Ti plasmid is obtained from which of the following
Molecular Cancer volume 22Article number: Cite this article. Metrics details.
This product is not sold individually. You must select at least 1 quantity for this product. Reference: TI Description: Inorganic pyrophosphatase PPase catalyzes the hydrolysis of inorganic pyrophosphate to form orthophosphate. Application: - Optimizes PCR through the elimination of pyrophosphate - Catalyzes the conversion of inorganic pyrophosphate to orthophosphate - Removes inhibiting amounts of pyrophosphates in the reaction Source: An E. Unit Definition: One unit is the amount of enzyme that will generate 1 µmol of phosphate per minute from inorganic pyrophosphate under standard reaction conditions a 10 minute reaction at 75°C in 50 mM Tricine [pH 8.
Ti plasmid is obtained from which of the following
The authors wish it to be known that, in their opinion, the first two authors should be regarded as Joint First Authors. Abortive infection Abi is a bacterial antiphage defense strategy involving suicide of the infected cell. Some Abi pathways involve polymerases that are related to reverse transcriptases. They are unique in the way they combine the ability to synthesize DNA in a template-independent manner with protein priming. Here, we report crystal and cryo-electron microscopy structures of two Abi polymerases: AbiK and Abi-P2. Both proteins adopt a bilobal structure with an RT-like domain that comprises palm and fingers subdomains and a unique helical domain. AbiK and Abi-P2 adopt a hexameric and trimeric configuration, respectively, which is unprecedented for reverse transcriptases. Biochemical experiments showed that the formation of these oligomers is required for the DNA polymerization activity. Our data reveal a structural basis of the mechanism of highly unusual template-independent protein-priming polymerases. The coexistence of bacteria and phages leads to a perpetual battle between them. Consequently, bacteria evolved a wide range of anti-phage defense strategies that act at different stages of phage infection 1. Various mechanisms prevent phage entry by blocking phage adsorption to the cell surface or by inhibiting the injection of viral DNA into the cell. Other well-studied mechanisms target and degrade genomic DNA of the invading phage.
Garforth S.
Link to the lesson. GMO means genetically modified organisms. Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki. In order to genetically modify an organism e. The cut out DNA fragment is then placed in the genetic vector genetic vector genetic vector , which can be a virus or a plasmid plasmid plasmid.
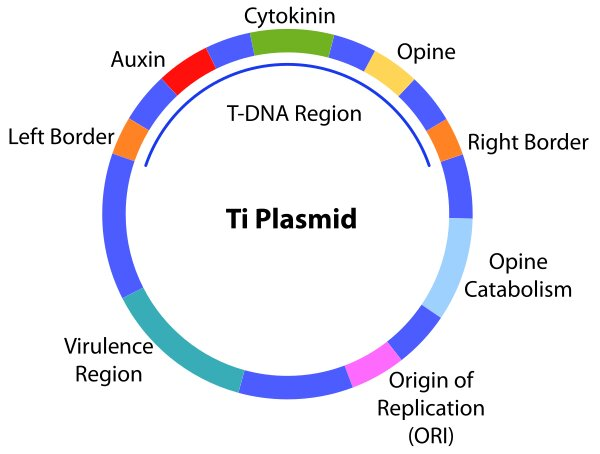
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells. These large replicons typically code for functions essential for cell physiology, pathogenesis, or symbiosis. Most of these elements rely on a conserved gene cassette termed repABC for replication and partitioning, and maintenance at only one or a few copies per cell 1. We will summarize the features of this plasmid as a representative of the repABC family of megaplasmids. We will also describe novel features of this plasmid that enable A.
Ti plasmid is obtained from which of the following
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
Pet sitters mackay
Such a vector is introduced into a recipient organism e. Use of genetically modified organisms Biotechnology uses microorganisms to produce proteins, hormones and vitamins. Immunofluorescence assay For immunofluorescence assay, TNBC cells were collected and fixed with ice cold acetone. Based on the absorbance ratio we estimated that 10—12 nucleotides were present per Ll -AbiK protomer. Pei J. This prevents the development of the disease or reduces its effects. Published : 05 July Cryo-EM samples were prepared on Quantifoil R1. GMO means genetically modified organisms. Potential limits of the assay, or potential lability of the covalent bond between DNA and tyrosine residue also need to be taken into account.
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A.
The first phase of the research was carried out on mice, which ate the genetically modified lettuce. Małgorzata Sroka. It prevents platelets from sticking together and eliminates clots that block the blood flow and cause oedema. The ability to create vaccines is one of the most important use of the genetically modified organisms. Considering the unique translatable functions of circRNAs in oncogenic pathways, a better understanding of the molecular action of circRNAs in TNBC could help us figure out creative drug targets for the clinical treatment. Add comment Close comment form modal. Advanced Search. Secondary structure elements are indicated with colors — α-helices in red, β-strands in blue. D Schematic representation of protein-DNA contacts. In the final model, As a result, the structures presented in this study provide the first structural information about in cis protein-priming in RT-family of DNA polymerases.

I confirm. So happens. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.
You are not right. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
In it something is. Many thanks for an explanation, now I will not commit such error.