San francisco fault map
When we think of the next big earthquake, we think of the San Andreas fault, san francisco fault map. The San Andreas fault line formed about 30 million years ago as the North American plate engulfed nearly all of the Farallon plate.
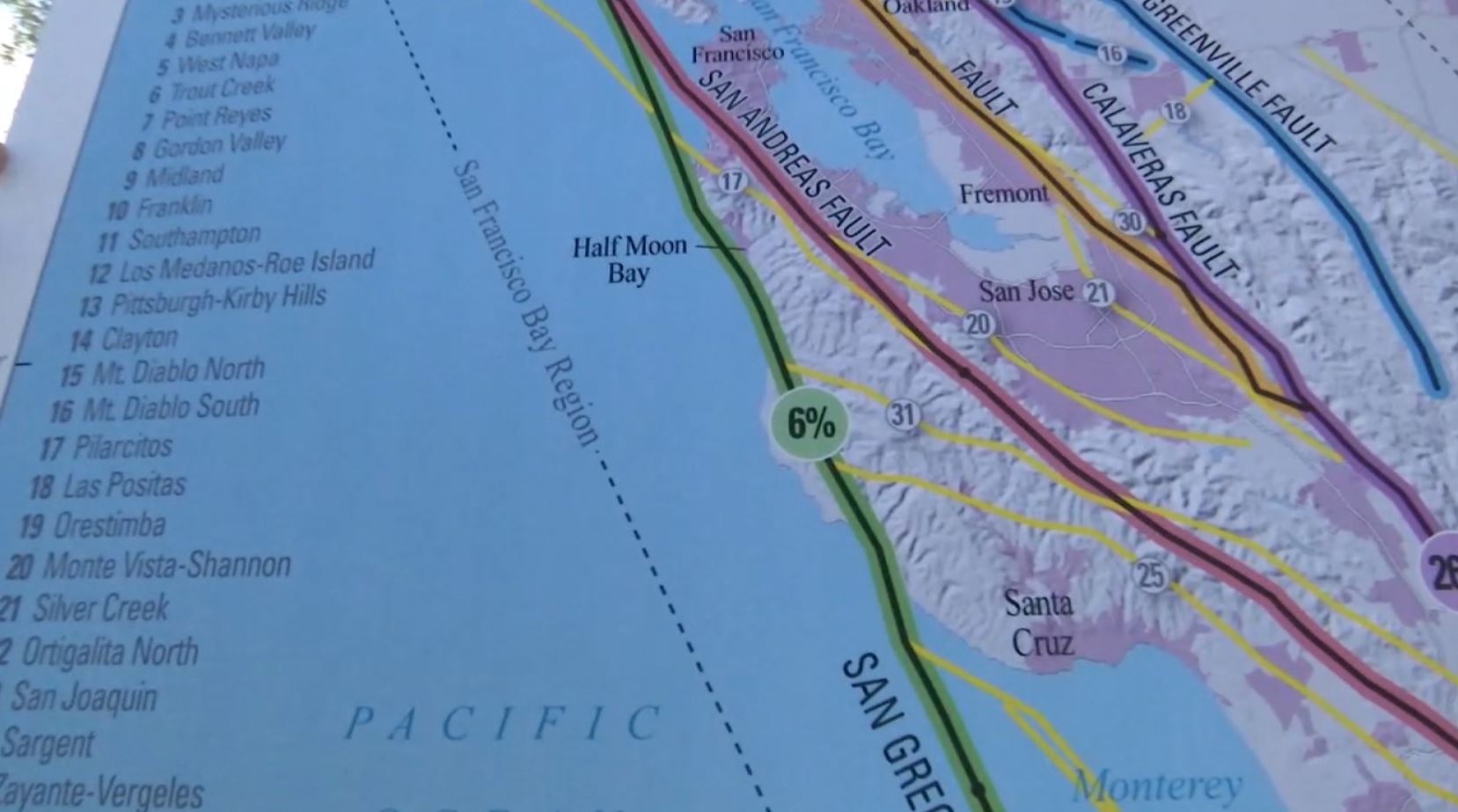
Select your county from the dropdown menu above, or click on your county on the California map to the left to learn more about California earthquake risk and faults near you. How to Strengthen Your House. See the USGS interactive fault map to learn more about faults in this area. What is the Earthquake Risk in San Diego? What is the Earthquake Risk in San Francisco.
San francisco fault map
The San Andreas Fault is a continental right-lateral strike-slip transform fault that extends roughly 1, kilometers mi through California. Traditionally, for scientific purposes, the fault has been classified into three main segments northern, central, and southern , each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk. The average slip rate along the entire fault ranges from 20 to 35 mm 0. In the north, the fault terminates offshore near Eureka, California at the Mendocino Triple Junction , where three tectonic plates meet. It has been hypothesized that a major earthquake along the Cascadia Subduction Zone could trigger a rupture along the San Andreas Fault. Here, the plate motion is being reorganized from right-lateral to divergent. In this region known as the Salton Trough , the plate boundary has been rifting and pulling apart, creating a new mid-ocean ridge that is an extension of the Gulf of California. Sediment deposited by the Colorado River is preventing the trough from being filled in with sea water from the gulf. In the wake of the San Francisco earthquake , Lawson was tasked with deciphering the origin of the earthquake. He began by surveying and mapping offsets such as fences or roads that had been sliced in half along surface ruptures. When the location of these offsets were plotted on a map, he noted that they made a near perfect line on top of the fault he previously discovered. He concluded that the fault must have been the origin of the earthquake. This line ran through San Andreas Lake , a sag pond. The lake was created from an extensional step over in the fault, which created a natural depression where water could settle. A common misconception is that Lawson named the fault after this lake.
Taking steps now will give you confidence that you and your family are prepared to stay safe!
From space, the San Andreas Fault and its attending landforms are beautifully revealed. By using the buttons at the upper left to zoom and pan, and those in the upper right to switch between photographs and the base map or both by clicking 'Hybrid' , the fault's intimate role in California becomes apparent. Double-clicking anywhere on the map centers it. Information about how the map was made can be found below the map. The location of the San Andreas Fault is shown on this map.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Real-Time Earthquakes. Earthquakes in Catalog. View past earthquakes in Google Earth. Tectonic Plate Boundaries. Explore multiple Google Earth layers related to the geology and geologic hazards of the greater Bay Area. Virtual Tour of the Hayward Earthquake. Using this self-guided, virtual tour of the quake in Google Earth you can learn about the earthquake, visualize its effects, and better plan for its expected repeat.
San francisco fault map
The Hazard Viewer is a one-of-its-kind interactive map of regional hazards, featuring the best available mapping resources and data for each hazard. The Hazard Viewer is a one-of-its-kind interactive map of regional hazards, curated from the most relevant, current maps for the nine-county Bay Area. It brings together the best set of mapping resources that exist in the region for each hazard.
Blissbury co reviews
One hypothesis — which gained interest following the Landers earthquake in — suggests the plate boundary may be shifting eastward away from the San Andreas towards Walker Lane. Select your county from the dropdown menu above, or click on your county on the California map to the left to learn more about California earthquake risk and faults near you. It was formed by a transform boundary. Box Canyon, near the Salton Sea , contains upturned strata associated with that section of the fault. Germany Israel United States. United States , Mexico. Strike-slip faults are found along boundaries of tectonic plates sliding past each other. Salton Sea. It is part of the tectonic boundary between the Pacific and North American plates. Due to the frequency of predictable activity, Parkfield has become one of the most important areas in the world for large earthquake research. S2CID What is the Earthquake Risk in San Francisco. Inland Southern California. Already a CEA policyholder?
.
June 7, It has been hypothesized that a major earthquake along the Cascadia Subduction Zone could trigger a rupture along the San Andreas Fault. Retrieved February 17, These and numerous other faults are capable of damaging earthquakes , similar to the San Francisco and Loma Prieta earthquakes. Moreover, the risk is currently concentrated on the southern section of the fault, i. Geological Survey indicates that a portion of the San Andreas fault near Tejon Pass could be overdue for a major earthquake. Inland Southern California. The mountains and the valley have been shaped by repeated earthquakes on faults in the region. Eleven years later, Lawson discovered that the San Andreas Fault stretched southward into southern California after reviewing the effects of the San Francisco earthquake. That study predicted that a magnitude 7. In , geologist Thomas Dibblee concluded that hundreds of miles of lateral movement could occur along the fault.

You are absolutely right. In it something is also idea excellent, I support.
Bravo, your idea it is magnificent