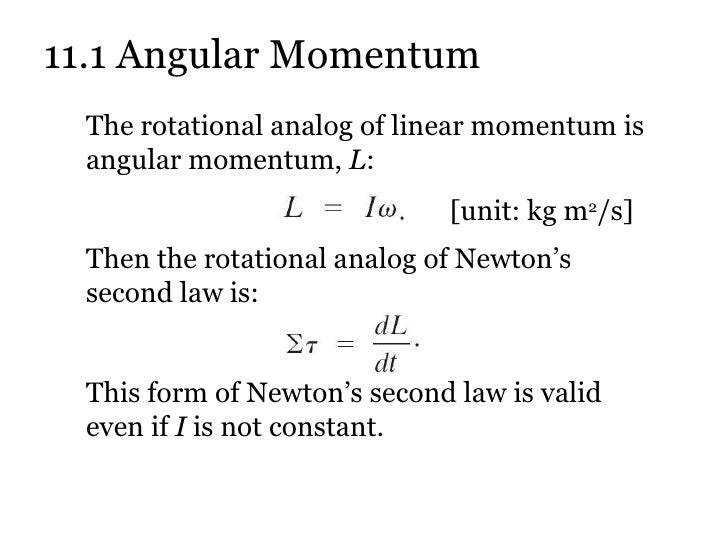
Si unit of angular momentum is
Angular Momentum is a kinematic characteristic of a si unit of angular momentum is with one or more point masses. Angular momentum is sometimes called Rotational Momentum or Moment of Momentum, which is the rotational equivalent of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity as it is conserved for a closed system and follows the Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum. Angular Momentum is a vector quantity.
Angular momentum : The vector product of the distance r and linear momentum mv. Additional Information. Last updated on Dec 30, HTET Notificatoon to be out soon! Candidates applied online from 30th October to 11th November This is a great opportunity for teaching job aspirants. Get Started.
Si unit of angular momentum is
Momentum is the product of mass and the velocity of the object. Any object moving with mass possesses momentum. The only difference in angular momentum is that it deals with rotating or spinning objects. So is it the rotational equivalent of linear momentum? If you try to get on a bicycle and balance without a kickstand, you will probably fall off. But once you start pedalling, these wheels pick up angular momentum. They are going to resist change, thereby making balancing gets easier. It is the property of a rotating body given by the product of the moment of inertia and the angular velocity of the rotating object. It is a vector quantity , which implies that the direction is also considered here along with magnitude. Point object: The object accelerating around a fixed point. For example, Earth revolving around the sun. Here the angular momentum is given by:. Extended object: The object, which is rotating about a fixed point. For example, Earth rotates about its axis. Angular momentum quantum number is synonymous with Azimuthal quantum number or secondary quantum number.
Puducherry Fireman. Magnetic Moment Of Electron. Bihar Primary Teacher.
In physics , angular momentum sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity — the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycles and motorcycles , flying discs , [1] rifled bullets , and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes [2] form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. Unlike linear momentum, angular momentum depends on where this origin is chosen, since the particle's position is measured from it.
Dive into the world of rotational motion as we explore these important concepts. By understanding these principles, we can predict the behavior of rotating objects in real-world examples, such as spinning figure skaters or orbiting planets. Join us as we break down the equations, provide examples, and discuss the conservation of angular momentum. The first quantity is the angular velocity. Angular velocity describes how quickly an object is rotating and is measured in radians per second. The moment of inertia varies depending on the shape of the object.
Si unit of angular momentum is
Angular momentum AM is a physical quantity possessed by a body moving around a point. We can also define AM as the product of the linear momentum of the object and the perpendicular distance between the object and the axis of rotation. In the above image, we have an object of mass m revolving around the circle of radius r with speed v about an axis passing through center O. As we know the AM is the product of linear momentum and perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation so,. Also, m r 2 is the formula of the moment of inertia I , so we can write the equation of angular momentum as.
Wettmelons
Whereas, Moment of Inertia MOI is the measure of how the mass of object is distributed about the axis of rotation. CISF Tradesman. Conservation of angular momentum applies to J , but not to L or S ; for example, the spin—orbit interaction allows angular momentum to transfer back and forth between L and S , with the total remaining constant. Unlike linear momentum it also involves elements of position and shape. BEL Trainee Engineer. By the rules of velocity composition , these two velocities add, and point C is found by construction of parallelogram BcCV. This can be compared to the work done as calculated using Newton's laws. DDA JE. Haryana Civil Services. JSSC Stenographer. Rajasthan Housing Board JE.
Why does Earth keep on spinning? What started it spinning to begin with?
Article Talk. Bernoulli wrote in a letter of a "moment of rotational motion", possibly the first conception of angular momentum as we now understand it. BIS Stenographer. Ginn and Co. Feynman's Lectures on Physics volume 2. KSP Constable. Bihar TET. Karnataka Bank PO. Torque can be defined as the rate of change of angular momentum, analogous to force. Just as for angular velocity , there are two special types of angular momentum of an object: the spin angular momentum is the angular momentum about the object's centre of mass , while the orbital angular momentum is the angular momentum about a chosen center of rotation. Goa Police Constable. At point C , the object receives another impulse toward S , again deflecting its path during the third interval from d to D. MP SET. APCOB staff assistant. Airforce Group X.

It is nonsense!
Just that is necessary, I will participate. Together we can come to a right answer. I am assured.