Sf4 bond angle
What is the shape of SF 4 including bond angles? The formula used to calculate the hybridization of a molecule is as follows:.
Within the context of VSEPR theory , you can count electrons to determine the electron geometry "parent" geometry. Sulfur : 6 valence electrons Fluorine : 7x4 valence electrons Total : 34 valence electrons. You can put sulfur in the middle because fluorine tends to make single bonds. Therefore, you can put 6x4 on each fluorine, 2x4 to account for four single bonds, and 2 for the last 2 valence electrons available. As a result, you have 5 electron groups, so the electron geometry would be trigonal bipyramidal.
Sf4 bond angle
Hybridization of SF4 is sp 3 d. In this hybridization, a total of five hybrid orbitals are formed. Sulfur tetrafluoride, or SF4 is a chemical compound made up of four fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom. It is a colorless compound that releases poisonous HF gas when reacts with water or moisture. In this article, we will learn about the hybridization of SF4 and its geometry with a brief introduction to the SF4 molecule and the hybridization process. Sulfur Tetrafluoride is a gaseous compound that consists of one sulfur atom and is bonded to four fluorine atoms. It is a colorless compound and when reacts with water or moisture releases Hydrogen Fluoride gas. The molecular compound SF4 is well-known for its unique characteristics. In this hybridization, one s orbital, three p orbitals and one d orbital of third shell participate in creating five hybrid orbitals. In hybridization of SF4, sulphur is the central atom which is bonded to four flourine atoms. Sulfur has 6 valence electrons.
The number of hybrid orbitals formed equals the number of atomic orbitals involved during hybridization, sf4 bond angle. We use cookies to ensure you have the best browsing experience on our website. The SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles of molecules having the chemical formula AX4E are trigonal bipyramidal.
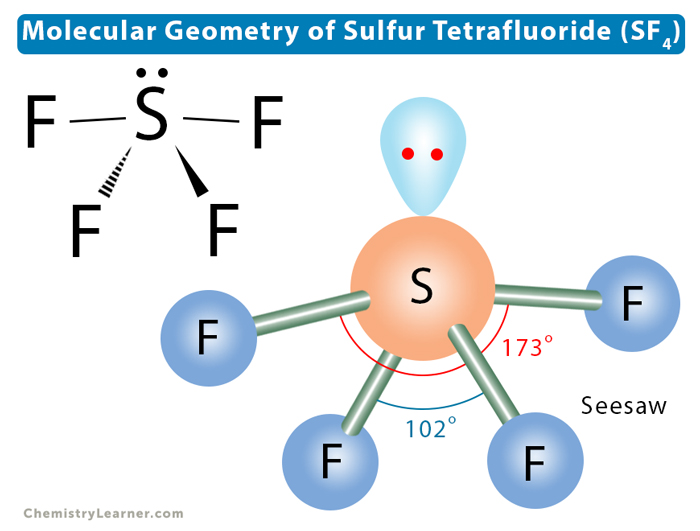
Let us learn about the SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. The structure of SF4 molecular geometry may be predicted using VSEPR theory principles: A nonbonding lone pair of electrons occupy one of the three equatorial locations. As a result, there are two types of F ligands in the molecule: axial and equatorial. The SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles of molecules having the chemical formula AX4E are trigonal bipyramidal. The equatorial orientations of two fluorine atoms establishing bonds with the sulphur atom are shown, while the axial locations of the other two are shown. Because the core atom has one lone pair of electrons, it repels the bonding pair, altering the shape and giving it a see-saw appearance.
The Lewis electron-pair approach can be used to predict the number and types of bonds between the atoms in a substance, and it indicates which atoms have lone pairs of electrons. This approach gives no information about the actual arrangement of atoms in space, however. Keep in mind, however, that the VSEPR model, like any model, is a limited representation of reality; the model provides no information about bond lengths or the presence of multiple bonds. The VSEPR model can predict the structure of nearly any molecule or polyatomic ion in which the central atom is a nonmetal, as well as the structures of many molecules and polyatomic ions with a central metal atom. Instead, it is a counting procedure that accurately predicts the three-dimensional structures of a large number of compounds, which cannot be predicted using the Lewis electron-pair approach. We can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing on only the number of electron pairs around the central atom , ignoring all other valence electrons present. According to this model, valence electrons in the Lewis structure form groups , which may consist of a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond, a lone pair of electrons, or even a single unpaired electron, which in the VSEPR model is counted as a lone pair. Because electrons repel each other electrostatically, the most stable arrangement of electron groups i.
Sf4 bond angle
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space Figure 7. A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common atom, usually measured in degrees. A bond distance or bond length is the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms along the straight line joining the nuclei.
Science tube clipart
Ans : Draw the SF 4 Lewis structure that is appropriate. See all questions in Molecular Geometry. Complete Tutorials. Frequently Asked Questions. As a result, there are two types of F ligands in the molecule: axial and equatorial. Hybridization of SF4 is sp 3 d. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. In comparison, the other three fluorines are equatorial. Question b Allotment of Examination Centre.
Hybridization of SF4 is sp 3 d. In this hybridization, a total of five hybrid orbitals are formed.
Standard XII Chemistry. Question bf. Login To View Results. Note that the bending angle is degrees, not Last Updated : 04 Mar, The molecular compound SF4 is well-known for its unique characteristics. Conclusion Around the core sulphur atom, SF4 contains five electron density zones 4 bonds and one lone pair. Which of the following molecules has a dipole moment? View Result. Get subscription. Law of Thermodynamics. Maximize your earnings for your published articles in Dev Scripter ! What is SF4's molecular geometry?

In my opinion you are mistaken. Write to me in PM.