Moment of inertia of lamina
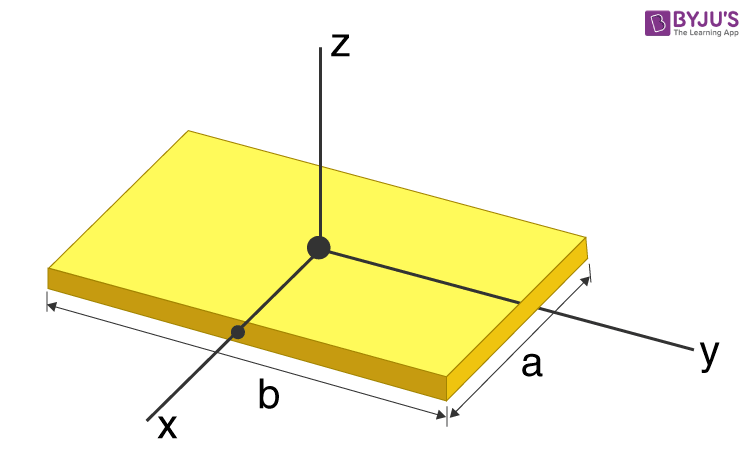
Use app Login. Statement: The moment of inertia of a plane lamina about an axis perpendicular to its moment of inertia of lamina is equal to the sum of its moment of inertia about two mutually perpendicular axes concurrent with perpendicular axis and lying in the plane of the laminar body.
Courses for Kids. Free study material. Offline Centres. Talk to our experts Last updated date: 03rd Mar
Moment of inertia of lamina
The moment of inertia of a square lamina about the perpendicular axis through its center of mass is 20 kg per meter square then its moment of inertia about an axis touching its side and in the plane of the lamina will be. Step 2: Calculating moment of inertia about an axis touching its side and in the plane of the lamina. The moment of inertia must be specified with respect to a chosen axis of rotation. Hence, the moment of inertia about an axis touching its side and in the plane of the lamina is 40 kgm 2. Byju's Answer. Open in App. Then, its moment of inertia about an axis touching its side and in the plane of the lamina will be:. The moment of inertia of a square lamina about the perpendicular axis through its centre of mass is 20 k g m 2. Then its moment of inertia about an axis touching its side and in the plane of the lamina will be:. A symmetric lamina of mass M consists of a square shape with a semicircular section over of the edge of the square as shown in figure. The side of the square is 2 a. The moment of inertia of the lamina about an axis through its centre of mass and perpendicular to the plane is 1. The moment of inertia of the lamina about the tangent A B in the plane of the lamina is A symmetric lamina of mass M consists of a square shape with a semi-circular section over each of the edges of the square, as shown. Calculate the moment of inertia of the lamina about the tangent AB in the plane of the lamina.
Practice Papers.
The moment of inertia MOI of a rectangle of width b and height d, about each of its centroidal axis, is:. MOI about a centroidal axis parallel to the width i. Parallel axis theorem: The moment of inertia of a body about an axis parallel to the body passing through its center is equal to the sum of moment of inertia of the body about the axis passing through the center and product of the mass of the body times the square of the distance between the two axes. The following table shows the Second moment of inertia of different shapes:. Moment of Inertia. Last updated on Oct 14,
We have already discussed a few applications of multiple integrals, such as finding areas, volumes, and the average value of a function over a bounded region. In this section we develop computational techniques for finding the center of mass and moments of inertia of several types of physical objects, using double integrals for a lamina flat plate and triple integrals for a three-dimensional object with variable density. The density is usually considered to be a constant number when the lamina or the object is homogeneous; that is, the object has uniform density. The center of mass is also known as the center of gravity if the object is in a uniform gravitational field. If the object has uniform density, the center of mass is the geometric center of the object, which is called the centroid. The lamina is perfectly balanced about its center of mass. Refer to Moments and Centers of Mass for the definitions and the methods of single integration to find the center of mass of a one-dimensional object for example, a thin rod.
Moment of inertia of lamina
In Figure II. Now imagine what happens if the dashed line is moved to the right. The moment of inertia decreases — and decreases - and decreases. After that is by no means obvious that the moment of inertia is going to continue to decrease. Just where is the dashed line when the moment of inertia is a minimum? That is, the moment of inertia is least for an axis passing through the centre of mass.
Chandler hallow age
JEE Main Result. Start Now. Quarter circle. The centre of gravity of a uniform lamina lies at. Chemistry Mock Test. Last updated date: 03rd Mar The moment of inertia of a square lamina about the perpendicular axis through its centre of mass is 20 k g m 2. Preparation Tips. It shows up in the connections for the dynamics of rotational movement. Step 2: Calculating moment of inertia about an axis touching its side and in the plane of the lamina. The centroid of a quarter circle is:. Talk to our experts The selection of the candidates for the Junior Engineer Civil post will be based on the Online Examination. Last updated on Oct 14, Important Exams.
In the preceding subsection, we defined the moment of inertia but did not show how to calculate it. In this subsection, we show how to calculate the moment of inertia for several standard types of objects, as well as how to use known moments of inertia to find the moment of inertia for a shifted axis or for a compound object.
A symmetric lamina of mass M consists of a square shape with a semicircular section over each of the edge of the square as shown in the figure. Other Pages. Moment of Inertia of a Rod. Standard XII Physics. Admit Card. The moment of inertia of a square lamina about the perpendicular axis through its center of mass is 20 kg per meter square then its moment of inertia about an axis touching its side and in the plane of the lamina will be. The side of the square is 2 a. Mathematics Syllabus. Eligibility Criteria. Using parallel axis and perpendicular axis theorems, find out the moment of inertia of the same ring :- 1 About any one diameter 2 About a tangent lying on its plane 3 About a tangent perpendicular to its plane. Hence, the moment of inertia about an axis touching its side and in the plane of the lamina is 40 kgm 2. Suggested Test Series.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM.