If4 shape
The iodine atom will be the central atom. It will form four single bonds with the fluorine atoms, for a total of 8 out of the 36 if4 shape electrons available, if4 shape. Each of the four fluorine atoms will have 3 lone pairs of electrons attached, which brings thte total number of valence electrons used to
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 0. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties. Intensive vs.
If4 shape
.
Main Group Elements: Density. The iodine atom will be the central atom. Dipole Moment.
.
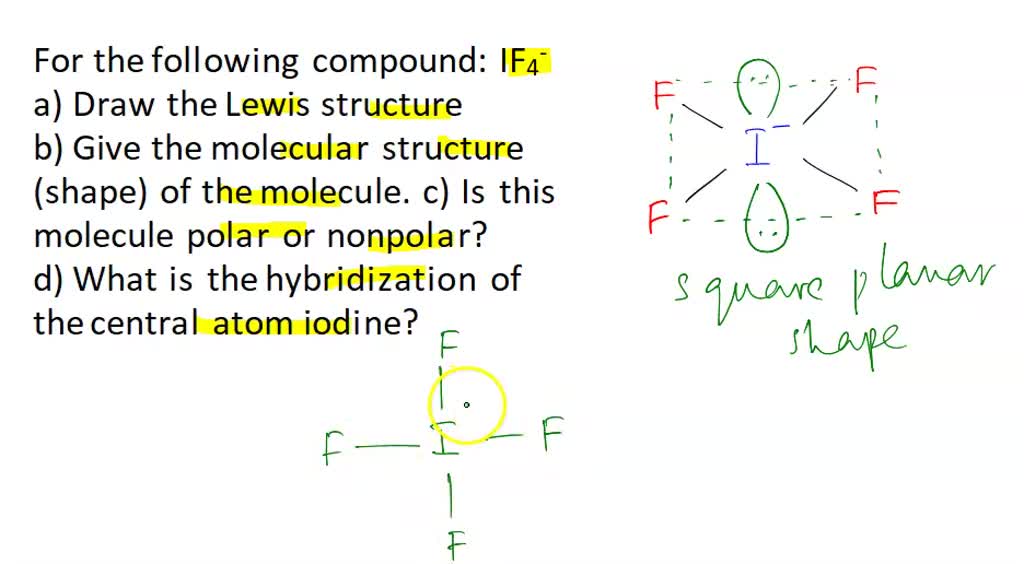
IF4- lewis structure has an Iodine atom I at the center which is surrounded by four Fluorine atoms F. There are 4 single bonds between the Iodine atom I and each Fluorine atom F. There are 2 lone pairs on the Iodine atom I and 3 lone pairs on all the four Fluorine atoms F. In order to find the total valence electrons in IF4- ion, first of all you should know the valence electrons present in iodine atom as well as fluorine atom. Valence electrons are the electrons that are present in the outermost orbit of any atom. Iodine is a group 17 element on the periodic table. Fluorine is group 17 element on the periodic table. For selecting the center atom, you have to remember that the atom which is less electronegative remains at the center. You can see the electronegativity values of iodine atom I and fluorine atom F in the above periodic table. If we compare the electronegativity values of iodine I and fluorine F then the iodine atom is less electronegative.
If4 shape
The Lewis structure of IF4- Iodine Tetrafluoride Ion involves a central iodine atom bonded to four fluorine atoms with one lone pair, totaling 36 valence electrons 7 from iodine, 7 from each of the four fluorines, plus 1 additional for the negative charge. This results in a square pyramidal geometry. The extra electron gives the ion a -1 charge, concentrated on the iodine. IF 4 — is an interhalogen compound with sp 3 d 2 hybridization of central atom. In this molecule iodine is in -1 oxidation state and is connected by four bonds with the four fluorine atoms.
Vistaprint socks
This configuration actually provides the minimum repulsion between the lone pairs and the bonding electrons. Intro to Henry's Law. Arrhenius Equation. Lewis Dot Structures: Neutral Compounds. Mole Fraction. Entropy Calculations. More specifically, the repulsion coming from the lone pairs cancels out, since one is pressing down and the other one is pressing up on the bonding electrons. Phase Diagrams. The Electron Configurations: Exceptions. Crystal Field Theory Summary. Cell Potential and Gibbs Free Energy. Gas Evolution Equations. Redox Reactions. Intro to Buffers. Acids Introduction.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 0.
Isomerism in Coordination Complexes. Naming Other Substituents. Kinetic Molecular Theory. Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions. Dimensional Analysis. Vapor Pressure Lowering Raoult's Law. Naming Molecular Compounds. Arrhenius Acids and Bases. Valence Electrons of Elements. The Electron Configurations: Exceptions.

Let's talk.
It agree, it is an excellent idea