Lewis structure of c2cl4
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m. Classification of Matter.
Ready to learn how to draw the lewis structure of C2Cl4? Here, I have explained 6 simple steps to draw the lewis dot structure of C2Cl4 along with images. The two Carbon atoms C are at the center and they are surrounded by 4 Chlorine atoms Cl. All the four Chlorine atoms have 3 lone pairs. Note: Take a pen and paper with you and try to draw this lewis structure along with me.
Lewis structure of c2cl4
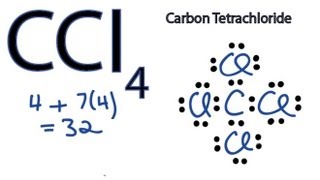
C2Cl4 lewis structure has a double bond between the two Carbon atoms C and a single bond between the Carbon atom C and Chlorine atoms Cl. There are 3 lone pairs on all the Chlorine atoms Cl. In order to find the total valence electrons in a C2Cl4 molecule , first of all you should know the valence electrons present in carbon atom as well as chlorine atom. Valence electrons are the electrons that are present in the outermost orbit of any atom. Carbon is group 14 element on the periodic table. Chlorine is group 17 element on the periodic table. For selecting the center atom, you have to remember that the atom which is less electronegative remains at the center. You can see the electronegativity values of carbon atom C and chlorine atom Cl in the above periodic table. If we compare the electronegativity values of carbon C and chlorine Cl then the carbon atom is less electronegative. So here, the carbon atoms C are the center atom and the chlorine atoms Cl are the outside atoms. Now in the C2Cl4 molecule, you have to put the electron pairs between the carbon-carbon atoms and between the carbon-chlorine atoms. This indicates that these atoms are chemically bonded with each other in a C2Cl4 molecule.
Valence electrons are the number of electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom. Noble Gas Compounds. Hydrohalogenation Reactions.
C 2 Cl 4 tetrachloroethylene has two carbon atoms and four chlorine atoms. In C 2 Cl 4 Lewis structure, there is a double bond between the two carbon atoms, and each carbon is attached with two chlorine atoms, and on each chlorine atom, there are three lone pairs. In the periodic table , carbon lies in group 14, and chlorine lies in group Hence, carbon has four valence electrons and chlorine has seven valence electrons. Learn how to find: Carbon valence electrons and Chlorine valence electrons.
In all cases, these bonds involve the sharing or transfer of valence shell electrons between atoms. In this section, we will explore the typical method for depicting valence shell electrons and chemical bonds, namely Lewis symbols and Lewis structures. We use Lewis symbols to describe valence electron configurations of atoms and monatomic ions. A Lewis symbol consists of an elemental symbol surrounded by one dot for each of its valence electrons:. Lewis symbols can also be used to illustrate the formation of cations from atoms, as shown here for sodium and calcium:. Likewise, they can be used to show the formation of anions from atoms, as shown here for chlorine and sulfur:. We also use Lewis symbols to indicate the formation of covalent bonds, which are shown in Lewis structures , drawings that describe the bonding in molecules and polyatomic ions. For example, when two chlorine atoms form a chlorine molecule, they share one pair of electrons:.
Lewis structure of c2cl4
C 2 Cl 4 tetrachloroethylene has two carbon atoms and four chlorine atoms. In C 2 Cl 4 Lewis structure, there is a double bond between the two carbon atoms, and each carbon is attached with two chlorine atoms, and on each chlorine atom, there are three lone pairs. In the periodic table , carbon lies in group 14, and chlorine lies in group Hence, carbon has four valence electrons and chlorine has seven valence electrons.
Cedar county news
Electrochemistry 2h 42m. Hence, there will not be any change in the above structure and the above lewis structure of C2Cl4 is the final stable structure only. Note: Take a pen and paper with you and try to draw this lewis structure along with me. Bohr Equation. Titrations: Strong Acid-Strong Base. Energy Diagrams. Alkane Reactions. Jay Rana. Read more about our Editorial process. Gases 3h 54m.
We begin our discussion of the relationship between structure and bonding in covalent compounds by describing the interaction between two identical neutral atoms—for example, the H 2 molecule, which contains a purely covalent bond. Each hydrogen atom in H 2 contains one electron and one proton, with the electron attracted to the proton by electrostatic forces.
Aqueous Equilibrium 4h 42m. Intro to Redox Reactions. Gases 3h 54m. Note: Take a pen and paper with you and try to draw this lewis structure along with me. Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment. The Alkyl Groups. Equilibrium Constant K. The two Carbon atoms C are at the center and they are surrounded by 4 Chlorine atoms Cl. Carboxylic Acid Reactions. Enthalpy of Formation. Now to make this carbon atom stable, you have to convert the lone pair into a double bond so that the carbon atom can have 8 electrons i. Solution Stoichiometry.

This topic is simply matchless :), it is very interesting to me.
Also that we would do without your excellent idea