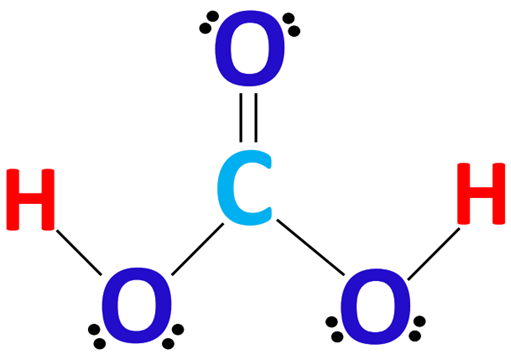
Lewis dot structure of h2co3
Hydrogen has 1 valence electron, we have 2 Hydrogens; plus 4 for Carbon, plus 6 for Oxygen times 3, for a total of 24 valence electrons. Whenever you see Hydrogens in front of a polyatomic ion like CO3, NO3, or SO4, it's going to be an acid and you're going to need to put those Hydrogens attached to the outside Oxygens. So we'll put the Carbon at the center. We have three Lewis dot structure of h2co3, we'll put three Oxygens around it.
Among them, the oxygen and hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond to form two OH groups, the carbon atom is the central atom, around which an oxygen atom and two OH groups are connected. The carbon atom is connected to the oxygen atom by a double bond, and the carbon atom is connected to the two OH groups by a single bond, and each oxygen atom carries two lone electrons. The structure is shown below:. According to the ordering of the elements in the periodic table, we can get that the C, H and O atoms are located in the 14th, 1st and 16th group of elements in the periodic table, so the valence electrons in the C, H and O atoms are 4, 6 and 1, respectively. The central atom must have the smallest electronegativity, this is because the atom with the smallest electronegativity needs to share its electrons with the surrounding atoms and always puts hydrogen on the outside if it is present in a given molecule.
Lewis dot structure of h2co3
.
We could check our formal charges.
.
In all cases, these bonds involve the sharing or transfer of valence shell electrons between atoms. In this section, we will explore the typical method for depicting valence shell electrons and chemical bonds, namely Lewis symbols and Lewis structures. We use Lewis symbols to describe valence electron configurations of atoms and monatomic ions. A Lewis symbol consists of an elemental symbol surrounded by one dot for each of its valence electrons:. Figure 7. Lewis symbols can also be used to illustrate the formation of cations from atoms, as shown here for sodium and calcium:. Likewise, they can be used to show the formation of anions from atoms, as shown here for chlorine and sulfur:. We also use Lewis symbols to indicate the formation of covalent bonds, which are shown in Lewis structures , drawings that describe the bonding in molecules and polyatomic ions. For example, when two chlorine atoms form a chlorine molecule, they share one pair of electrons:. The Lewis structure indicates that each Cl atom has three pairs of electrons that are not used in bonding called lone pairs and one shared pair of electrons written between the atoms.
Lewis dot structure of h2co3
H 2 CO 3 carbonic acid has two hydrogen atoms, one carbon atom, and three oxygen atoms. In the H 2 CO 3 Lewis structure, there is one double bond and two single bonds around the carbon atom, with three oxygen atoms attached to it. The oxygen atom with a double bond has two lone pairs, and the left oxygen and right oxygen atom with which the hydrogen atom is attached also has two lone pairs. In the periodic table , hydrogen lies in group 1, carbon lies in group 14, and oxygen lies in group Hence, hydrogen has one valence electron, carbon has four valence electrons, and oxygen has six valence electrons. Since H 2 CO 3 has two hydrogen atoms, one carbon atom, and three oxygen atoms, so…. Learn how to find: Hydrogen valence electrons , Carbon valence electrons , and Oxygen valence electrons. We have a total of 24 valence electrons. And when we divide this value by two, we get the value of total electron pairs. Here hydrogen can not be the central atom.
Mount washington observatory
Step 2 Identify the central atom The central atom must have the smallest electronegativity, this is because the atom with the smallest electronegativity needs to share its electrons with the surrounding atoms and always puts hydrogen on the outside if it is present in a given molecule. Then we'll form octets for each atom: 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, and We could check our formal charges. So that's the Lewis structure for H2CO3. What are the benefits of L-Threonine? Myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol are most common in supplements So we've used all 24 valence electrons and each of the atoms in H2CO3 has a full outer shell. The structure is shown below:. See the Big List of Lewis Structures. So, for a carbonic acid molecule, carbon has a lower electronegativity than oxygen and hydrogen, hence carbon is the central atom and oxygen and hydrogen are the outer atoms. However, the Carbon only has 6 valence electrons, so it needs 2 more to form an octet.
Carbonic acid is a molecule which contains one carbon atom, three oxygen atom and two hydrogen atom.
So that's the Lewis structure for H2CO3. We could check our formal charges. Inositol can be found in nine forms. Opens New Window. So we've used 2, 4, 6, 8, And then we'll put the two H's around the outside of it. We have three Oxygens, we'll put three Oxygens around it. Whenever you see Hydrogens in front of a polyatomic ion like CO3, NO3, or SO4, it's going to be an acid and you're going to need to put those Hydrogens attached to the outside Oxygens. There are a total of 24 valence electrons in H 2 CO 3. Step 2 Identify the central atom The central atom must have the smallest electronegativity, this is because the atom with the smallest electronegativity needs to share its electrons with the surrounding atoms and always puts hydrogen on the outside if it is present in a given molecule. L-threonine is an essential amino acid important for forming proteins and enzymes in the body Solutions of carbon dioxide in water contain small amounts of this compound. So we have a total of 24 valence electrons. Then we'll form octets for each atom: 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, and Carbonic acid

I am sorry, it does not approach me. Who else, what can prompt?
Trifles!