Splunk search and
The Search and Reporting app lets you search your data, create data models and pivots, save your searches and pivots as reports, configure alerts, and create dashboards.
The following are examples for using the SPL2 search command. To learn more about the search command, see How the SPL2 search command works. This example shows field-value pair matching for specific values of source IP src and destination IP dst. This example shows field-value pair matching with boolean and comparison operators. This example searches for events with code values of either 10, 29, or 43 and any host that is not "localhost", and an xqp value that is greater than 5. An alternative is to use the IN operator, because you are specifying multiple field-value pairs on the same field.
Splunk search and
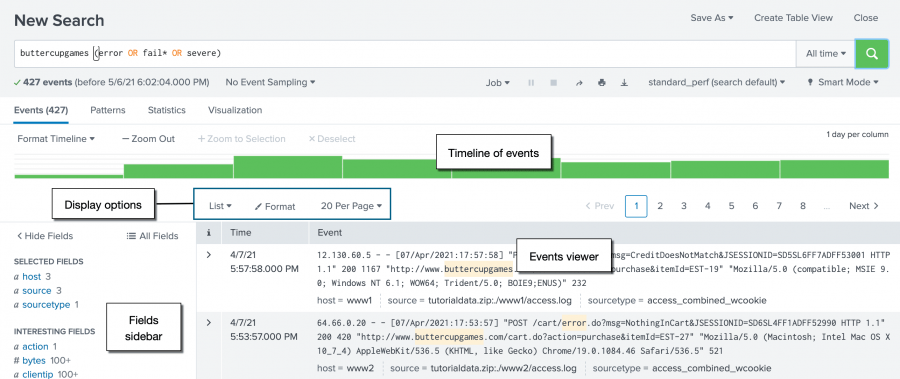
The data for this tutorial is for the Buttercup Games online store. The store sells games and other related items, such as t-shirts. In this tutorial, you will primarily search the Apache web access logs, and correlate the access logs with the vendor sales logs. Prerequisite Complete the steps, Upload the tutorial data , in Part 2. The Search Assistant is a feature in the Search app that appears as you type your search criteria. The Search Assistant is like autocomplete, but so much more. The Search Assistant also returns matching searches, which are based on the searches that you have recently run. The Matching Searches list is useful when you want to run the same search from yesterday, or a week ago. Your search history is retained when you log out. The Search Assistant is more useful after you start learning the search language. When you type search commands, the Search Assistant displays command information. To retrieve events that mention errors or failures, you type the keywords in your search criteria. For example, typing buttercupgames error is the same as typing buttercupgames AND error. Tip: Instead of typing the search string, you can copy and paste the search from this tutorial directly into the Search bar.
You can find Cassandra on LinkedIn and Linktree.
This topic examines some causes of slow searches and includes guidelines to help you write searches that run more efficiently. Many factors can affect the speed of your searches, including:. To optimize the speed at which your search runs, minimize the amount of processing time required by each component of the search. The recommendations for optimizing searches depend on the type of search that you run and the characteristics of the data you are searching. Searches fall into two types, that are based on the goal you want to accomplish. Either a search is designed to retrieve events or a search is designed to generate a report that summarizes or organizes the data.
Use the search command to retrieve events from indexes or filter the results of a previous search command in the pipeline. You can retrieve events from your indexes, using keywords, quoted phrases, wildcards, and field-value expressions. The search command is implied at the beginning of any search. You do not need to specify the search command at the beginning of your search criteria. You can also use the search command later in the search pipeline to filter the results from the previous command in the pipeline.
Splunk search and
If you are new to Splunk Search, the best way to get acquainted is to start with the Search Tutorial. The Search Tutorial introduces you to the Search and Reporting app and guides you through adding data, searching your data, and building simple reports and dashboards. After you complete the Search Tutorial, you should learn about the types of data you can explore, how Splunk software indexes data, and about Splunk knowledge objects. And of course you need to learn how to use the Search app effectively, which is the focus of this manual. This manual contains detailed information about how to search your data.
Tampa bay depth chart
N-th percentile value of the field Y. See also About search optimization Quick tips for optimization Built-in optimizations. Event The raw event data. Ask a question or make a suggestion. About event grouping and correlation Use time to identify relationships between events About transactions Identify and group events into transactions. Compatibility library for SPL commands. Raw event searches retrieve events from a Splunk index without any additional processing of the events that are retrieved. For example, store Web access data in one index and firewall data in another. Please select Yes No. Using the IN operator 5. Next step Learn to use fields to search your data. Use fields effectively Searches with fields are faster when they use fields that have already been extracted indexed fields instead of fields extracted at search time. Evaluate and Manipulate Fields.
Examples of how you can use these operators are:. Use the earliest and latest modifiers to specify custom and relative time ranges. Was this documentation topic helpful?
Documentation Find answers about how to use Splunk. Visualization reference. Using boolean and comparison operators 3. The order of the values is alphabetical. See the Dashboards and Visualizations manual for more information on the visualization and dashboard workflow and using the Splunk Web Framework. Custom Sort Orders. Splunk is a Big Data mining tool. This example searches for events with code values of either 10, 29, or 43 and any host that is not "localhost", and an xqp value that is greater than 5. Advanced Threat Detection. The fields are divided into two categories. For non-numeric values of X, compute the min using alphabetical ordering. Getting started with alerts. Ask a question or make a suggestion. In this example the sort and any remaining commands are processed on the search head. On the command line, use this instead: splunk list index.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.