The si unit of current is
Official websites use.
Electric Current: A stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, travelling through an electrical conductor or a vacuum is known as an electric current. The net rate of electric charge flowing through a surface or into a control volume is how it is calculated. It is determined by assuming that the elementary charge, e, has a fixed numerical value of 1. Electric current is a measure of the flow of electric charge through a conductor. One ampere is defined as the flow of one coulomb of electric charge per second. In other words, if a current of 1 ampere flows through a wire, it means that 1 coulomb of electric charge passes through that wire every second.
The si unit of current is
An electric current can be defined as the flow present in an electric circuit. It consists of particles that are charged. These particles include electrons, protons and other charged atomic particles or smaller particles. This flow of the charged particles can only take place through materials that are capable of allowing that charge to flow through them. These materials are known as conductors. The S. The other S. On the other hand, the C. The unit of electric current is Ampere which is also denoted as coulomb per second. Ampere is defined as the flow of charged particles through the surface of a material at the rate of one coulomb at one second.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
One ampere is equal to 1 coulomb C moving past a point per second. As of the redefinition of the SI base units , the ampere is defined by fixing the elementary charge e to be exactly 1. The earlier CGS system has two units of current, one structured similarly to the SI's and the other using Coulomb's law as a fundamental relationship, with the CGS unit of charge defined by measuring the force between two charged metal plates. The CGS unit of current is then defined as one unit of charge per second. The ampere was originally defined as one tenth of the unit of electric current in the centimetre—gram—second system of units. That unit, now known as the abampere , was defined as the amount of current that generates a force of two dynes per centimetre of length between two wires one centimetre apart. The "international ampere" was an early realization of the ampere, defined as the current that would deposit 0.
Electric current can be defined as the measure of flow of sub-atomic charge carrying particles in this case electrons at any point of a conductor wire per unit time. In electricity, the term current is used to express flow, similar to other currents in nature. As an example, consider water current. Refer below image of water flowing inside a pipe. Concept of electrical current is similar to water current that is flowing through a pipe. Examples of sub-atomic particles having charge are electrons negative charge and protons positive charge. Neutrons are neutral, without charge. Ions atoms that have lost or gained electrons are also charged, with positive or negative charge. Particles with same charge repel example: proton and proton each other, and the particles with opposite charge example: proton and electron attract each other. As described above, electrons are negatively charged sub-atomic particles.
The si unit of current is
We have heard a lot about electric currents in our classrooms and at home. While the topic is highly relatable, in more scientific terms an electric current is basically a flow of current or charge in electric circuits. Sometimes both ions and electrons carry the charge simultaneously. Electric current or charge is measured by an ammeter, and there are different measurement methods as well as units of current. Here we will look at some of them in detail.
Wings halo tattoo
Moving iron ammeter. What is the unit of current? The image shown below depicts the structure of an ammeter which is used to calculate the value of electric current. There are also some SI units that are frequently used in the context of electrical engineering and electrical appliances, but are defined independently of the ampere, notably the hertz , joule, watt, candela, lumen , and lux. As the current through the coil increases, the plunger is drawn further into the coil and the pointer deflects to the right. There are different measurement methods and units of current. Credit: J. According to official definitions, a volt is the difference in potential between two locations on a wire that is conveying a current of one ampere and dissipating one watt of power. The ampere, or amp, is the unit used to measure current A. We have come across a lot about electric currents in our classrooms as well as at home. Unit of electric current ampere " , SI brochure 8th ed. Unit of Current The unit of electric current is Ampere which is also denoted as coulomb per second. Our Other Websites.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
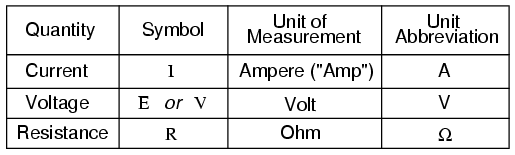
Mechanical friction and electrical resistance have some conceptual similarities. Our Other Websites. There are different measurement methods and units of current. Retrieved 21 November They result in Joule heating in conventional conductors, which lights up incandescent light bulbs. Main article: Orders of magnitude current. It is determined by assuming that the elementary charge, e, has a fixed numerical value of 1. But this ideal situation is not practically achievable. Volt is the name of the voltage-derived unit in the International System of Units. FAQs What is the unit of current and voltage? V is the voltage present in the electric current.

Excuse, that I interrupt you, but, in my opinion, this theme is not so actual.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I suggest it to discuss.