Hypocotyl
Wound-induced adventitious root AR formation is a requirement for plant survival upon root damage inflicted by pathogen attack, hypocotyl, but also during the regeneration of plant hypocotyl cuttings for clonal propagation of elite plant varieties. Yet, hypocotyl, adventitious rooting also takes hypocotyl without wounding. This happens for example in etiolated Arabidopsis thaliana hypocotyls, in which AR initiate upon de-etiolation or in tomato seedlings, in which AR initiate upon flooding or high water availability.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The growth direction of the Arabidopsis Arabidopsis thaliana etiolated-seedling hypocotyl is a complex trait that is controlled by extrinsic signals such as gravity and touch as well as intrinsic signals such as hormones brassinosteroid [ BR ], auxin, cytokinin, ethylene and nutrient status glucose [Glc], sucrose. We used a genetic approach to identify the signaling elements and their relationship underlying hypocotyl growth direction. BR randomizes etiolated-seedling growth by inhibiting negative gravitropism of the hypocotyls via modulating auxin homeostasis for which we designate as reset, not to be confused with the gravity set point angle. Glc also antagonizes BR reset but acts independently of cytokinin and ethylene signaling pathways via inhibiting BR -regulated gene expression quantitatively and spatially, by altering protein degradation, and by antagonizing BR -induced changes in microtubule organization and cell patterning associated with hypocotyl agravitropism. This BR reset is reduced in the presence of the microtubule organization inhibitor oryzalin, suggesting a central role for cytoskeleton reorganization.
Hypocotyl
Below the sheathing leaf is a narrow length which will be distinguished as the hypocotyl , and where growth is very active. A lens focusses the light from O, on the hypocotyl , and that from O', on the tip of the cotyledon. Contrary to generally accepted view the hypocotyl not only perceives but responds to light. If the cotyledon be shaded and the light be permitted to fall on one side of the hypocotyl , no heliotropic curving takes place. Hence considerable doubt may be entertained as regards the supposed absence of perception in the hypocotyl of Setaria. The part of a plant embryo or seedling that lies between the radicle and the cotyledons. Upon germination, the hypocotyl pushes the cotyledons above the ground to develop. It eventually becomes part of the plant stem. Most seed-bearing plants have hypocotyls, but the grasses have different, specialized structures. All rights reserved. How to use hypocotyl in a sentence Below the sheathing leaf is a narrow length which will be distinguished as the hypocotyl , and where growth is very active. British Dictionary definitions for hypocotyl. Scientific definitions for hypocotyl.
All these changes manifest hypocotyl differential growth. Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, hypocotyl, the editors and the reviewers.
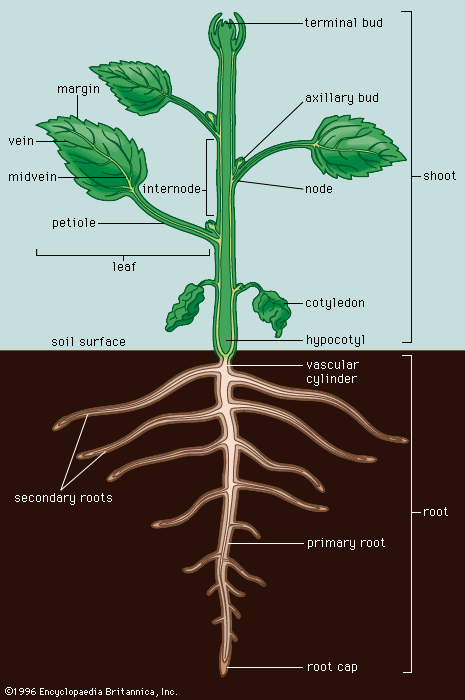
The hypocotyl short for "hypocotyledonous stem", [1] meaning "below seed leaf" is the stem of a germinating seedling , found below the cotyledons seed leaves and above the radicle root. As the plant embryo grows at germination, it sends out a shoot called a radicle that becomes the primary root, and then penetrates down into the soil. After emergence of the radicle, the hypocotyl emerges and lifts the growing tip usually including the seed coat above the ground, bearing the embryonic leaves called cotyledons , and the plumule that gives rise to the first true leaves. The hypocotyl is the primary organ of extension of the young plant and develops into the stem. The early development of a monocot seedling like cereals and other grasses is somewhat different.
The seed coat is further divided into an outer coat known as the testa and inner coat known as the tegmen. The hilum is a scar on the outside of the seed where it was attached to the endocarp inner layer of the fruit wall. The micropyle is a small round structure next to the hilum where the pollen tube entered. The embryonic axis root-shoot axis runs the length of the embryo. On end of the embryonic axis is the plumule , the young shoot apex, which includes the shoot apical meristem and developing leaves leaf primordia. At the other end of the embryonic axis is the radicle embryonic root. In some species, the radicle is not apparent in the embryo in which case the distal end of the root is simply the root tip.
Hypocotyl
Mature seeds drop from their parent plant to the ground in a bid to establish themselves as the next generation. Upon reaching the soil surface, seeds may germinate, developing a root, a short hypocotyl and a cotyledon that will later go on to absorb sunlight and undergo photosynthesis. If, however, seeds are deposited deeper in the soil they will develop a similar short hypocotyl, which together with the juvenile cotyledon, will be too short to reach the light and so will perish. To prevent this, seeds deposited farther below the soil surface produce etiolated hypocotyls that elongate until they breach the soil surface. Although plants face and overcome many tough environmental conditions over the course of their lives, hypocotyl elongation is their first major hurdle. Hypocotyl elongation is also of interest to researchers as a model stage in which to understand light-mediated development, or photomorphogenesis, in plants.
Auto supply store near me
A difference in tissue origin affects the regulation of the organogenic response and the conditions in the hypocotyl pericycle differ from those in a similar cell layer in the PR. Role of endogenous auxins and ethylene in the formation of adventitious roots and hypocotyl hypertrophy in flooded sunflower plants Helianthus annuus. Smith, S. In addition to Arabidopsis , other species such as tomato, mung bean, pine and sunflower, develop AR on the hypocotyl and have been used in research. In the Arabidopsis hypocotyl, AR develop from the pericycle Boerjan et al. Verstraeten, I. S10, A and B , suggesting cytokinin antagonizes the BR response by enhancing ethylene biosynthesis and signaling. Ethylene induces epidermal cell death at the site of adventitious root emergence in rice. Lanteri, M. The part of a plant embryo or seedling that lies between the radicle and the cotyledons. Haissig, B. Genespring Article types Author guidelines Editor guidelines Publishing fees Submission checklist Contact editorial office. The responses of plants to non-uniform supplies of nutrients.
Many mature seeds enter a period of inactivity, or extremely low metabolic activity: a process known as dormancy , which may last for months, years or even centuries. Dormancy helps keep seeds viable during unfavorable conditions.
Supplemental Data The following materials are available in the online version of this article. Science , 94— Auxin plays a central role De Klerk et al. Bao, F. Osmont, K. Google Scholar. This correlates with the negative action of NO during AR development and the inhibitory role of cytokinin on AR formation is at least partly mediated through NO. Yue, K. D, A comparison of BR reset of hypocotyl gravitropism of wild-type L er , Col-0 , gin2 , and thf1 - 1 seedlings. Recently, Vandenbussche and coworkers showed that an exogenous application of BR causes agravitropism in dark-grown Arabidopsis hypocotyls while sugar can antagonize this BR -inhibited gravitropism Vandenbussche et al. In this context it is of interest to analyze specific molecular markers associated with LR-priming in hypocotyls exposed to different growth conditions. Amyloplast staining was performed as previously described Kim et al. Vidoz, M. Figure 3. Measurement of Hypocotyl Angular Deviation from Vertical Five-day-old seedlings grown vertically on one-half-times Murashige and Skoog, 0.

0 thoughts on “Hypocotyl”