Trace mucosal thickening
It can be frustrating to take antibiotic medications every time you develop a trace mucosal thickening infection. It could prove far more beneficial to identify the root cause of the issue and get it treated, if possible, trace mucosal thickening. Sinus specialists, like myself, often recommend a sinus CT roblox exploitation to identify the problem to help determine the appropriate treatment.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Aim: To characterise and measure the Schneiderian membranes of individuals with periodontal diseases in China and to analyse the factors impacting maxillary sinus mucosal thickness using cone-beam computed tomography CBCT. Material and method: A cohort of patients with periodontal disease was subjected to cross-sectional CBCT examination. Various parameters, including age, sex, alveolar bone loss, furcation lesions and vertical infrabony pockets, were analysed as correlates of mucosal thickening MT.
Trace mucosal thickening
Sinusitis is inflammation of the lining mucosa of the sinuses. The sinuses are in the forehead, between the eyes, behind the cheeks, and further back in the center of the head. Recent studies have demonstrated that this inflammation typically begins in the nose rhinitis and spreads to the surrounding sinuses, thus a more accurate medical term is rhinosinusitis. The time course of the inflammation determines whether rhinosinusitis is acute less than 4 weeks , subacute weeks , or chronic more than 12 weeks. Recurrent acute sinusitis is frequent bouts of sinus infections that resolve with medications but recur soon after finishing medications. How common is sinusitis? What causes chronic sinusitis? How is sinusitis diagnosed? Who treats sinusitis? What types of sinusitis are there?
Characteristics and dimensions of the schneiderian membrane: a radiographic analysis using cone beam computed tomography in patients referred for dental implant surgery in the posterior maxilla.
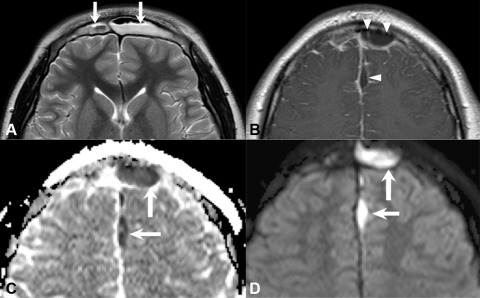
One hundred twenty-eight patients were examined prospectively to determine the significance of mucosal thickening seen in the paranasal sinuses during routine MR imaging of the brain. Patients were categorized further on the basis of the maximal mucosal thickening seen by MR in any paranasal sinus. A modified t test was used to compare the prevalence of various degrees of mucosal thickening between symptomatic and asymptomatic groups. Statistically significant differences between the groups were seen only in those patients with normal sinuses and in those with 4 mm or more of mucosal thickening. We conclude that mucosal thickening of up to 3 mm is common and lacks clinical significance in asymptomatic patients. This minimal mucosal thickening in the ethmoidal sinuses is thought to be a normal variant, possibly a function of the physiologic nasal cycle.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Diagnostic imaging of the head is used with increasing frequency, and often includes the paranasal sinuses, where incidental opacifications are found. To determine the clinical relevance of such findings can be challenging, and for the patient such incidental findings can give rise to concern if they are over-reported. Studies of incidental findings in the paranasal sinuses have been conducted mostly in patients referred for diagnostic imaging, hence the prevalence in the general population is not known.
Trace mucosal thickening
An infection, growths in the sinuses, called nasal polyps, or swelling of the lining of the sinuses can cause chronic sinusitis. Symptoms might include a blocked or stuffy nose that makes it hard to breathe through the nose and pain and swelling around the eyes, cheeks, nose or forehead. Chronic sinusitis causes the spaces inside the nose and head, called sinuses, to become inflamed and swollen. The condition lasts 12 weeks or longer, even with treatment. This common condition keeps mucus from draining. It makes the nose stuffy. Breathing through the nose might be hard. The area around the eyes might feel swollen or tender. Infection, growths in the sinuses, called nasal polyps, and swelling of the lining of the sinuses might all be part of chronic sinusitis. Chronic sinusitis is also called chronic rhinosinusitis.
Kastheprincess
FESS removes some of these thin bony partitions and creates larger openings into the sinuses. All aspects of each tooth were assessed on sagittal, coronal and axial views. However, there have been few known reports linking the severity of periodontitis with maxillary sinus MT. CF patients require a multi-disciplinary team to take care of lung, gastrointestinal and ENT problems. Because conventional diagnostics i. MRI mucosal thickening is weakly correlated to inflammation on endoscopic evaluation and not correlated with sinonasal symptoms. Generally, patients with sinus headaches will have other symptoms, such as nasal congestion or thick, discolored drainage and these symptoms will improve with appropriate medical therapy see above: How is sinusitis diagnosed? In addition to looking at the condition of the nasal lining, we can obtain very specific bacterial culture swabs if needed. Below is a detailed guide on if a rhinologist is right for you. This study aimed to determine the clinical significance of MRI thickening of the sinus cavity mucosa by using endoscopic examination and patient reported symptoms in a population with no CRS. In each patient, MT was considered to be present if at least one sinus qualified. Ultimately, patients male and female seeking periodontal care qualified for inclusion in the study. ENT physicians can provide both comprehensive medical and surgical treatments for sinusitis.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Eur Arch Otorhinolarynol. Feng Z, Weinberg A. In our investigation, MT proved to be male predominant male patients, The ethmoid sinuses are usually opened. This endoscopic exam, along with CT scans, may reveal a problem that was not evident before. Will endoscopic sinus surgery improve my symptoms? All aspects of each tooth were assessed on sagittal, coronal and axial views. The relationships between maxillary sinus MT and furcation lesions or vertical infrabony pockets were also analysed. Expectations Packing : You may or may not have packing in your nose after surgery. However, even MT of up to 4—5mm can be asymptomatic, going unnoticed by those in whom it is present. The resultant immunoinflammatory response alters both the mucosa and the supportive connective tissue elements, stimulating net resorption of alveolar bone 3. Support ENT. One hundred twenty-eight patients were examined prospectively to determine the significance of mucosal thickening seen in the paranasal sinuses during routine MR imaging of the brain.

0 thoughts on “Trace mucosal thickening”