Nadh2 full form in biology
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD is a coenzyme central to metabolism. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD, nadh2 full form in biology. It is also used in other cellular processes, most notably as a substrate of enzymes in adding or removing chemical groups to or from proteinsin posttranslational modifications.
NADH is preferred except in cases where the use Access to the complete content on Oxford Reference requires a subscription or purchase. Public users are able to search the site and view the abstracts and keywords for each book and chapter without a subscription. Please subscribe or login to access full text content. If you have purchased a print title that contains an access token, please see the token for information about how to register your code. For questions on access or troubleshooting, please check our FAQs , and if you can''t find the answer there, please contact us.
Nadh2 full form in biology
The process of using oxygen and food molecules to produce energy, carbon dioxide, water, and waste products is known as cellular respiration. Respiration is the process through which humans transform food into energy by utilising water and oxygen. Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain are the three metabolic processes of respiration. The redox cofactor FADH 2 , which stands for Flavin adenine dinucleotide, is generated during the last steps of the electron transport chain process. FADH 2 , or flavin adenine dinucleotide, is a redox cofactor that is produced throughout the Krebs cycle and used in the electron transport chain, the final stage of respiration. Electrons produced in the Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle are transported to the Electron Transport Chain by a high-energy electron carrier. In the last stage of respiration, when the majority of the energy is lost and created from mitochondria, these two chemicals are utilised in the movement of electrons in the electron transport chain. The food we eat cannot be used directly as a source of energy. Metabolism, which entails a sequence of chemical events, aids in the conversion of energy from meals into energy that our bodies can utilise. This immediately available energy is stored in the nucleotide ATP adenosine triphosphate. The Krebs cycle works in a similar way to a wheel. Energy is generated and released every time it completes one full cycle. Glycolysis, acetyl CoA production, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain are all part of the cellular respiration process. Sugar is broken down in glycolysis to produce pyruvate as the result. Pyruvate is a three-carbon molecule that transforms into acetyl coenzyme-A.
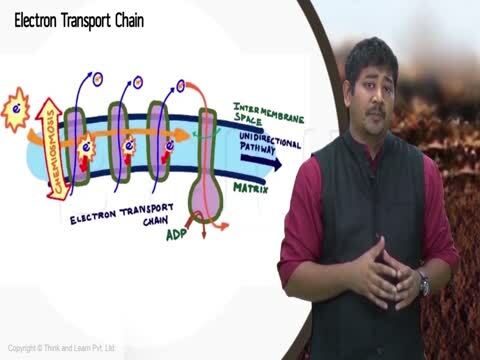
It can transfer from one partner to another, nadh2 full form in biology. The electron transport chain is a set of chemical events in which electrons from high-energy molecules like NADH and FADH 2 are transferred to low-energy molecules like oxygen energy acceptors. Access free live classes and tests on the app.
.
During cellular respiration, the cells use these coenzymes to turn fuel from food into energy. However, the brain cells may contain more than one mitochondrion, since they are involved in lot of processing and require more energy to perform multiple tasks. NADH is the reduced version of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD , which is essentially a co-enzyme form of niacin vitamin B3 , present in all living cells. The enzyme is present in all livings organisms including plants. These redox reduction-oxidation reactions play a crucial role in energy generation. These conversions also assist in cellular energy production. The food that is consumed cannot be directly used as a source of energy. Metabolism that involves a series of chemical reactions, help to convert energy from food into energy that can be easily used by our body. Also referred to as energy currency of the cell, the ATP molecule serves as the main storage of energy in cells. Cellular respiration is essentially a 4-step process that includes glycolysis, acetyl CoA formation, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain.
Nadh2 full form in biology
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Cellular respiration. Overview of oxidative phosphorylation. The electron transport chain forms a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which drives the synthesis of ATP via chemiosmosis.
1975 chevrolet nova
This ratio is an important component of what is called the redox state of a cell, a measurement that reflects both the metabolic activities and the health of cells. Retrieved 16 December Here, reduced compounds such as glucose and fatty acids are oxidized, thereby releasing energy. The sirtuins mainly seem to be involved in regulating transcription through deacetylating histones and altering nucleosome structure. Journal of Biological Chemistry. FEMS Microbiol. Sign in with your library card Please enter your library card number. Implications for investigations of hormone action". It has been studied for its potential use in the therapy of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease as well as multiple sclerosis. Glycolysis, acetyl CoA production, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain are all part of the cellular respiration process. In bacteriology, NAD, sometimes referred to factor V, is used as a supplement to culture media for some fastidious bacteria. Isoniazid is a prodrug and once it has entered the bacteria, it is activated by a peroxidase enzyme, which oxidizes the compound into a free radical form. The redox reactions catalyzed by oxidoreductases are vital in all parts of metabolism, but one particularly important area where these reactions occur is in the release of energy from nutrients. The redox cofactor FADH 2 , which stands for Flavin adenine dinucleotide, is generated during the last steps of the electron transport chain process. Read full.
The major source of NADPH in animals and other non-photosynthetic organisms is the pentose phosphate pathway , by glucosephosphate dehydrogenase G6PDH in the first step. The pentose phosphate pathway also produces pentose, another important part of NAD P H, from glucose.
Alternatively, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from nutritive compounds such as niacin ; similar compounds are produced by reactions that break down the structure of NAD, providing a salvage pathway that recycles them back into their respective active form. The energy released during the transport of these electrons is utilised to create ATP. Archived from the original on 5 December C N. Read More. FADH 2 , or flavin adenine dinucleotide, is a redox cofactor that is produced throughout the Krebs cycle and used in the electron transport chain, the final stage of respiration. Rahway NJ: Merck. Related articles. Chemical compound which is reduced and oxidized. American Journal of Physiology. Plant Cell. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. Retrieved 8 January Expert Opin. Article Talk.

Attempt not torture.