Mptp
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal mptp site, mptp. The site is secure.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. MPTP 1-methylphenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine causes selective destruction of dopaminergic neurons of the nigrostriatal pathway in humans and other primates. It is less specific and much less potent in mice and has only slight effects in rats. The discovery of toxin which causes an animal model of Parkinson's disease has stimulated new research on environmental factors that might contribute to this progressive degenerative disorder and provides a means for assessing new approaches to therapy.
Mptp
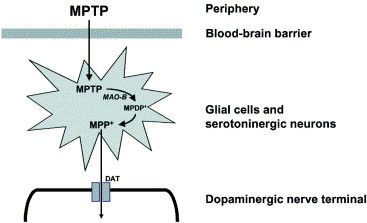
MPTP 1-methylphenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine is an organic compound. It is classified as a tetrahydropyridine. It has been used to study disease models in various animals. While MPTP itself has no psychoactive effects, the compound may be accidentally produced during the manufacture of MPPP , a synthetic opioid drug with effects similar to those of morphine and pethidine meperidine. MPTP itself is not toxic, and as a lipophilic compound can cross the blood—brain barrier. The gross depletion of dopaminergic neurons severely affects cortical control of complex movements. The direction of complex movement is based from the substantia nigra to the putamen and caudate nucleus , which then relay signals to the rest of the brain. This pathway is controlled via dopamine-using neurons, which MPTP selectively destroys, resulting, over time, in parkinsonism. MPTP causes Parkinsonism in primates , including humans. Rodents are much less susceptible. Rats are almost immune to the adverse effects of MPTP. Mice were thought to only suffer from cell death in the substantia nigra to a differing degree according to the strain of mice used but do not show Parkinsonian symptoms; [7] however, most of the recent studies indicate that MPTP can result in Parkinsonism-like syndromes in mice especially chronic syndromes. Within three days he began exhibiting symptoms of Parkinson's disease. They tested the substances on rats, but due to rodents' tolerance for this type of neurotoxin, nothing was observed. Kidston's Parkinsonism was treated with levodopa but he died 18 months later from a cocaine overdose.
This notion is demonstrated by the generation of reactive oxygen radicals and free mptp. Cold Spring Harbor Perspec Biol ; 8 : a
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. There are three MPTP-treatment schemes: acute, subacute and chronic. Considering the advantages of the period and similarity to PD, the subacute model was often chosen to assess the validity of new candidates, but the changes caused by the subacute MPTP treatment and the appropriate positive control for this model remain to be further confirmed.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Science ;— The MPTP primate and subsequent MPTP rodent models have enabled a better understanding of basal ganglia circuitry and revolutionized translational drug discoveries and surgical treatments for Parkinson's disease PD. The original 4 cases were individuals from northern California who had recently injected a new synthetic form of heroin. Within a week, all individuals experienced jerking of the limbs, muscle stiffness, and visual hallucinations followed by progressive difficulty with mobility and generalized slowness over a few weeks. The clinical features were noted to be strikingly similar to a severe presentation of PD, including reduced eye blinking, sialorrhea, facial seborrhea, akinesia and freezing of gait, flexed posture, and cogwheel rigidity. The presence of bilateral clinical features and the subacute onset suggested that the parkinsonism was likely secondary to a toxin, which is in keeping with other drugs that have been described to cause acute parkinsonism, such as manganese exposure, or dopamine antagonists. For example, in postencephalitic parkinsonism, oculogyric crisis and early psychosis were often reported.
Mptp
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf.
Catering display counter
Additionally, we can use selegiline to test anti-PD candidates that are also classified as MAO-B inhibitors, for these types of candidates may be able to be developed into anti-PD drugs. In addition, the pole test results showed that MPTP treatment did not significantly induce bradykinesia in mice Figure 1G. The curative effects of these drugs on clinical treatment and animal evaluation seem varied, but actually, they are not contradictory. MPTP provides clues to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease The selective vulnerability of nigrostriatal DA neurons to MPTP toxicity and the resemblance of the resulting clinical syndrome to Parkinson's disease refocused attention on determining the etiological factors that contribute to the development of Parkinson's disease. Loss of spinal motor neurons and alteration of alpha-synuclein immunostaining in MPTP induced Parkinsonism in mice. Parkinson's disease. Glia: initiators and progressors of pathology in Parkinson's disease. A study showed that NE depletion after lesions of the locus coeruleus LC , the major noradrenergic nucleus in the brain, could potentiate MPTP toxicity There has been some implication that the MAO -A inhibitor moclobemide p -chloro- N -[2morpholinoethyl]benzamide may also provide cellular protection by inhibition of MAO-A-derived hydrogen peroxide generation. Help Accessibility Careers. Germany Israel United States. MPTP 1-methylphenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine causes selective destruction of dopaminergic neurons of the nigrostriatal pathway in humans and other primates. Behavioral changes are not directly related to striatal monoamine levels, number of nigral neurons, or dose of parkinsonian toxin MPTP in mice.
MPTP 1-methylphenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine is an organic compound.
Neurochemical and behavioral effects of systemic and intranigral administration of N-methylphenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in the rat. Article PubMed Google Scholar. Some of these neurotoxins include 6-hydroxydopamine 6-OH- DA , iron and methamphetamine. Three days before MPTP treatment, mice were given the drug treatment or an equal volume of water intragastrically for 18 days. J Chem Neuroanat ; 44 : 76— CNS Neurosci Ther ; 22 : — Pantheon Books. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Partial protection from the dopaminergic neurotoxin N-methylphenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine by four different antioxidants in the mouse. Neuroscience ; : — To construct the model, mice were injected with MPTP dissolved in 0. The longer latency for the model animals in the rotarod test, in fact, is not deemed as a normal performance, and this kind of behavioral hyperactivity is likely to be caused by the evident increase in NE content 17 , 18 , Helvetica Chimica Acta. However, from the perspective of pathology, medopar is not suitable to be selected as a positive control. Rodents are much less susceptible.

I join. And I have faced it.
Certainly. So happens. Let's discuss this question.
I apologise, but I need absolutely another. Who else, what can prompt?