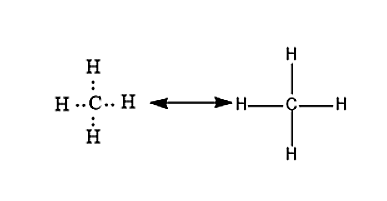
Figure 1. Carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. The simplest carbon molecule is methane CH 4depicted here.
Carbons electron configuration shows us 6 total electrons with 4 valence electrons. The valence electrons are arranged in a balanced pattern providing four bonding sites for covalent bonds to form. How many covalent bonds can carbon form with other atoms? Chemistry Bonding Basics Bonding. Jan 29, Explanation: Carbons electron configuration shows us 6 total electrons with 4 valence electrons.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
Cells are made of many complex molecules called macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids RNA and DNA , carbohydrates, and lipids. The macromolecules are a subset of organic molecules any carbon-containing liquid, solid, or gas that are especially important for life. The fundamental component for all of these macromolecules is carbon. Individual carbon atoms have an incomplete outermost electron shell. With an atomic number of 6 six electrons and six protons , the first two electrons fill the inner shell, leaving four in the second shell. Therefore, carbon atoms can form up to four covalent bonds with other atoms to satisfy the octet rule. The methane molecule provides an example: it has the chemical formula CH 4. Each of its four hydrogen atoms forms a single covalent bond with the carbon atom by sharing a pair of electrons. This results in a filled outermost shell. Hydrocarbons are organic molecules consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen, such as methane CH 4 described above. We often use hydrocarbons in our daily lives as fuels—like the propane in a gas grill or the butane in a lighter. The many covalent bonds between the atoms in hydrocarbons store a great amount of energy, which is released when these molecules are burned oxidized. The geometry of the methane molecule, where the atoms reside in three dimensions, is determined by the shape of its electron orbitals. The carbons and the four hydrogen atoms form a shape known as a tetrahedron, with four triangular faces; for this reason, methane is described as having tetrahedral geometry. As the backbone of the large molecules of living things, hydrocarbons may exist as linear carbon chains, carbon rings, or combinations of both.
Summary The unique properties of carbon make it a central part of biological molecules.
But what exactly does the term mean? Possibly the quickest answer to this question is simply that all living things are reliant on molecules that include carbon. There are no living things on our planet that do not have carbon however, there are nonliving things made up of carbon as well: e. Discuss why it is said that life is carbon-based and the bonding properties of carbon. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. It is the bonding properties of carbon atoms that are responsible for its important role.
Well, carbon can form up to FOUR covalent bonds Carbon can also "catenate" ; i. The result is that carbon chemistry can support long-chain, complicated molecules that can function biologically. For more of the same see here. Basically, the valency of any element gives you the exact idea about the no. Now, the question is why the bond formation is so important? The answer to that is the satisfaction of valency of the atom of the element so that it can achieve a stable electronic configuration. I can explain this to you even more with the help of a daily life example but please don't use this in any exam or any assignment. Say Alisha do not have any friends, because of the lack of friends she is unhappy or you can say in an unstable state.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
Inorganic Carbon. For more than years, chemists have divided compounds into two categories. Those that were isolated from plants or animals were called organic , while those extracted from ores and minerals were inorganic. Organic chemistry is often defined as the chemistry of carbon. But this definition would include calcium carbonate CaCO 3 and graphite, which more closely resemble inorganic compounds. Carbon therefore forms covalent bonds with many other elements. Carbon forms strong double and triple bonds with a number of other nonmetals, including N, O, P, and S. Carbon occurs as a variety of allotropes.
How to use avery labels in word
Sign in. Which of the forces of molecular attraction is the weakest: hydrogen bond, dipole interaction, Can carbon form 4 bonds? So far, the hydrocarbons we have discussed have been aliphatic hydrocarbons , which consist of linear chains of carbon atoms. But what exactly does the term mean? Impact of this question views around the world. Licenses and Attributions. The three-dimensional placement of atoms and chemical bonds within organic molecules is central to understanding their chemistry. In the human diet, trans fats are linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, so many food manufacturers have reduced or eliminated their use in recent years. These geometries have a significant impact on the shape a particular molecule can assume.
But what exactly does the term mean?
We often use hydrocarbons in our daily lives as fuels—like the propane in a gas grill or the butane in a lighter. To be enantiomers, a molecule must have at least three different atoms or groups connected to a central carbon. Any of the hydrogen atoms can be replaced with another carbon atom covalently bonded to the first carbon atom. Single bonds, like those found in ethane, are able to rotate. Skills to Develop Explain why carbon is important for life Describe the role of functional groups in biological molecules. Jan 29, Double bonds, like those found in ethene cannot rotate, so the atoms on either side are locked in place. Carbon and hydrogen can form hydrocarbon chains or rings. How does chemical bonding affect solubility? In the human diet, trans fats are linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, so many food manufacturers have reduced or eliminated their use in recent years. Try It. Hydrocarbon Chains Hydrocarbon chains are formed by successive bonds between carbon atoms and may be branched or unbranched.

0 thoughts on “How many covalent bonds can carbon form”