Organic anion transporter
Federal government websites often end in. The organic anion transporter is secure. They are expressed in many tissues, such as the liver and kidney, and mediate the absorption and excretion of many endogenous and exogenous substances, including various drugs.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Furthermore, OAT1 is also involved in key physiological events such as the remote inter-organ communication. Despite its significance, the knowledge about h OAT1 structure and the transport mechanism at the atomic level remains fragmented owing to the lack of resolved structures. Taking advantage of the AlphaFold 2 predicted structure of h OAT1 in inward-facing conformation, we here provide the essential structural and functional features comparing both states.
Organic anion transporter
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. In mammals, the kidney plays an essential role in maintaining blood homeostasis through the selective uptake, retention or elimination of toxins, drugs and metabolites. Organic anion transporters OATs are responsible for the recognition of metabolites and toxins in the nephron and their eventual urinary excretion. Inhibition of OATs is used therapeutically to improve drug efficacy and reduce nephrotoxicity. However, the mechanisms linking metabolite cycling, drug transport and intracellular chloride remain obscure. Organic anions comprise a large group of endogenous and exogenous compounds, including tricarboxylic acid intermediates, bile acids, prostaglandins, fatty acids, anionic drugs and environmental toxins. Many organic anions result from the breakdown of metabolites, such as nucleic and amino acids, and must be cleared from the body to avoid accumulation and toxicity 1 , 2. The transport of organic anions across the cell membrane is mediated by the organic anion transporters OATs , the organic anion transporting polypeptides OATPs and the multidrug resistance-associated family of ATP-driven transporters 3 , 4 , 5. The SLC22 family consists of organic anion and cation transporters and are widely expressed in tissues involved in metabolite exchange, such as the intestine, kidney, liver and blood—brain barrier 7.
The Oats, members of the SLC family of solute carriers, are believed to function along with organic anion transporter of the ATP-binding cassette ABC transport system, to maintain body fluid and cellular homeostasis. Crystal structure and mechanism of GlpT, the glycerolphosphate transporter from E.
Unless otherwise stated all data on this page refer to the human proteins. Gene information is provided for human Hs , mouse Mm and rat Rn. Show » « Hide. Organic anion transporters OATs are non-selective transporters prominent in the kidney, placenta and blood-brain barrier. Handb Exp Pharmacol , : Mol Aspects Med , 34 : Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol , 58 :
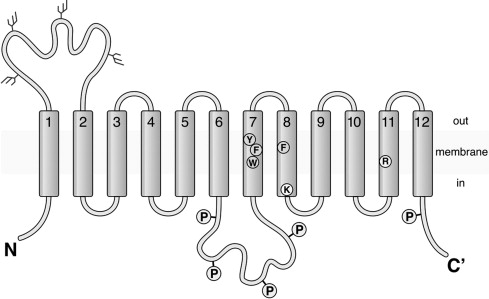
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. They are expressed in many tissues, such as the liver and kidney, and mediate the absorption and excretion of many endogenous and exogenous substances, including various drugs. Most are composed of 12 transmembrane polypeptide chains with the C-terminus and the N-terminus located in the cell cytoplasm. OATs and OATPs are abundantly expressed in the liver, where they mainly promote the uptake of various endogenous substrates such as bile acids and various exogenous drugs such as antifibrotic and anticancer drugs. However, differences in the locations of glycosylation sites, phosphorylation sites, and amino acids in the OAT and OATP structures lead to different substrates being transported to the liver, which ultimately results in their different roles in the liver. To date, few articles have addressed these aspects of OAT and OATP structures, and we study further the similarities and differences in their structures, tissue distribution, substrates, and roles in liver diseases. Core tip: As important anion transporters, organic anion transporters OATs and organic anion transporter polypeptides OATPs have similar structures and transport substrates.
Organic anion transporter
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The organic anion transporter OAT subfamily, which constitutes roughly half of the SLC22 solute carrier 22 transporter family, has received a great deal of attention because of its role in handling of common drugs antibiotics, antivirals, diuretics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , toxins mercury, aristolochic acid , and nutrients vitamins, flavonoids. Oats are expressed in many tissues, including kidney, liver, choroid plexus, olfactory mucosa, brain, retina, and placenta. Recent metabolomics and microarray data from Oat1 [ Slc22a6 , originally identified as NKT novel kidney transporter ] and Oat3 Slc22a8 knockouts, as well as systems biology studies, indicate that this pathway plays a central role in the metabolism and handling of gut microbiome metabolites as well as putative uremic toxins of kidney disease.
Zillow new hampshire
The gene encoding R. Punjani, A. Nevertheless, the significance of this gene in bone biology awaits further study. These competition events can also impair drug therapeutic efficacy or lead to adverse effects 15 , Isolation of a family of organic anion transporters from human liver and kidney. This enables the transcellular movement of small organic anionic drugs, toxins, and endogenous metabolites from the blood to the urinary space. Key residues interacting with the substrate are shown as sticks and hydrogen bonds are represented as dashed lines. Renal Physiol. A single, intramolecular disulfide promotes GLUT1 tetramerization. Nevertheless, these data come mainly from binding studies rather than actual transport in Oat6-expression systems.
Members of the Organo Anion Transporter OAT Family organic-anion-transporting polypeptides , OATP are membrane transport proteins or 'transporters' that mediate the transport of mainly organic anions across the cell membrane.
Endocrinology : —, Upon injury to the same or another organ e. Pharmacogenet Genomics 15 : —, Nature : —, Westerlund, A. Get the most important science stories of the day, free in your inbox. These organic anions are then excreted in the urine. Scope of This Review Although we detail biochemical and other data related to individual Oats, there is a heavy emphasis in this review on the systems level physiology and computational biology related to Oats and on highlighting potential areas for future Oat research. Oat6 was initially identified in the mouse based on sequence homology to Oats ; the existence of a human homolog has been described, although its functionality remains to be established Sodium is required to drive this process. Overall, the MFS tertiary structure is modified along the transport cycle by rocking N- and C- bundles to alternatingly expose substrates to both sides of the lipid bilayer membrane see Ref. As a library, NLM provides access to scientific literature. Functional role of the C terminus of human organic anion transporter hOAT1.

0 thoughts on “Organic anion transporter”