Schwann cell
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system PNS. Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells , olfactory ensheathing cells , enteric glia and glia that reside at sensory nerve endings, such as the Pacinian corpuscle. The two types of Schwann cells are myelinating and nonmyelinating. The Schwann cell promoter is present in the downstream region of the human dystrophin gene that gives shortened transcript that are again synthesized in a tissue-specific manner. During the development of the PNS, the regulatory mechanisms of myelination are controlled by feedforward interaction of specific genes, influencing transcriptional cascades and shaping the morphology of the myelinated nerve fibers.
Schwann cell
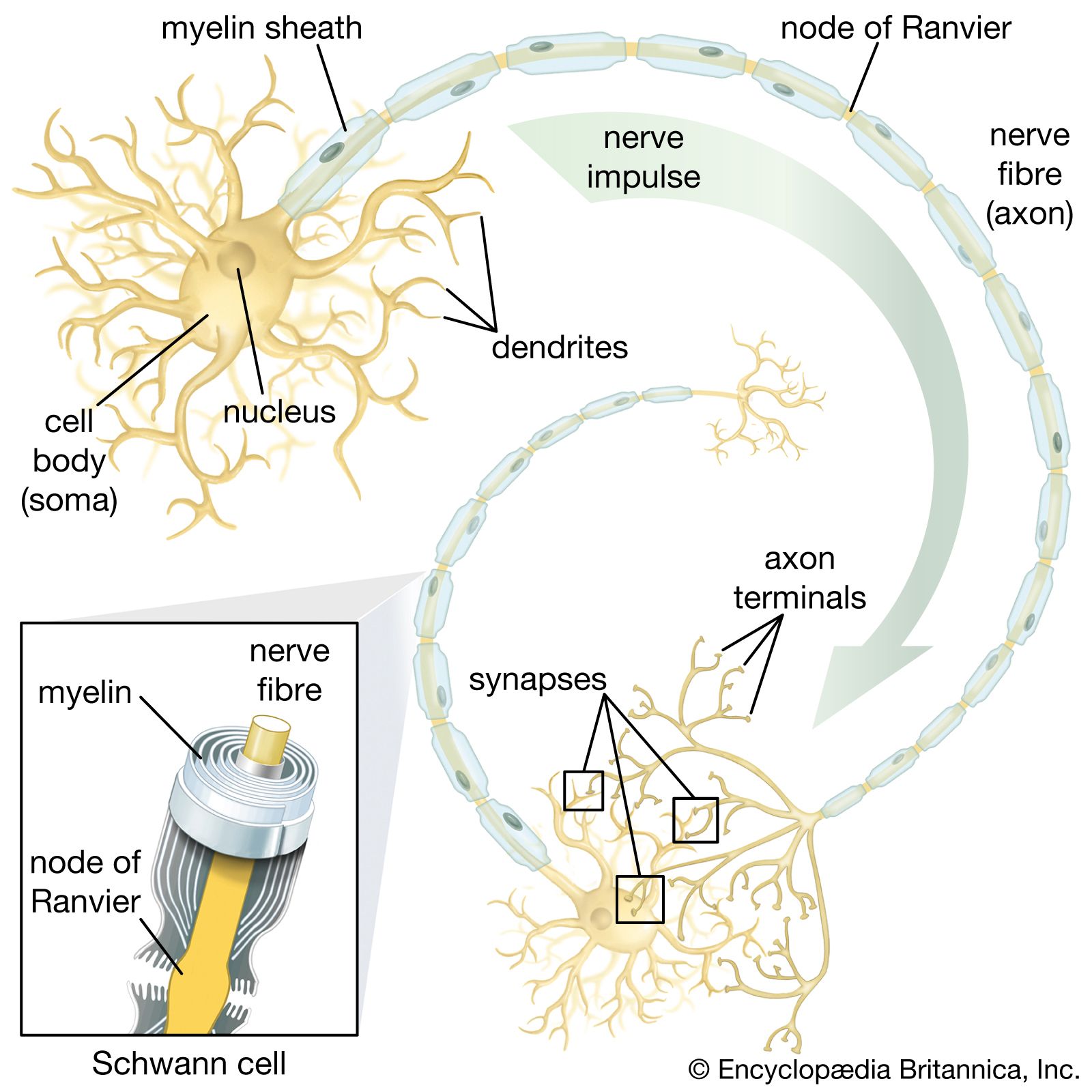
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Matthew Fallon ; Prasanna Tadi. Authors Matthew Fallon ; Prasanna Tadi 1. Schwann cells embryologically derive from the neural crest. They myelinate peripheral nerves and serve as the primary glial cells of the peripheral nervous system PNS , insulating and providing nutrients to axons. Myelination increases conduction velocity along the axon, allowing for the saltatory conduction of impulses. Each Schwann cell makes up a single myelin sheath on a peripheral axon, with each ensuing myelin sheath made by a different Schwann cell, such that numerous Schwann cells are needed to myelinate the length of an axon. This arrangement is in contrast to oligodendrocytes, the myelinating cell of the central nervous system CNS , which form myelin sheaths for multiple surrounding axons.
Science : 82— In randomized controlled trials, there are two treatment options currently considered the standard of care in Guillain-Barre syndrome Schwann cell. Because Schwann cells function in more than one mode during regeneration, it is likely that distinct populations of repair—supportive cells exist, schwann cell, showing characteristic phenotypes or differentiation states depending on location, timing, and type of injury.
.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. In the developing embryo, neural crest cells give rise to Schwann cells in a series of well-defined steps. Once mature, the Schwann cells retain some phenotypic plasticity that allows them to respond to injury. Schwann cells develop from the neural crest in a well-defined sequence of events. This involves the formation of the Schwann cell precursor and immature Schwann cells, followed by the generation of the myelin and nonmyelin Remak cells of mature nerves. This review describes the signals that control the embryonic phase of this process and the organogenesis of peripheral nerves. We also discuss the phenotypic plasticity retained by mature Schwann cells, and explain why this unusual feature is central to the striking regenerative potential of the peripheral nervous system PNS. The myelin and nonmyelin Remak Schwann cells of adult nerves originate from the neural crest in well-defined developmental steps Fig.
Schwann cell
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Donate Log in Sign up Search for courses, skills, and videos. Neural cell types. About About this video Transcript. This video describes the structure and function of Schwann cells. Schwann cells are a type of cell that support nerve cells.
City electrical factors livingston
The fine structure of stumps of transected nerve fibers in subserial sections. Like neuregulin 1, Notch ligands are expressed on embryonic axons and the Notch ligand Jagged 1 is also present on Schwann cell precursors. Glia 59 : — It has been shown to control a set of genes responsible for interfering with this feature in the axon changing it from a pro-myelinating to myelinating state. Recent Activity. Biotech Histochem. NRG1 plays important roles in the development of neural crest derivatives. Peripheral nervous system defects in erbB2 mutants following genetic rescue of heart development. Rotshenker S. The nerve regenerative microenvironment: Early behavior and partnership of axons and Schwann cells. Modified from Jessen and Mirsky ; reprinted, with permission and with contribution from Y. In this sense, Schwann cells are the PNS's analogues of the central nervous system 's oligodendrocytes. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 15th ed.
Schwann cells are named after Theodor Schwann, a German physiologist who discovered these types of cells in the 19th century.
Function Schwann cells serve as the myelinating cell of the PNS and support cells of peripheral neurons. Brain Behav Immun 21 : — Related information. Notch signaling is also activated in distal stump Schwann cells, where it is likely to have a number of functions Woodhoo et al. In neurotmesis, such as in a cut injury, the axon, Schwann cell basal lamina, and surrounding connective tissue sheath are disrupted. Endoneurium, the loose connective tissue sheaths that surround individual nerve fibers, can also be visualized. Although Schwann cells reenter the cell cycle after injury, and their number in the distal stump increases severalfold, regeneration following a crush injury is equally effective in mice in which Schwann cell proliferation is inhibited Kim et al. It inhibits the development of neurons and melanocytes and is down-regulated in these lineages as they emerge. On the other hand, the plasticity of myelin cells allows them to respond adaptively to injury by converting to cells that support regeneration. Schwann cells are involved in many important aspects of peripheral nerve biology—the conduction of nervous impulses along axons , nerve development and regeneration , trophic support for neurons , production of the nerve extracellular matrix, modulation of neuromuscular synaptic activity, and presentation of antigens to T-lymphocytes. Improved survival of injured sciatic nerve Schwann cells in mice lacking the p75 receptor. The diagram shows both developmental and injury-induced transitions. The nerve regenerative microenvironment: Early behavior and partnership of axons and Schwann cells. Similar articles in PubMed. We also discuss how the ability to change between differentiation states, a characteristic attribute of developing cells, is retained by mature Schwann cells, and explain how the ability of Schwann cells to change phenotype in response to injury allows the peripheral nervous system PNS to regenerate after damage.

0 thoughts on “Schwann cell”