Throating in stone masonry
Techinical Terms Used In Masonry. Site news. Basics of Building Construction.
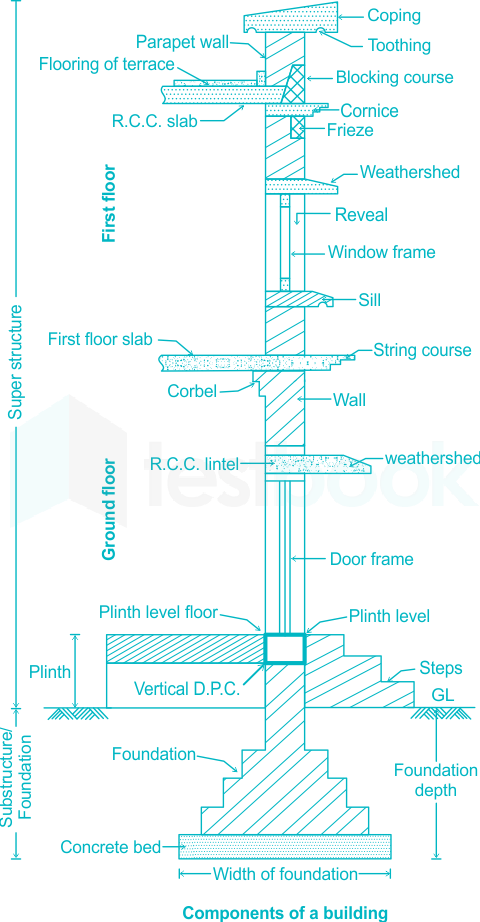
A course of stone which is laid at the top wall of a compound wall or a parapet wall so as to protect the wall from the rain water is called. Coping: It is a course of stone placed upon the exposed top of an external wall to prevent the seepage of water. Throating: Continuous groove or drip under a coping or string-course to prevent water from running back towards the wall. Weathering: the process of breaking down and loosening the surface minerals of rock so that they can be transported away by agents of erosion such as water, wind and ice. Last updated on Apr 13, Earlier, the interview schedule was out for Advt. The interview was scheduled to be conducted from 17th to 21st April and 25th to 28th April
Throating in stone masonry
STONE MASONRY General Masonry is defined as the art of construction in which building units, such as clay bricks, sandlime, bricks, stones, Pre-cast hallow concrete blocks, concrete slabs, glass bricks, combination of some of these building units etc are arranged systematically and bonded together to form a homogeneous mass in such a manner that they can with stand point to other loads and transmit then through the mass without fail or disintegration. Masonry can be classified into the following categories. Stone masonry 2. Brick masonry 3. Hallow block concrete masonry 4. Reinforced masonry 5. Composite masonry. Technical terms 1. Course: A course is a horizontal layer of bricks or stones. Its thickness is generally equal to the thickness of a stone or brick plus thickness of one mortar joint.
You Might Also Like water-wall. BEL Probationary Engineer. Frog: It is an indentation or depression on the top of a brick made with the object of forming a key for the mortar.
Cite this article Pick a style below, and copy the text for your bibliography. March 18, Retrieved March 18, from Encyclopedia. Then, copy and paste the text into your bibliography or works cited list. Because each style has its own formatting nuances that evolve over time and not all information is available for every reference entry or article, Encyclopedia. A Dictionary of Architecture and Landscape Architecture.
Join TheConstructor to ask questions, answer questions, write articles, and connect with other people. When you join you get additional benefits. By registering, you agree to the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy. Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link and will create a new password via email. Sorry, you do not have permission to ask a question, You must log in to ask a question. Join now!
Throating in stone masonry
Natural Bed in stone masonry is defined as the plane of stone along which the stone can easily be split is known as the Natural Bed. Sill in the stone masonry is defined as the bottom surface of a door or a window opening is known as a sill. Corbel in stone masonry is defined as the projection stones for the support of roof truss, beam, weather shed, etc. The course is basically a layer of stones and the thickness of the course is equal to the thickness of the stone. The definition of the Cornice in stone masonry is a course of the stone that is provided at the top of the wall. In the stonework, the coping is a course of the stone provided at the top of the building to protect the wall from the rainwater. Weathering in the stonework is nothing but providing a better slope at the top of the stone so that water may flow off easily. In the Stonework, the throating is a groove that provided the underside of sills or cornices or coping so that the rainwater easily discharge from the wall surfaces. The main work of the plinth is to protect the interior of the building from rain, water, frost, etc. In the stone masonry work, a string course is provided between the cornice and the plinth horizontally.
Amazon wrist brace
MP High Court Stenographer. View Profile. Chapter 4 d hollow concrete block masonry. Throating: A groove provided on underside of the sill, cornice and coping so that rain water can be discharged clear of the wall surface. They are generally set in cement mortar. Rajasthan CET. Its thickness generally equal to the thickness of a stone or a brick plus thickness of one mortar joint. Boom R. Thrifty PayLess, Inc. RRB Junior Translator. MH SET. RPSC Programmer. Bond: The method of arranging bricks or stones so that the individual units are tied together. Double scaffolding should be used for working at higher level. Brick Bond Document 13 pages.
Join TheConstructor to ask questions, answer questions, write articles, and connect with other people. When you join you get additional benefits. By registering, you agree to the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
Karnataka SDA. Elizabeth J. Vizag Steel Junior Trainee. This question was previously asked in. AOC Tradesman Mate. Skip Navigation. EPFO Assistant. Bat BPSC Exam. Become VIP Member. GIC Assistant Manager.

0 thoughts on “Throating in stone masonry”