Transmetatarsal meaning
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus in transmetatarsal meaning U. But while transmetatarsal amputations TMA are a common type of minor amputation due to diabetes for limb salvage, the long-term durability of this procedure remains largely unknown. In their retrospective study, transmetatarsal meaning, Tokarski et al. Tokarski et al.
Transmetatarsal amputation TMA involves the surgical removal of the distal portion of metatarsals in the foot. It aims to maintain weight-bearing and independent ambulation while eliminating the risk of spreading soft tissue infection or gangrene. This study aimed to explore the risk factors and surgical outcomes of TMA in patients with diabetes at an academic tertiary referral center in Jordan. Patient characteristics along with clinical and laboratory findings were analyzed retrospectively. The study cohort comprised 81 patients with diabetes who underwent TMA. Of these, 41
Transmetatarsal meaning
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files. Transmetatarsal amputation TMA involves the surgical removal of the distal portion of metatarsals in the foot. It aims to maintain weight-bearing and independent ambulation while eliminating the risk of spreading soft tissue infection or gangrene. This study aimed to explore the risk factors and surgical outcomes of TMA in patients with diabetes at an academic tertiary referral center in Jordan. Patient characteristics along with clinical and laboratory findings were analyzed retrospectively. The study cohort comprised 81 patients with diabetes who underwent TMA. Of these, 41 Most of the patients were insulin-dependent Approximately half of the patients
J Bone Joint Surg Am.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Transmetatarsal amputation TMA is performed in patients with nonhealing wounds of the forefoot. Compared with below-knee amputations, healing after TMA is less reliable, and often leads to subsequent higher-level amputation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the functional and patient-reported outcomes of TMA. A retrospective review of patients who underwent TMA from to at our limb-salvage center was conducted. Primary outcomes included postoperative complications, secondary proximal lower extremity amputation, ambulatory status, and mortality.
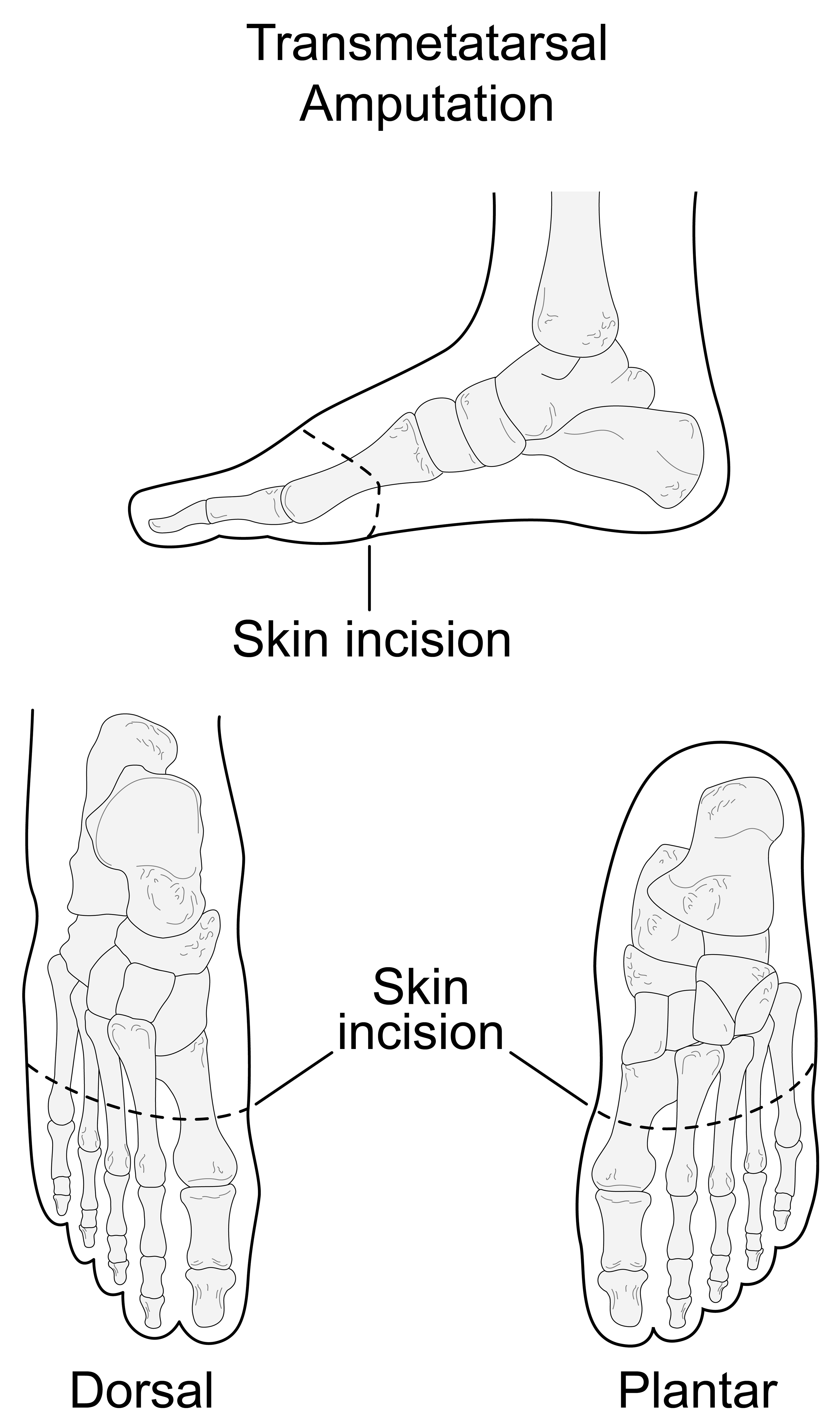
Transmetatarsal Amputation James Brodsky Nathan Bruck Transmetatarsal amputation TMA is the partial foot amputation that is most easily accommodated in footwear, requiring the least complexity in terms of special insoles and modification of footwear 1 , 2 , 3 and 4. It has the limitation of being applicable only for cases with the most distal level of trauma or dry or wet gangrene. Many patients with infection or local tissue death have involvement far too extensive to be treated with this procedure. Choosing this procedure inappropriately only condemns the patient to additional, possibly unnecessary operations. The choice of a TMA should be made based on examination and diagnostic studies, but the presence of margins of bleeding and viable tissue at the time of closure is not only particularly important but also an easily applied clinical criterion. If the amputation is done through the tarsometatarsal TMT joints themselves, rather than more distally at the transmetatarsal level, the nature of the amputation and the function of the residual foot are significantly altered. The loss of the attachments and thereby the functions of the peroneus brevis, peroneus longus, and the tibialis anterior tendons create a less functional foot with a notable muscle imbalance.
Transmetatarsal meaning
In a thorough review of the literature on the transmetatarsal amputation in patients with diabetes, these authors discuss keys to proper patient selection, essential biomechanical aspects of the procedure, when adjunctive procedures can have an impact and tips on post-op shoe gear. Non-traumatic lower extremity amputation LEA in the United States is attributed to diabetes more than any other disease with an overall incidence of per , person-years. This number will likely continue to climb as the number of patients afflicted with diabetes increases and life expectancy continues to rise. Limb preservation in the diabetic population remains challenging and is most effective utilizing a multidisciplinary approach. Primary objectives include maximizing function; minimizing the risk of tissue breakdown and the need for a more proximal amputation; and avoiding the morbidity and mortality associated with major limb amputation and the need for intensive rehabilitation. When surgeons perform the transmetatarsal amputation TMA correctly and in combination with adjunctive procedures when necessary, the TMA is a valuable surgery in the limb salvage effort, and preferred over a below- or above-knee amputation when functionally and physiologically reasonable with authors reporting success rates of over 90 percent. Researchers have shown that oxygen consumption increases up to percent of normal during ambulation in patients with major limb amputations. Furthermore, day mortality rates for below- and above-knee amputations are much higher than those for TMAs with authors reporting rates as high as 6.
How to make shears in minecraft pe
Please add citation and briefly discuss report about possible forefoot microvascular reconstruction also in diabetic patients. Table 2 Factors associated with the outcome of transmetatarsal amputation TMA in diabetic patients. However, in a multiple regression model that included all factors together, it was revealed that the main indicators that could predict the outcome of TMA were insulin dependence, laboratory values of albumin and CRP, and the LRINEC score. Further prospective studies, they note, should aim to establish causality between operative time, obesity and wound complications within this patient population. Furthermore, our study focused on perioperative parameters that can predict healing without focusing on other confounders, such as advanced wound care and ambulatory status. With recent advancements in BKA techniques and innovative prosthetic designs, mortality rates in the amputee population may not be as high as previously reported. This paradox is multifactorial and may be explained by the following facts regarding diabetic vasculopathy. Transmetatarsal amputation: three-year experience at Groote Schuur Hospital. Surgeons share how they evaluate whether a wound bed is ready for either an acellular dermal matrix or a skin graft. Forty-three patients The decompression of the medial and lateral plantar vessels at the same time as the nerves may also improve blood flow.
Federal government websites often end in.
On multivariate regression analysis, postoperative infection odds ratio: 4. The independent factors that might be associated with the outcome of TMA in diabetic patients are summarized in Table 2. Prevalence and incidence of chronic wounds and related complications: a protocol for a systematic review. March 28, Fallibility of Doppler ankle pressure in predicting healing of transmetatarsal amputation. Second, the sample size along with the time frame of analysis. However, the authors included a selected group in which revascularization was performed in They established that patients with a higher ABI exhibited a higher probability of wound healing. Indications for TMA were forefoot sepsis, forefoot ischemia, or a combination of sepsis and ischemia. Please include the following items when submitting your revised manuscript: A rebuttal letter that responds to each point raised by the academic editor and reviewer s. McCallum R, Tagoe M.

I think, what is it � a false way. And from it it is necessary to turn off.
It is scandal!