Sliding filament theory coloring answers
Log In Join. View Wish List View Cart.
Each skeletal muscle is an organ that consists of various integrated tissues. These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue called mysia that enclose it, provide structure to the muscle, and compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle Figure Each muscle is wrapped in a sheath of dense, irregular connective tissue called the epimysium , which allows a muscle to contract and move powerfully while maintaining its structural integrity. The epimysium also separates muscle from other tissues and organs in the area, allowing the muscle to move independently. Inside each skeletal muscle, muscle fibers are organized into bundles, called fascicles , surrounded by a middle layer of connective tissue called the perimysium.
Sliding filament theory coloring answers
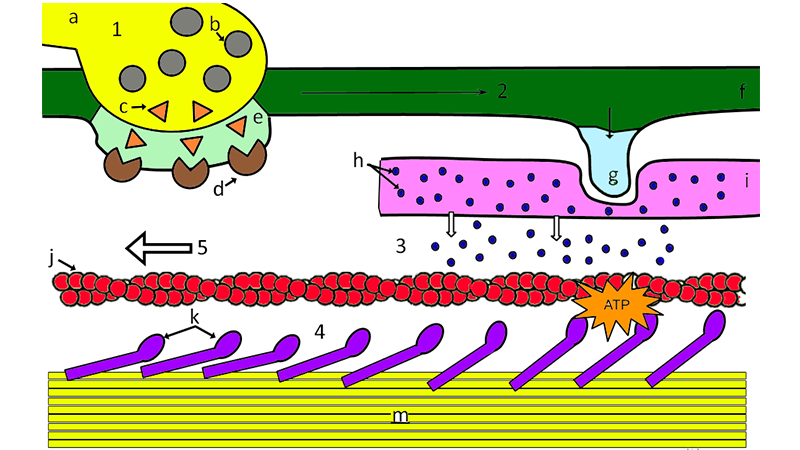
Sarcomeres are composed of thick and thin filaments. The thin filament is composed of polymerized actin, while the thick filament is composed of myosin. Titin is a protein that spans the full range of the sarcomere, and is involved in stability and elasticity in the muscle. Collagen is not a primary component of sarcomeres. The protein complex formed is classically named actomyosin and helps facilitate the "stroke" part of muscle contraction. The sliding filament theory describes the mechanism that allows muscles to contract. According to this theory, myosin a motor protein binds to actin. The myosin then alters its configuration, resulting in a "stroke" that pulls on the actin filament and causes it to slide across the myosin filament. The overall process shortens the sarcomere structure, but does not change the actual length of either filament. The correct answer is ATP and calcium ions. Calcium is required to expose actin binding sites for myosin in conjunction with troponin. Muscles require a supply of ATP in order to contract. What function is enabled by the release of energy from ATP? In the sliding filament theory, myosin heads attach to an actin filament, bend to pull the actin filaments closer together, then release, reattach, and pull again. Energy from ATP is required for the myosin head to release from the actin filament—otherwise the myosin heads would remain in the same place, and the muscle would not contract.
Within the motor neuron are vesicles that contain the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. Independent work packet. Titin, which is the largest known protein, helps align the thick filament and adds an elastic element to the sarcomere.
For complaints, use another form. Study lib. Upload document Create flashcards. Flashcards Collections. Documents Last activity. Add to
The sliding filament theory explains muscle contraction based on how muscle fibers actin and myosin slide against each other to generate tension in the overall muscle. Step 1 : A muscle contraction starts in the brain, where a signal is sent to the motor neuron a. The combination of the motor neuron and the skeletal muscle fibers make up a motor unit. Color the motor neuron a yellow. Vesicles that contain the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. Color vesicles b gray. Color the triangles that represent the acetylcholine c orange.
Sliding filament theory coloring answers
This worksheet lists the steps involved in the sliding filament model of muscle contraction and includes a coloring page of the model. Students color and answer questions. This download has two versions of the student worksheet 2 pages vs 1 pages and the answer key to the questions. Log In Join. View Wish List View Cart. Middle school.
Followplus.me
The sliding filament theory is a fundamental concept in muscle physiology that explains how muscles contract and generate force. Native Americans. Anatomy Muscular System quiz, sliding filament theory , muscle contraction type, muscle fibers. Color the motor neuron yellow. Wish List. Basic operations. Includes questions to answer. School counseling. Muscle fibers are composed of myofibrils which are composed of sarcomeres linked in series. Titin is a protein that spans the full range of the sarcomere, and is involved in stability and elasticity in the muscle. Color the ATP bright orange. The sarcoplasmic reticulum i is only partially pictured, color this structure pink. Instrumental music.
It starts with a signal from the nervous system.
What are the two filaments found in muscles? Science by grade. Hispanic Heritage Month. Black History Month. Place value. Black History Month. Rated 5. When is ATP required for muscles according to the sliding filament theory? The correct answer is ATP and calcium ions. Comprehensive K personalized learning. Sarcomere and Sliding filament Theory Coloring Worksheet. Also included in: Muscular System Unit Bundle. High school science. Teacher manuals. This notification is accurate.

These are all fairy tales!
Between us speaking, in my opinion, it is obvious. You did not try to look in google.com?