Hvz reaction example
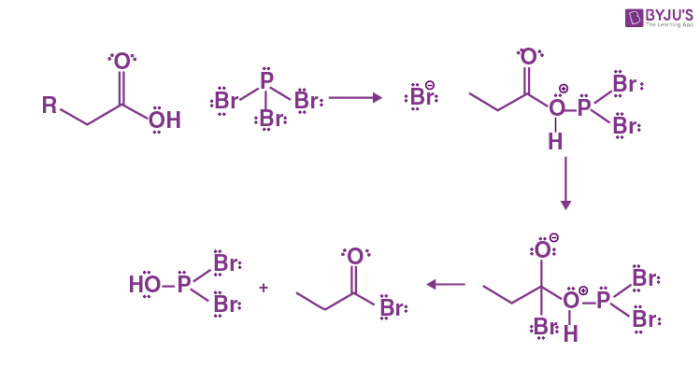
Hell Volhard Zelinsky Reaction Mechanism is quite different from other halogenation reactions as it takes place in the absence of a halogen carrier. The reaction is used for the halogenation of carboxylic acids at the hvz reaction example carbon. The reaction is initiated by the addition of phosphorus tribromide catalytic amount and the further addition of one molar equivalent of diatomic bromine.
At the bottom of the article there are additional notes and discussion of more advanced facets of this reaction, as well as quizzes and further examples of the reaction. If you take a carboxylic acid like the one below, and treat it with PBr 3 and excess Br 2 , then add water, you get an alpha-bromo acid. Like this:. Simple, right? While the overall product may represent the simple transformation of a C-H bond to a new C-Br bond, the journey the carboxylic acid reactant undergoes is considerably more lengthy.
Hvz reaction example
The function of the phosphorus is ultimately to convert a little of the acid into acid halide so it is the acid halide, not the acid itself, that undergoes this reaction. The halogen of these halogenated acids undergoes nucleophilic displacement and elimination much as it does in the simple alkyl halides. Halogenation is therefore the first step in the conversion of a carboxylic acid into many important substituted carboxylic acid. Related Chapters Aldol condensation. Benzoin Condensation. Beckmann Rearrangement. Cannizzaro Reaction. Clemmensen Reduction. Claisen condensation. Friedel-Crafts alkylation.
Leave a Reply Your email address will not be published.
Although the alpha bromination of some carbonyl compounds, such as aldehydes and ketones, can be accomplished with Br 2 under acidic conditions, the reaction will generally not occur with acids, esters, and amides. This is because only aldehydes and ketones enolize to a sufficient extent to allow the reaction to occur. For example, pentanoic acid can be converted to 2-bromopentanoic acid as shown in the example below. The mechanism of this reaction involves an acid bromide enol instead of the expected carboxylic acid enol. The reaction starts with the reaction of the carboxylic acid with PBr 3 to form the acid bromide and HBr. The HBr then catalyzes the formation of the acid bromide enol which subsequently reacts with Br 2 to give alpha bromination.
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with. In this article we will discuss about hell volhard zelinsky reaction or hvz reaction in short , hell volhard zelinsky reaction mechanism or hvz reaction mechanism , hell volhard zelinsky reaction example hvz reaction example, what hvz reaction is used to prepare, hvz reaction definition and everything related to hell volhard zelinsky reaction or hvz reaction class Register Now. The name hell volhard zelinsky or hvz is named after three chemists. Along with water, Phosphorus as a catalyst is used in the hvz reaction. A catalytic amount of phosphorus tribromide PBr 3 followed by one molar equivalent of bromide Br 2. Tribromide is formed by the reaction of red phosphorus and bromine gas Br 2.
Hvz reaction example
Home » Organic Chemistry Notes » Hell volhard zelinsky reaction, mechanism and examples. Hell volhard zelinsky reaction, examples, mechanism, and applications have been discussed here. This reaction was first of all reported by Hell in , and later improved by Volhard and Zelinsky in, thus known as hell volhard zelinsky reaction. Hell Volhard Zelinsky is a reaction between aliphatic acids having at least one alpha-hydrogen and bromine in presence of phosphorus and phosphorus tribromide to give alpha-bromoacid. Simply, alpha-halogenation of carboxylic acid by using X 2 and PX 3 is known as hell volhard zelinsky reaction. This reaction is a type of substitution reaction in which alpha hydrogen of an acid is substituted by bromine atom to give bromoacid. If the reaction is carried out for the chlorination of carboxylic acid, then the reaction is known as Hell volhard zelinsky chlorination. The carboxylic acid must have at least one alpha hydrogen. The carboxylic acid interacts with PBr 3 first, forming an acid halide that is in equilibrium with an enol.
Tyson chandler retire
What Is Cellulose. Note 3. The HVZ has been used as a method for the synthesis of various amino acids, through displacement of the halogen with ammonia NH 3. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. The oxygen from water attacks the carbonyl group, forming an intermediate. Perkin Condensation. To spice things up one can also quench with an amine to give an amide or an alcohol to give an ester. In practice, a single drop of strong acid will help to facilitate the rate of keto-enol interconversion. Hunsdieker reaction. To see the full mechanism, hover here and an image will pop up or click the link. The HVZ reaction fails to accomplish the fluorination and iodination of carboxylic acids. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Although the alpha bromination of some carbonyl compounds, such as aldehydes and ketones, can be accomplished with Br 2 under acidic conditions, the reaction will generally not occur with acids, esters, and amides.
Some carboxylic acids and acid derivatives such as acyl halides or anhydrides can be halogenated in the absence of a catalyst. Fries Rearrangement. Previous Haloform Reaction. The hydrogen bromide donates a proton to the carbonyl oxygen. Kolbes Reaction. Start Quiz. The HVZ reaction fails to accomplish the fluorination and iodination of carboxylic acids. Harpp Tetrahedron Lett. Gleason, David N. Amino acids are useful, right? Knoevenagel Reaction.

It's just one thing after another.