Kupffer
Sponsored by the Carcinogenesis Speciality Section. Ruth A.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are a critical component of the mononuclear phagocytic system and are central to both the hepatic and systemic response to pathogens. Kupffer cells are reemerging as critical mediators of both liver injury and repair. Multiple M2 phenotypes can be distinguished, each involved in the resolution of inflammation and wound healing. Here, we have provided an update on recent research that has contributed to the developing delineation of the contribution of Kupffer cells to different types of liver injury, with an emphasis on alcoholic and nonalcoholic liver diseases. These recent advances in our understanding of Kupffer cell function and regulation will likely provide new insights into the potential for therapeutic manipulation of Kupffer cells to promote the resolution of inflammation and enhance wound healing in liver disease.
Kupffer
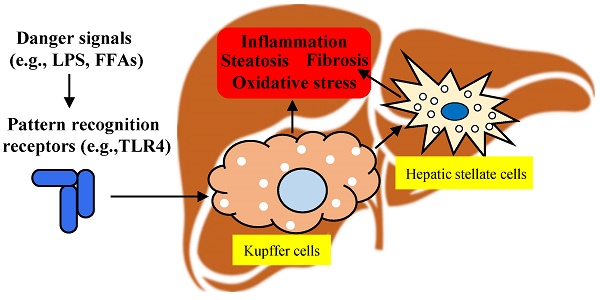
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role in maintaining liver functions. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections. Under pathological conditions, they are activated by different components and can differentiate into M1-like classical or M2-like alternative macrophages. The metabolism of classical or alternative activated Kupffer cells will determine their functions in liver damage. Special functions and metabolism of Kupffer cells suggest that they are an attractive target for therapy of liver inflammation and related diseases, including cancer and infectious diseases. Here we review the different types of Kupffer cells and their metabolism and functions in physiological and pathological conditions. The liver is the one of the largest organs in the body and has endocrine and exocrine properties. Initially, KCs were associated to the family of perivascular cells of the connective tissues or to the adventitial cells pericytes. Finally, after fundamental research by Tadeusz Browicz, KCs were identified as macrophages [ 3 ]. Kupffer cells are liver resident macrophages that localize within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adherent to the endothelial cells that compose the blood vessel walls. KCs are the first immune cells in the liver that come in contact with the gut bacteria and gut bacterial endotoxins and microbial debris derived from the gastrointestinal tract that have been transported to the liver via the portal vein [ 4 ]. They also play an essential role in the host defense [ 5 , 6 ] and participate in the metabolism of multiple compounds such as protein complexes, small particles, and lipids, and in removing apoptotic cells from the circulation [ 7 , 8 ]. Consequently, modifications or alterations of KC functions are associated with various liver diseases: viral hepatitis, steatohepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, intrahepatic cholestasis, activation or rejection of the liver during liver transplantation [ 9 ] and liver fibrosis [ 10 ].
J Infect Dis, kupffer. Hepatocyte injury by activated neutrophils in vitro is mediated by proteases.
Kupffer cells , also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer—Browicz cells , are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident macrophages in the body. Gut bacteria, bacterial endotoxins, and microbial debris transported to the liver from the gastrointestinal tract via the portal vein will first come in contact with Kupffer cells, the first immune cells in the liver. It is because of this that any change to Kupffer cell functions can be connected to various liver diseases such as alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis, steatohepatitis, activation or rejection of the liver during liver transplantation and liver fibrosis. Kupffer cells can be found attached to sinusoidal endothelial cells in both the centrilobular and periportal regions of the hepatic lobules. Kupffer cell function and structures are specialized depending on their location. Periportal Kupffer cells tend to be larger and have more lysosomal enzyme and phagocytic activity, whereas centrilobular Kupffer cells create more superoxide radical.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Hajira Basit ; Michael L. Tan ; Daniel R.
Kupffer
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Liver macrophages comprise Kupffer cells — which are self-maintaining, non-migratory tissue-resident phagocytes that originate from yolk sac-derived precursors during embryogenesis — and monocyte-derived macrophages.
Sedat peker serdar han peker
Peripheral blood monocytes can enter the liver and then mature into a phenotype characteristic of tissue macrophages. Molecular mechanism for adiponectin-dependent M2 macrophage polarization: Link between the metabolic and innate immune activity of full-length adiponectin. M2b macrophages exhibit a high production and secretion of IL, and their activation turns off IL It is clear that the rate of influx of peripheral monocytes into the liver is higher than in other tissues, such as the lung; however, there is controversy over the life span of Kupffer cells in the liver. Thus, understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms of immune tolerance to these adducts will lead to the identification of risk factors that determine patients' susceptibility to IADR. NODs: Intracellular proteins involved in inflammation and apoptosis. Kupffer cells are amoeboid in character, with surface features including microvilli , pseudopodia and lamellipodia , which project in every direction. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident macrophages in the body. Once they are activated, KCs display the ability to differentiate into M1-like macrophages classical or M2-like macrophages alternative depending on the signals they receive from their environment [ 40 ]. J Immunol. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in autoimmunity: Pretty girl or old witch?
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS.
Blockade of liver macrophages by gadolinium chloride reduces lethality in endotoxemic rats—Analysis of mechanisms of lethality in endotoxemia. Ablation of Kupffer cells prevents the development of fatty liver and inflammation in rats chronically exposed to ethanol via intragastric feeding 1. The stage of hepatic tumor promotion involves the selective clonal expansion of preneoplastic focal cells. It was only in the s, that Stein, Doyle and co-workers demonstrated the existence of an alternative activation phenotype of macrophages induced by IL-4 and IL [ 42 , 43 ]. Macrophages Histiocytes Kupffer cells Alveolar macrophage Microglia Osteoclasts Epithelioid cells giant cells Langhans giant cells Foreign-body giant cell Touton giant cells. Complement activation during ethanol exposure is mediated via C1q, the key protein in the classical pathway of activation 22 and leads to an increase in inflammatory cytokine expression in the liver that is dependent both on the presence of the anaphylatoxin receptors, C3aR and C5aR, and hepatic macrophages Of particular interest to studies in liver, additional phenotypes for resident macrophages in the liver have been identified. In , after several years of research, Tadeusz Browicz identified them, correctly, as macrophages. Enteric dysbiosis associated with a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease. Tumor necrosis factor alpha is not required for WY14,induced cell proliferation. Dietary glycine prevents increases in hepatocyte proliferation caused by the peroxisome proliferator WY, Activation of the complement pathway can occur via the classical, lectin, or alternative pathways Epidermal growth factor prevents acetaldehyde-induced paracellular permeability in Caco-2 cell monolayer. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. J Clin Invest.

0 thoughts on “Kupffer”